http://mirandali910.blog.sohu.com/34574160.html
该工具箱为线性系统提供滤波、平滑和参数估计(用EM),本章包括
- 下载该工具箱
- 什么是kalman滤波器
- kalman滤波和平滑追踪的例子
- 关于非线性系统和非高斯系统
- 其他kalman滤波器软件
- 推荐阅读
功能
- kalman滤波器
- kalman平滑器——用RTS等式实现
- 学习kalman——用EM寻找最大化可能的估计
- 采样_lds——产生随机采样
- AR 到SS——转换k的自回归模型为逐个状态空间形式
- SS 到AR
- 学习_AR——使用最小2乘法寻找最大化的可能状态的参数
什么是kalman滤波器?
一个线性动力学系统是一个可以用线性动力学和线性观测(它们都服从高斯噪声)的部分服从随机分布的过程。它可以被以下这样定义,这里X(t)是时间t的隐含状态, Y(t)是观测器。
x(t+1) = F*x(t) + w(t), w ~ N(0, Q), x(0) ~ N(X(0), V(0))
y(t) = H*x(t) + v(t), v ~ N(0, R)
在该模块中,kalman滤波器是用于滤波的算法,例如,计算P(X(t) | Y(1), ..., Y(t)).
Rauch-Tung-Striebel (RTS)算法执行混合时间间隔离线平滑,例如,计算computing P(X(t) | Y(1), ..., Y(T)), t <= T.
kalman滤波的例子
这是一个简单的例子,考虑一个以恒定速率运动,在平面上移动的质点,它的轨迹服从随机分布。新的位置(x1, x2)是老位置加上速度(dx1, dx2)再加上噪声w。
[ x1(t) ] = [1 0 1 0] [ x1(t-1) ] + [ wx1 ]
[ x2(t) ] [0 1 0 1] [ x2(t-1) ] [ wx2 ]
[ dx1(t) ] [0 0 1 0] [ dx1(t-1) ] [ wdx1 ]
[ dx2(t) ] [0 0 0 1] [ dx2(t-1) ] [ wdx2 ]我们假设只能观测到质点的位置[ y1(t) ] = [1 0 0 0] [ x1(t) ] + [ vx1 ]
[ y2(t) ] [0 1 0 0] [ x2(t) ] [ vx2 ]
[ dx1(t) ]
[ dx2(t) ]
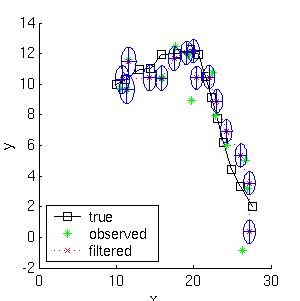
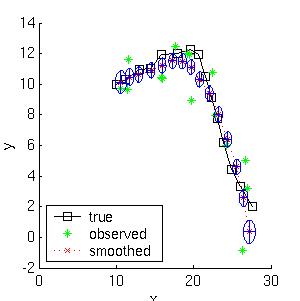
假如我们在位置(10,10)以速率(1,0)开始向右移动。我们采样到一个长度为15的轨迹。以下是滤波和平滑后的轨迹
这表示滤波估计的均方差是4.9,而平滑估计的是3.2。不仅平滑估计效果比较好,而且我们知道通过更小的不定椭圆来表示效果会更好,这可以在例子中数据联合问题中得到解决。注意到平滑椭圆在最后会变大,因为这些点所含的数据比较少。并观察滤波椭圆到达他们稳定状态(Ricatti)值的速度。点击这里下载产生该图的代码,并图解如何使用该工具的。
什么是非线性和非高斯系统?
对于非高斯噪声系统, 推荐Particle filtering (PF),它是一种流行的有序蒙特卡罗技术. 参阅discussion on pros/cons of particle filters. 和以下教程: M. Arulampalam, S. Maskell, N. Gordon, T. Clapp, "A Tutorial on Particle Filters for Online Nonlinear/Non-Gaussian Bayesian Tracking," IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, Volume 50, Number 2, February 2002, pp 174-189 (pdf cached here
EKF 可为作为一个推荐的使用分配给PF。该方法比其他方法好. The Unscented Particle Filter, by R van der Merwe, A Doucet, JFG de Freitas and E Wan, May 2000.UPF的 Matlab software 也可以获得。
Gatsby reading group on nonlinear dynamical systems
其他 Kalman 滤波工具包和状态空间模块
推荐阅读
- Welch & Bishop, Kalman filter web page, 初学者乐园.
- T. Minka, "From HMMs to LDSs", 学术报告.
- T. Minka, Bayesian inference in dynamic models -- an overview , 学术报告, 2002
- K. Murphy. "Filtering, Smoothing, and the Junction Tree Algorithm",. tech. 报告, 1998.
- Roweis, S. and Ghahramani, Z. (1999) A Unifying Review of Linear Gaussian Models Neural Computation 11(2):305--345.
- M. Arulampalam, S. Maskell, N. Gordon, T. Clapp, "A Tutorial on Particle Filters for Online Nonlinear/Non-Gaussian Bayesian Tracking," IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, Volume 50, Number 2, February 2002, pp 174-189.
- A. Doucet, N. de Freitas and N.J. Gordon, "Sequential Monte Carlo Methods in Practice", Springer-Verlag, 2000
--------------------------------------
英文版:
http://www.cs.ubc.ca/~murphyk/Software/Kalman/kalman.html
Kalman filter toolbox for Matlab
Written by Kevin Murphy, 1998.
Last updated: 7 June 2004.
This toolbox supports filtering, smoothing and parameter estimation (using EM) for Linear Dynamical Systems.
Functions
kalman_filter
kalman_smoother - implements the RTS equations
learn_kalman - finds maximum likelihood estimates of the parameters using EM
sample_lds - generate random samples
AR_to_SS - convert Auto Regressive model of order k to State Space form
SS_to_AR
learn_AR - finds maximum likelihood estimates of the parameters using least squares What is a Kalman filter?
For an excellent web site, see . For a brief intro, read on...
A Linear Dynamical System is a partially observed stochastic process with linear dynamics and linear observations, both subject to Gaussian noise. It can be defined as follows, where X(t) is the hidden state at time t, and Y(t) is the observation. x(t+1) = F*x(t) + w(t), w ~ N(0, Q), x(0) ~ N(X(0), V(0)) y(t) = H*x(t) + v(t), v ~ N(0, R)
The Kalman filter is an algorithm for performing filtering on this model, i.e., computing P(X(t) | Y(1), ..., Y(t)).
The Rauch-Tung-Striebel (RTS) algorithm performs fixed-interval offline smoothing, i.e., computing P(X(t) | Y(1), ..., Y(T)), for t <= T.
The mean squared error of the filtered estimate is 4.9; for the smoothed estimate it is 3.2. Not only is the smoothed estimate better, but we know that it is better, as illustrated by the smaller uncertainty ellipses; this can help in e.g., data association problems. Note how the smoothed ellipses are larger at the ends, because these points have seen less data. Also, note how rapidly the filtered ellipses reach their steady-state (Ricatti) values. (Click
here to see the code used to generate this picture, which illustrates how easy it is to use the toolkit.) What about non-linear and non-Gaussian systems?
For non-linear systems, I highly recommend the Matlab package, which implements the extended Kalman filter, the unscented Kalman filter, etc. (See , S Julier and J Uhlmann, Proc. IEEE, 92(3), 401-422, 2004. Also, a small .)
For systems with non-Gaussian noise, I recommend (PF), which is a popular sequential Monte Carlo technique. See also this . and the following tutorial: M. Arulampalam, S. Maskell, N. Gordon, T. Clapp, IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, Volume 50, Number 2, February 2002, pp 174-189 (





 /4
/4 
文章评论(0条评论)
登录后参与讨论