


WISHBONE为我们提供了灵活的连接结构,使我们能非常容易的定制自己的所需用途。它通过提供标准的数据交换协议,使
用户非常方便进行TEAMWORK,把系统组件化,增加了模块的重用性。节省了二次开发的时间。
WISHBONE地址和数据位都是32位(如果小于32位也可以这行通信),最多可以连接8个主设备,16个从设备,当多个主设
备申请控制时,通过仲裁机制决定什么时候哪个主设备能访问共享总线。
WISHBONE具有灵活的可变性连接方式,允许系统通过四种不同的方式实现IP CORES之间的互联:
一。点到点连接方式(point-to-point interconnection)
这是IP CORES之间最简单的连接方式,只需要一主一从两个IP CORES之间进行数据通信,例如,主设备可以是微处理器
IP CORE ,从设备可以使串口的I/O PORT.
二。数据流连接方式(data flow interconnection)
这种连接方式用于数据以时序的方式进行处理。一些时候,这种方式可用作流水线作业。比如下图三个IP CORES都是实现浮
点运算,假设它们工作的时间都相同,这样三个IP CORES互联在一起,可以实现高速的类似并行化的时序操作,使处理数据的
时间节省三分之二。
三。共享总线的连接方式(share bus interconnection)
这种方式通常用于两个或以上主设备和一个或以上从设备之间的互联,仲裁机制决定什么时候哪个主设备能够访问总线,
这种连接方式的主要优点是结构紧凑,能够用较少的逻辑资源去实现相关结构。缺点是:每次只能有一个主设备访问总线,
其他的主设备在总线忙时只能处于等待状态,降低了数据传输的速度。这种共享总线的连接方式我们可以在一些标准的总线
中看到,例如PCI,VMEbus。
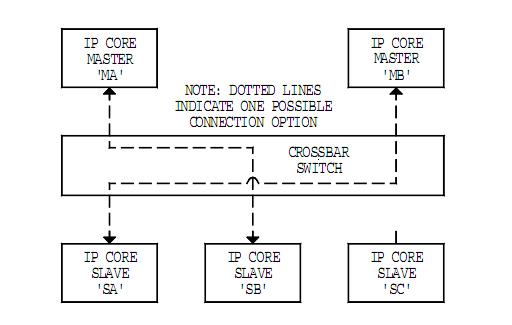
四,交叉开关连接方式(crossbar switch interconnection)
这种连接方式主要用于两个或以上主设备和两个或以上从设备之间进行数据传递。由仲裁机制决定哪个主设备可以访问指定
的从设备。和共享总线连接方式不同的是,这种连接方式允许一个以上主设备同时进行通信,只要两个主设备不同时访问相同
的从设备就可以。例如:RACEway,SKY Channel,Myrinet都是基于此结构。
注意:这种连接方式比共享总线连接方式数据传送速度快很多,但需要更多的资源来实现这种连接。
五。片外连接方式(off-chip interconnection)
这种方式可以用以上四种基本连接方式实现。
仲裁机制
仲裁机制(arbiter)的实现原理是通过循环共享的方式(a round robin arbiter),使每个主设备具有相同的优先权。
仲裁机制的时间其实就是一个状态机,通过八种状态决定那个主设备访问总线。部分代码如下:
 (state) // synopsys parallel_case full_case
(state) // synopsys parallel_case full_case grant0:
grant0: // if this req is dropped or next is asserted, check for other req's
// if this req is dropped or next is asserted, check for other req's if(!req[0] )
if(!req[0] ) begin
begin if(reqalways@(state or req )
if(reqalways@(state or req ) begin
begin next_state = state; // Default Keep State
next_state = state; // Default Keep State case[1]) next_state = grant1;
case[1]) next_state = grant1; else
else if(req[2]) next_state = grant2;
if(req[2]) next_state = grant2; else
else if(req[3]) next_state = grant3;
if(req[3]) next_state = grant3; else
else if(req[4]) next_state = grant4;
if(req[4]) next_state = grant4; else
else if(req[5]) next_state = grant5;
if(req[5]) next_state = grant5; else
else if(req[6]) next_state = grant6;
if(req[6]) next_state = grant6; else
else if(req[7]) next_state = grant7;
if(req[7]) next_state = grant7; end
end grant1:
grant1: // if this req is dropped or next is asserted, check for other req's
// if this req is dropped or next is asserted, check for other req's if(!req[1] )
if(!req[1] ) begin
begin if(req[2]) next_state = grant2;
if(req[2]) next_state = grant2; else
else if(req[3]) next_state = grant3;
if(req[3]) next_state = grant3; else
else if(req[4]) next_state = grant4;
if(req[4]) next_state = grant4; else
else if(req[5]) next_state = grant5;
if(req[5]) next_state = grant5; else
else if(req[6]) next_state = grant6;
if(req[6]) next_state = grant6; else
else if(req[7]) next_state = grant7;
if(req[7]) next_state = grant7; else
else if(req[0]) next_state = grant0;
if(req[0]) next_state = grant0; end
end grant2:
grant2: // if this req is dropped or next is asserted, check for other req's
// if this req is dropped or next is asserted, check for other req's if(!req[2] )
if(!req[2] ) begin
begin if(req[3]) next_state = grant3;
if(req[3]) next_state = grant3; else
else if(req[4]) next_state = grant4;
if(req[4]) next_state = grant4; else
else if(req[5]) next_state = grant5;
if(req[5]) next_state = grant5; else
else if(req[6]) next_state = grant6;
if(req[6]) next_state = grant6; else
else if(req[7]) next_state = grant7;
if(req[7]) next_state = grant7; else
else if(req[0]) next_state = grant0;
if(req[0]) next_state = grant0; else
else if(req[1]) next_state = grant1;
if(req[1]) next_state = grant1; end
end grant3:
grant3: // if this req is dropped or next is asserted, check for other req's
// if this req is dropped or next is asserted, check for other req's if(!req[3] )
if(!req[3] ) begin
begin if(req[4]) next_state = grant4;
if(req[4]) next_state = grant4; else
else if(req[5]) next_state = grant5;
if(req[5]) next_state = grant5; else
else if(req[6]) next_state = grant6;
if(req[6]) next_state = grant6; else
else if(req[7]) next_state = grant7;
if(req[7]) next_state = grant7; else
else if(req[0]) next_state = grant0;
if(req[0]) next_state = grant0; else
else if(req[1]) next_state = grant1;
if(req[1]) next_state = grant1; else
else if(req[2]) next_state = grant2;
if(req[2]) next_state = grant2; end
end grant4:
grant4: // if this req is dropped or next is asserted, check for other req's
// if this req is dropped or next is asserted, check for other req's if(!req[4] )
if(!req[4] ) begin
begin if(req[5]) next_state = grant5;
if(req[5]) next_state = grant5; else
else if(req[6]) next_state = grant6;
if(req[6]) next_state = grant6; else
else if(req[7]) next_state = grant7;
if(req[7]) next_state = grant7; else
else if(req[0]) next_state = grant0;
if(req[0]) next_state = grant0; else
else if(req[1]) next_state = grant1;
if(req[1]) next_state = grant1; else
else if(req[2]) next_state = grant2;
if(req[2]) next_state = grant2; else
else if(req[3]) next_state = grant3;
if(req[3]) next_state = grant3; end
end grant5:
grant5: // if this req is dropped or next is asserted, check for other req's
// if this req is dropped or next is asserted, check for other req's if(!req[5] )
if(!req[5] ) begin
begin if(req[6]) next_state = grant6;
if(req[6]) next_state = grant6; else
else if(req[7]) next_state = grant7;
if(req[7]) next_state = grant7; else
else if(req[0]) next_state = grant0;
if(req[0]) next_state = grant0; else
else if(req[1]) next_state = grant1;
if(req[1]) next_state = grant1; else
else if(req[2]) next_state = grant2;
if(req[2]) next_state = grant2; else
else if(req[3]) next_state = grant3;
if(req[3]) next_state = grant3; else
else if(req[4]) next_state = grant4;
if(req[4]) next_state = grant4; end
end grant6:
grant6: // if this req is dropped or next is asserted, check for other req's
// if this req is dropped or next is asserted, check for other req's if(!req[6] )
if(!req[6] ) begin
begin if(req[7]) next_state = grant7;
if(req[7]) next_state = grant7; else
else if(req[0]) next_state = grant0;
if(req[0]) next_state = grant0; else
else if(req[1]) next_state = grant1;
if(req[1]) next_state = grant1; else
else if(req[2]) next_state = grant2;
if(req[2]) next_state = grant2; else
else if(req[3]) next_state = grant3;
if(req[3]) next_state = grant3; else
else if(req[4]) next_state = grant4;
if(req[4]) next_state = grant4; else
else if(req[5]) next_state = grant5;
if(req[5]) next_state = grant5; end
end grant7:
grant7: // if this req is dropped or next is asserted, check for other req's
// if this req is dropped or next is asserted, check for other req's if(!req[7] )
if(!req[7] ) begin
begin if(req[0]) next_state = grant0;
if(req[0]) next_state = grant0; else
else if(req[1]) next_state = grant1;
if(req[1]) next_state = grant1; else
else if(req[2]) next_state = grant2;
if(req[2]) next_state = grant2; else
else if(req[3]) next_state = grant3;
if(req[3]) next_state = grant3; else
else if(req[4]) next_state = grant4;
if(req[4]) next_state = grant4; else
else if(req[5]) next_state = grant5;
if(req[5]) next_state = grant5; else
else if(req[6]) next_state = grant6;
if(req[6]) next_state = grant6; end
end endcase
endcase end
end /5
/5 
文章评论(0条评论)
登录后参与讨论