


[Linux-uvc-devel] C function to convert from Bayer to RGB24 pixel formats
Vojtech Pavlik vojtech at suse.cz
Thu Jan 11 23:44:47 CET 2007
On Thu, Jan 11, 2007 at 10:47:10PM +0100, Laurent Pinchart wrote:
> Hi Luca,
>
> > This is function in C to convert from Bayer to RGB24 pixel formats.
> > The linear interpolation is more efficient than the ones I saw in other
> > similar functions on internet, as the code omits "if-then-else" conditional
> > statements in the loops.
>
> Thanks for the code. This will be usefull for all the users who are interested
> in raw image processing. There seem to be quite a lot of them lately :-)
That is easy to explain: Those interested in raw processing are looking
for a webcam that can do USB 2.0 and is supported on Linux. Not that
much choice. ;)
Btw, my take on Bayer->RGB processing: (attached)
--
Vojtech Pavlik
Director SuSE Labs
-------------- next part --------------
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdint.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/mman.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <sys/ioctl.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <sys/select.h>
#define u8 uint8_t
#define u16 uint16_t
#define u32 uint32_t
static uint8_t rgb[640*480*3];
#define R(x,y) pRGB24[0 + 3 * ((x) + 640 * (y))]
#define G(x,y) pRGB24[1 + 3 * ((x) + 640 * (y))]
#define B(x,y) pRGB24[2 + 3 * ((x) + 640 * (y))]
#define Bay(x,y) pBay[(x) + 640 * (y)]
static void bayer_copy(u8 *pBay, u8 *pRGB24, int x, int y)
{
G(x + 0, y + 0) = Bay(x + 0, y + 0);
G(x + 1, y + 1) = Bay(x + 1, y + 1);
G(x + 0, y + 1) = G(x + 1, y + 0) = ((u32)Bay(x + 0, y + 0) + (u32)Bay(x + 1, y + 1)) / 2;
R(x + 0, y + 0) = R(x + 1, y + 0) = R(x + 1, y + 1) = R(x + 0, y + 1) = Bay(x + 0, y + 1);
B(x + 1, y + 1) = B(x + 0, y + 0) = B(x + 0, y + 1) = B(x + 1, y + 0) = Bay(x + 1, y + 0);
}
static void bayer_bilinear(u8 *pBay, u8 *pRGB24, int x, int y)
{
R(x + 0, y + 0) = ((u32)Bay(x + 0, y + 1) + (u32)Bay(x + 0, y - 1)) / 2;
G(x + 0, y + 0) = Bay(x + 0, y + 0);
B(x + 0, y + 0) = ((u32)Bay(x - 1, y + 0) + (u32)Bay(x + 1, y + 0)) / 2;
R(x + 0, y + 1) = Bay(x + 0, y + 1);
G(x + 0, y + 1) = ((u32)Bay(x + 0, y + 0) + (u32)Bay(x + 0, y + 2)
+ (u32)Bay(x - 1, y + 1) + (u32)Bay(x + 1, y + 1)) / 4;
B(x + 0, y + 1) = ((u32)Bay(x + 1, y + 0) + (u32)Bay(x - 1, y + 0)
+ (u32)Bay(x + 1, y + 2) + (u32)Bay(x - 1, y + 2)) / 4;
R(x + 1, y + 0) = ((u32)Bay(x + 0, y + 1) + (u32)Bay(x + 2, y + 1)
+ (u32)Bay(x + 0, y - 1) + (u32)Bay(x + 2, y - 1)) / 4;
G(x + 1, y + 0) = ((u32)Bay(x + 0, y + 0) + (u32)Bay(x + 2, y + 0)
+ (u32)Bay(x + 1, y - 1) + (u32)Bay(x + 1, y + 1)) / 4;
B(x + 1, y + 0) = Bay(x + 1, y + 0);
R(x + 1, y + 1) = ((u32)Bay(x + 0, y + 1) + (u32)Bay(x + 2, y + 1)) / 2;
G(x + 1, y + 1) = Bay(x + 1, y + 1);
B(x + 1, y + 1) = ((u32)Bay(x + 1, y + 0) + (u32)Bay(x + 1, y + 2)) / 2;
}
static void bayer_to_rgb24(u8 *pBay, u8 *pRGB24)
{
int i, j;
for (i = 0; i < 640; i += 2)
for (j = 0; j < 480; j += 2)
if (i == 0 || j == 0 || i == 640 - 2 || j == 480 - 2)
bayer_copy(pBay, pRGB24, i, j);
else
bayer_bilinear(pBay, pRGB24, i, j);
}
void writepnm(uint8_t *data, int i)
{
FILE *fd;
char name[32];
sprintf(name, "p5-%04d.pnm", i);
fd = fopen(name, "w");
fputs("P6\n", fd);
fputs("640 480\n", fd);
fputs("255\n", fd);
fwrite(data, 640*480*3, 1, fd);
fclose(fd);
}
int main(void)
{
int fdi;
u8 *ibot;
if ((fdi = open("bayer.raw", O_RDONLY)) < 0) {
perror("open");
return -1;
}
if ((ibot = mmap(NULL, 640 * 480 + 640*4, PROT_READ, MAP_SHARED, fdi, 0)) == MAP_FAILED) {
perror("mmap");
return -1;
}
bayer_to_rgb24(ibot, rgb);
writepnm(rgb, 0);
close(fdi);
return 0;
}
DE2_CCD中bayer图像格式转化为30位标准RGB格式
CIS mt9m011使用的是bayer颜色格式,如图1所示(黑的地方像素值为0)。奇数行包括green和red颜色的像素,偶数行包括blue和green颜色的像素。奇数列包括green和blue颜色的像素,偶数列包括red和green颜色的像素。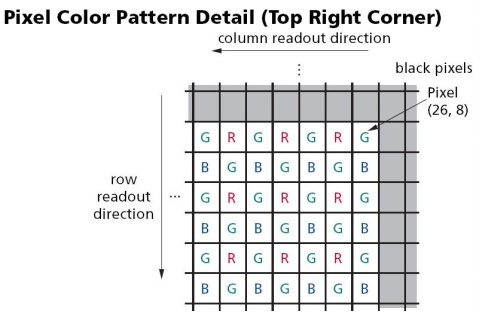
图1
过程总述:采用行缓冲+流水线的处理方式,将前一级抓取到的行数据(bayer color pattern),实时转换成标准的30位RGB数据并进行适当的下采样,以便于后继的图像处理及显示。
首先调用一个altshift_taps 的megafunction,altshift_taps 可以作为数据移动寄存器组,经常在图像处理程序中用到。采集进来一系列像素点数据,需要同时对2行像素点同时进行处理时,就可以用这个altshift_taps.共2个taps,每个taps数据宽度为图像每行像素点的个数(1280)。(针对这个megafunction做一下波形仿真就容易理解了)。
在格式转换时,用到4个量:
mDATA_0:第M行第N列的像素
mDATAd_0:第M行第N-1列的像素
mDATA_1:第M+1行第N列的像素
mDATAd_1:第M+1行第N-1列的像素
4个量组成一个以mDATA_0(位于左上角)为核心的模板:
|
mDATA_0 |
mDATAd_0 |
|
mDATA_1 |
mDATAd_1 |
模板中必定包含一个R、一个B、2个G像素点,那么R作为当前像素mDATA_0的R值,B作为当前像素mDATA_0的B值,取2个G的平均值作为当前像素mDATA_0的G值(通过取G的高10位,舍去最后一位来实现)。对这bayer颜色格式图,任取一个颜色的像素作为核心元素套进模板,这样就可以很好的理解RAW2RGB程序中关于图像格式转化的那部分代码了。
 /4
/4 
文章评论(0条评论)
登录后参与讨论