


进程间通讯——无名管道style="TEXT-ALIGN: left; LINE-HEIGHT: 20pt" class=MsoNormal align=left>无名管道用于有亲缘关系的进程间的通讯。
管道的编程接口如下:
#include<unistd.h>
int pipe(int pipe_fd[2]);
pipe函数用于创建管道,调用者必须传递一个有两个元素的整形数组的首地址作为参数。如果无名管道创建成功,则函数返回后数组中存放的是管道的文件描述符(我们之前常用fd表示)。
pipe_fd[0]为读端,可以使用read从中读出数据;
pipe_fd[1]为写端,可以使用write从中写入数据。
为了能进行让父、子进程进行数据传输,必须保证“系统调用fork()前,调用pipe(),否则子进程不会继承文件描述符。”
以下例程实现了父进程将数据写入无名管道,子进程从中读取数据。
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <errno.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
//#include <memory.h>
int main()
{
int pipe_fd[2];//定义2个文件描述符
pid_t pid;//进程ID
char buf_r[100];
char* p_wbuf;
int num_r;
memset(buf_r,0,sizeof(buf_r));
//创建管道,以便父子进程拥有同一个管道。
if(pipe(pipe_fd)<0)
{
printf("pipe creat error.\n");//创建管道失败
return -1;
}
//创建子进程
if((pid=fork())==0)//子进程进入
{
printf("wait...\n");
close(pipe_fd[1]);//关闭子进程的“写”
sleep(2);//让子进程休眠2秒,以便父进程写入数据。
if((num_r=read(pipe_fd[0],buf_r,100))>0)//从pipe_fd[0]中读,
//放到buf_r,读100个字节
{
printf("%d Bytes have been read from the pipe.\n",num_r);
printf("we read:%s\n",buf_r);
}
close(pipe_fd[0]);
exit(0);
}
else if(pid>0)//父进程进入
{
close(pipe_fd[0]);//关闭读
if(write(pipe_fd[1],"Hi,pipe.12345678",16)!=-1);
printf("Parent write Hi,pipe.12345678\n");
close(pipe_fd[1]);
sleep(3);
waitpid(pid,NULL,0);//等待子进程结束
exit(0);
}
//return 0;
}
实验结果截图:
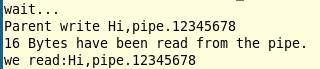
注:以上内容参考:《嵌入式Linux系统实用开发》何永琪主编,及国嵌视频教程。
 /5
/5 
文章评论(0条评论)
登录后参与讨论