


Appendix3 芯片级传输线和PCB传输线[7]
(1) RC网络。下图的RC网络由20ohm电阻和0.5pf电容构成,RC构成了一个低通滤波器。每当信号通过这个滤波器的时候,都会发生相位的变化;并且,由于电阻的存在,会产生一定的电压降。
(2) LC网络。LC网络与RC不同,施加在上面的信号尽管会有相移,但是不会有任何的衰减,因为L,C都是储能元件,不消耗能量。当信号通过这样的网络的时候,产生很大的相移,但没有衰减。
实际的传输线既有电阻,又有电感,而不是纯粹的电感或电阻;
On-chip: 芯片级的传输线类似RC网络,因为互联非常短,所以电阻起主要的作用。
Series resistance, not inductance, mostly dominates on-chip
interconnections in a 130-nm chip architecture.
On-board:PCB级传输线类似LC网络,与芯片级相比,互联非常长,
Scaling the cross-section makes the per-unit length resistance of a
pcb trace a whole lot smaller but doesn't affect the per-unit length
inductance that much. As a result, the roles of resistance and
inductance in a pcb trace are swapped-in a pcb trace, the inductance
matters most. At any digital logic speed above 10 MHz, typical pcb
traces act mostly like LC structures.
所以,芯片级传输线很少端接,而PCB传输线却需要端接;在
一个RC网络中,信号通过长线,自然就会产生衰减,这样的
环境中不会产生反射和过冲;在LC环境,没有能量损耗,实
际上即使低损耗传输线,信号在端到端来回发射好几次而衰
减很小,因此,需要端接。
Appendix4 传输线几何尺寸和传输线带宽的关系[9]
每一条传输线都有自己的带宽。下图显示了这种关系,图
中,带宽定义为衰减2dB.
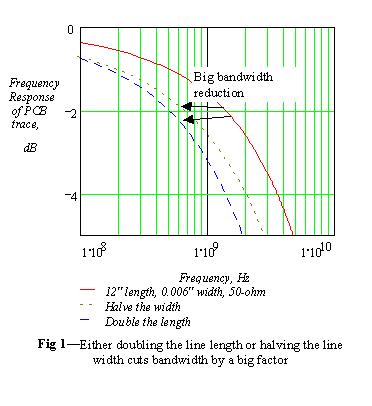
从图中可以看出,传输线的带宽和它的几何尺寸有关系
Here, nature profoundly helps us: The bandwidth for almost all
practical transmission lines varies in a simple way. For pc-board
traces, the bandwidth is proportional to the square of trace width,
W, and inversely proportional to the square of trace length, L. the
(W/L)2 model holds fairly well for pc-board applications. 这个关
系也可以定性的推导或思考:长度越长,电阻越大,传输线
的损耗就越大;越宽,电阻就越小,损耗就越小。
 /4
/4 
文章评论(0条评论)
登录后参与讨论