


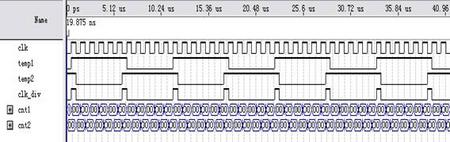
1、半整数分频占空比不为50%
//说明:设计的史上最好用的半整数分频占空比不为50%,包含设计思路
module div_5(clk,clk_div,cnt1,cnt2,temp1,temp2);//N+0.5
input clk;
output clk_div;
output reg[31:0]cnt1,cnt2;
output reg temp1,temp2;
initial begin temp1=0;temp2=1;end //首先进行初始化,temp1=0;temp2=1
parameter N=5; //设定分频系数为N+0.5
always @(posedge clk) //temp1上升沿跳变
begin
if(cnt1==2*N) //2*N
begin cnt1[31:0]<=32'd0;end
else begin cnt1[31:0]<=cnt1[31:0]+32'd1;end
if(cnt1==32'd0) begin temp1<=1;end //高电平时间为N+1;
if(cnt1==N+1) begin temp1<=0;end //低电平时间为N;
end
always@(negedge clk) //temp2下降沿跳变
begin
if(cnt2==2*N) //2*N
begin cnt2[31:0]<=32'd0;end
else begin cnt2[31:0]<=cnt2[31:0]+32'd1;end
if(cnt2==32'd0) begin temp2<=0;end //低电平时间为N;
if(cnt2==N) begin temp2<=1;end //高电平时间为N+1;
end
assign clk_div=temp1&&temp2; //逻辑与
endmodule
//如果要进行N+0.5分频
//思路:总的来说要进行N+1+N=2N+1次分频
//在时钟的上升沿和下降沿都进行跳变
//上升沿进行占空比为N+1比N的时钟temp1;
//下降沿进行占空比为N比N+1的时钟temp2;
//最后div=temp1&&temp2 即可得到所需要的半整数分频
分频5.5仿真结果
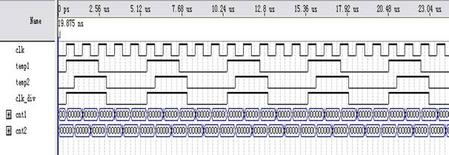
2、奇数分频占空比为50%
//说明:奇数分频。
module div_5(clk,clk_div,cnt1,cnt2,temp1,temp2);//
input clk;
output clk_div;
output reg[31:0]cnt1,cnt2;
output reg temp1,temp2;
parameter N=5; //设定分频系数
always @(posedge clk)
begin
if(cnt1==N-1) //N-1进行N计数
begin cnt1[31:0]<=32'd0;end
else begin cnt1[31:0]<=cnt1[31:0]+32'd1;end
if(cnt1==32'd0) begin temp1<=1;end //
if(cnt1==(N-1)/2) begin temp1<=0;end //当计数到(N-1)/2时翻转
end
always@(negedge clk)
begin
if(cnt2==N-1) //N-1
begin cnt2[31:0]<=32'd0;end
else begin cnt2[31:0]<=cnt2[31:0]+32'd1;end
if(cnt2==32'd0) begin temp2<=1;end //;
if(cnt2==(N-1)/2) begin temp2<=0;end //当计数到(N-1)/2时翻转;
end
assign clk_div=temp1||temp2; //逻辑或
endmodule
3任意小数分频
分数分频实现基本上都是靠吞脉冲方法实现,如5/2分频,就可以分成一个2分频,一个3分频接替出现,这样(2+3)/2就是5/2分频。
下面以68/9为例介绍下怎么计算。
68=9*7+5,即商为7,余数为5。可以推出68/9分频,可以看成5个8分频和4个7分频,即(5*8+4*7)/9=68/9。这个7分频和8分频中的数字7和8就是从商中得出来的。那5个8分频和4个7分频中的数字5和4就是从余数中的出来的,5是余数,4是(9-5)。
分子:numerator。分母denominator。商quotient。余数remainder。(翻译不是很准确,表达下意思就行了,呵呵)。
numerator=quotient*denominator+remainder.那么numerator/ denominator分频就可以通过remainder个(quotient+1)分频和(denominator -remainder)个quotient分频组成。
还是以68/9为例。我们得出了5个8分频和4个7分频可以实现这个分数分频,但这5个8分频和4个7分频怎么放置呢?
先放5个8分频,再放4个7分频,这样绝对是不行的。为了均匀的放置这两种频率,我从小数分频中学到一种方法。找个临时变量temp(程序中用的是sum)。初始化为0。每次分频完让它加上余数,判断是否大于分母,如果小于分母,择输出7分频,否则输出8分频,并且将这个值减去分母(让它小于分母)。这样temp值就变成了5 1 6 2 7 3 8 4 0 5……
分频值就成了7 8 7 8 7 8 7 8 8 7 8 7 8 7 8 7 8 8……可以统计一下7分频和8分频的比例就正好是4:5,这样就实现了分数分频。
程序如下所示:
输入信号:clk,rst,clkin(要分频的时钟信号),numerator(分子), denominator,(分母)
输出信号:pulse
中间信号:quotient(商),remainder(余数)等
hightime为输出信号pulse输出高电平时间,可控制占空比
/*************************************************
//module name:fredivAB
//designer:kang
//date:2010-10-08
//version:1.00
*************************************************/
module fredivAB(
//input signals
clk,
rst,
clkin,
numerator, //fenzi
denominator, //fenmu
//output signals
pulse
);
input clk;
input rst;
input clkin;
input [15:0] numerator;
input [15:0] denominator;
output pulse;
reg pulse;
//parameter HIGHTIME=16'd2;
wire [15:0] quotient; //shang
wire [15:0] remainder; //yushu
reg ina;
reg inb;
reg upclk;
reg counter_clkin;
reg [15:0] counter;
reg [15:0] divnum;
reg [15:0] sum;
reg flag;
reg [15:0] counter_pulseh;
wire [15:0] hightime;
assign quotient=(denominator)?numerator/denominator:16'h0;
assign remainder=(denominator)?numerator%denominator:16'h0;
assign hightime={1'b0,quotient[15:1]};
//assign hightime=16'h1;
//save the prior and current state of clkin
always @(posedge clk or negedge rst)
begin
if(!rst)
begin
ina<=0;
inb<=0;
end
else
begin
ina<=clkin;
inb<=ina;
end
end
//check posedge pf clkin
always @(posedge clk or negedge rst)
begin
if(!rst) upclk<=0;
else if(!inb&ina) upclk<=1'b1;
else upclk<=0;
end
//fre div counter
always @(posedge clk or negedge rst)
begin
if(!rst)
begin
counter<=0;
end
else if(counter==divnum) counter<=16'h0;
else if(upclk) counter<=counter+1'b1;
else counter<=counter;
end
always @(posedge clk or negedge rst)
begin
if(!rst)
begin
sum<=0;
flag<=0;
end
else if(counter==divnum)
begin
if((sum+remainder)>=denominator) //fenmu
begin
sum<=sum+remainder-denominator;
flag<=1;
end
else
begin
sum<=sum+remainder;
flag<=0;
end
end
end
always @(posedge clk or negedge rst)
if(!rst) divnum<=0;
else if(flag) divnum<=quotient+1'b1;
else divnum<=quotient;
//counter_plush
always @(posedge clk or negedge rst)
begin
if(!rst) counter_pulseh<=hightime+16'h1;
else if((counter==divnum)&&divnum) counter_pulseh<=0;
else if(upclk) counter_pulseh<=counter_pulseh+1'b1;
end
//pulse produce
always @(posedge clk or negedge rst)
if(!rst) pulse<=1'b0;
else if(counter_pulseh<=(hightime-1)) pulse<=1'b1;
else pulse<=1'b0;
endmodule
用户377235 2015-7-21 18:41
一种非常简单的方法能任意分频。思路很好,稍稍改一下可以作为一个标准的任意分频程序。谁要源码给我留言。
用户418606 2013-9-10 11:11
用户1529931 2013-8-15 14:40
sunyzz 2013-8-15 14:03
用户443267 2013-8-15 10:57