


2.电容
电容表征了两个导体之间存储电荷的能力。当两个导体带上电荷之后,这两个导体之间就建立起了电势差,电容越大,这种电势差就越大。
2.1 电容定义:C=QV
2.2 平板电容公式
两个平行平板导体,间距为d,面积为A。permittivity of free space = 0.089 pF/cm or 0.225 pF/inch
该公式的详细推倒见[3]
2.3 介电常数Dielectric Constant:
The presence of an insulating material between the conductors will increase the capacitance between them. er。<?xml:namespace prefix = o ns = "urn:schemas-microsoft-com:office:office" />
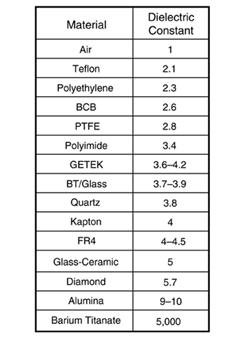
空气的介电常数为1.其他材料的介电常数作为和空气介电常数的比值,因此没有单位。
如何测得一种材料的介电常数。当介质为空气是,电容为C。,当介质为某种材料是,电容为C,该种材料的介电常数定义为:er=C/C0。The way to measure the dielectric constant of an insulator is to compare the capacitance of a pair of conductors when they are surrounded by air, C0, and when they are completely surrounded by the material, C. [6]
介电常数表征了材料对电容的增大的能力,介电常数越大,电容增大的就越大。材料的介电常数和它内部的dipoles的数目和大小有关系,dipoles越多,介电常数越大。
常见的材料的介电常数的比较。
2.4 平板电容器的应用
最常见的平板电容器是PCB中的电源层和地层构成的电容器。一对电源平面和地平面起到了的去耦电容和低阻抗路径的双重作用,尽管去耦的效果可能十分不理想。Fr4板材的PCB,电源平面和地平面间距10mil,他们之间形成的电容是:
C= e0 erA/h=0.225pF/inX4X1in2/10mil=100pF。降低电源平面和地平面的间距,电容还会增大。
现在考虑这样的一对电源和地平面提供的去耦电容的效果。假设芯片的功率是1W,工作电压V,允许的电压降5%V,PCB面积为10 in2,则电源和地平面提供的去耦电容的供电时间dt=CX0.05VXV/P=10*100pf*0.05*3.3*3.3/1=0.54ns.这么短的时间,电源模块还不足以提供足够的电流!
Voltage Droop的简单解释[7]
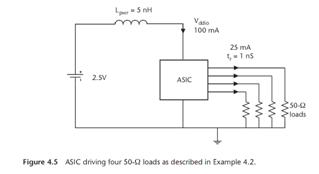
[6]More typically, enough decoupling capacitance is required to provide decoupling for at least 5 μsec, until the power supply regulator can provide adequate current.
2.5 有效介电常数Effective Dielectric Constant:
当pcb走线完全被介质包围的时候,导体之间的介电常数就是介质的介电常数,当走线部分存在于PCB中部分存在于空气中的时候,介电常数是介质和空气的混合。
[6]The combination of air and partial filling of the dielectric creates an "effective dielectric constant."

Just as the dielectric constant is the ratio of the filled capacitance to the empty capacitance, the effective dielectric constant is the ratio of the capacitance when the material is in place with whatever distribution is really there, compared to the capacitance between the conductors when there is only air surrounding them.
The first step in calculating the effective dielectric constant, eeff is to calculate the capacitance per length between the two conductors with empty space between them, C0. The second step is to add the material as it is distributed and calculate the resulting capacitance per length, Cfilled. The effective dielectric constant is just the ratio: eeff= Cfilled/ C0
2.6 电容的非理想效应
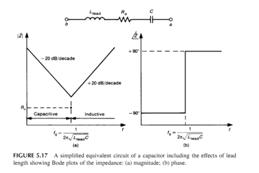
一个平行板电容由2块导体和夹在导体之间的介质构成,介质会发生损耗,这种损耗会导致有电流流过介质,可以等效为一个电阻Rdiel;平行板的电阻等效为Rplate;而电容的两个引脚具有相应的电感Llead和电容Clead。因此,一个电容可以建模为
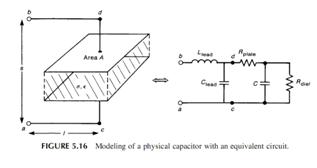
通常,Rdiel非常大(损耗很小,或理解为直流时电流无法流过因此电阻很大),可以忽略;Rplate就是电容的ESR;Clead与C相比很小,也可以忽略,这样,一个电容就可以等效为一个电感、电阻和电容的串联。
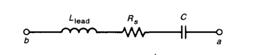
可以预计,这样的电容模型将会与理想的电容的特性不同!
建模:一个0.15uF的电容Pspice模型如下,引线电感14nH,ESR(等效串联电阻)5欧
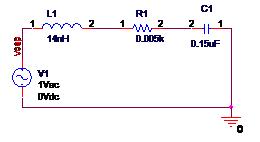
电容pspice仿真的文档。
频率逐渐提高,电路表现出感性,阻抗开始增加。100MHz时,阻抗为10欧,在1GHz时,阻抗变为88欧,3G时,阻抗已经达到266欧。因此,如果用这个电容作为200Mhz的噪声的低阻抗路径的话,电容表现出来的阻抗比理想值要大;如果想作为10G噪声的低阻抗路径话,它已经不是低阻抗的了(877欧)。当频率不断提高时,决定电容阻抗的主要是它的封装的引脚电感。
2.7 电容的进一步讨论
[3]中有关于电容的进一步讨论,解释了电容的定义以及电容公式Q=Cv的推导过程。
 /4
/4 
文章评论(0条评论)
登录后参与讨论