时域分析性能指标是以系统对单位阶跃输入的瞬态响应形式给出的。
控制系统的实际运行都是在时域内进行的,所以可用时域法分析 系统性能。时域分析法是研究控制系统在输入信号作用下,其输出随时间变化的 情况,方便分析系统的动态和稳态特性,是控制系统最基本的分析方法,也是频域 分析法和根轨迹分析法的基础。时域分析包括稳定性分析、瞬态性能分析和稳态 性能分析。
对控制系统进行时域分析时虽然可以由输出响应得出系统的性能,但是对于稳定性和 准确性来说,采用输出响应来分析较为麻烦,时域性能分析常采用的方法如下:
(1)稳定性分析采用的是代数判据,即劳斯稳定性判据和赫尔维兹稳定性判据。
(2)稳态性能分析就是通过计算稳态误差来分析系统的准确性。
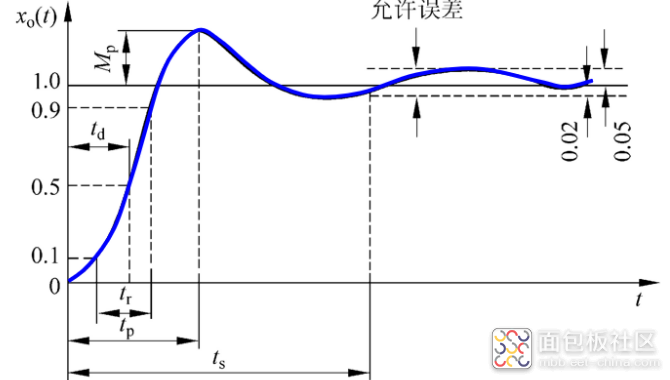
(3)瞬态性能也称为动态性能,用动态性能指标表示,是通过求系统在典型输入时的输 出响应得出的。输出响应的求取方法有两种,一是直接由微分方程求解得出,二是借助于传 递函数采用拉氏反变换的方法求出。
通常,把控制系统的时间响应按时间的顺序划分为动态过程和稳态过程两部分。
动态过程
动态过程也称为暂态过程或过渡过程,指系统在典型输入信号作用下,系统输出量从初始状态到最终状态的过程。根据系统结构和参数选择的情况,动态过程表现为衰减、发散和等幅振荡几种形态。
显然,一个可以正常运行的控制系统,其动态过程必须是衰减的,即系统必须是稳定的。
稳态过程
稳态过程也称为系统的稳态响应,指系统在典型输入信号作用下,当时间t趋于无穷大时,系统输出量的表现形式。
稳态过程表征系统输出量最终复现输入量的程度,提供系统稳态误差的信息,用系统的稳态性能描述。
翻译成英文:
Time domain analysis performance index
The time domain analysis performance index is given in the form of the system's transient response to unit step input.
The actual operation of the control system is carried out in the time domain, so the time domain method can be used to analyze the system performance.
The time domain analysis method is to study the change of the output of the control system with time under the action of the input signal, so as to facilitate the analysis of the dynamic and steady-state characteristics of the system.
It is the most basic analysis method of the control system, as well as the frequency domain analysis method and root locus analysis. The basis of law. Time domain analysis includes stability analysis, transient performance analysis and steady-state performance analysis.
Although the performance of the control system can be derived from the output response when performing time domain analysis of the control system, it is more troublesome to analyze the output response for stability and accuracy.The methods often used in time domain performance analysis are as follows:
(1) Stability analysis uses algebraic criteria, namely Routh's stability criterion and Helviz's stability criterion.
(2) The steady-state performance analysis is to analyze the accuracy of the system by calculating the steady-state error.
(3) Transient performance is also called dynamic performance. It is expressed by dynamic performance index, which is obtained by calculating the output response of the system at typical input.
There are two methods for obtaining the output response. One is to directly solve the differential equation, and the other is to use the transfer function to obtain the inverse Laplace transform.
Generally, the time response of the control system is divided into two parts, the dynamic process and the steady-state process, in the order of time.
Dynamic Process
The dynamic process is also called the transient process or the transition process, which refers to the process of the system output from the initial state to the final state under the action of a typical input signal.
According to the system structure and parameter selection, the dynamic process is manifested in several forms of attenuation, divergence and constant amplitude oscillation.
Obviously, for a control system that can operate normally, its dynamic process must be attenuated, that is, the system must be stable.
Steady state process
The steady-state process is also called the steady-state response of the system, which refers to the expression of the output of the system when the time t tends to infinity under the action of a typical input signal.
The steady-state process represents the degree to which the output of the system finally reproduces the input, and provides information about the steady-state error of the system, which is described by the steady-state performance of the system.
参考资料:百度
英文翻译:Google翻译
本文由learningyard学苑原创,部分资料、图片来源于网络,如有侵权请联系。






 /5
/5 


