来源:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_46826913/article/details/106289647
1、简介
简单工厂方法定义一个用于创建对象的类,该类接受一个参数,通过参数决定创建不同的对象。
GOF并没有把简单工厂方法定义为23种设计模式之一,可以认为简单工厂方法是工厂方法的简化形式。
为了体现简单工厂方法和工厂方法的区别和联系,此处把简单工厂方法先单独讲一下。
2、模拟场景 假设你要生产电脑,电脑由硬盘、内存条、CPU、主板的部件组成。你为了保证供应链可靠,每种部件都选择了至少两家供应商。比如:
硬盘供应商 seagate、Toshiba内存条供应商 SAMSUNG、CrucialCPU供应商 intel、AMD主板供应商 intel、AMD
此处列出多个部件是为了后面讲解工厂方法、抽象工厂方法时使用同一个模拟场景。本章讲简单工厂方法暂时不需要涉及这么多部件,所以仅以硬盘这一个部件为例进行讲解。
3、实现的思路 硬盘就是要创建的对象(即:产品)。为了让不同供应商提供的硬盘可以通用,要定义一个硬盘产品类,并让不同供应商的硬盘都继承硬盘产品类的接口。
还需要定义一个创建硬盘对象的类(即:工厂)。工厂类根据参数决定创建哪家供应商的硬盘对象。
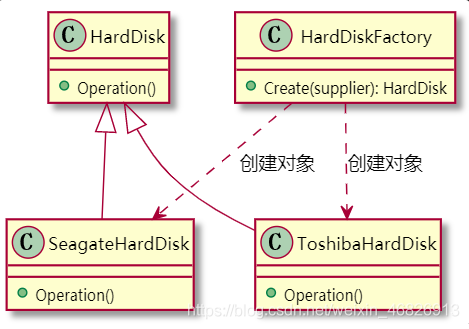
4、实现硬盘对象创建 参与者:
(1)Product: HardDisk 定义硬盘对象的接口
(2)Concrete Product: SeagateHardDisk, ToshibaHardDisk 实现不同供应商的硬盘
(3)SimpleFactory: HardDiskFactory 根据参数,创建不同供应商的硬盘对象
UML:
HardDisk代码示例:
hard_disk.h:
#ifndef HARD_DISK_H #define HARD_DISK_H struct HardDisk { void (*Operation)(struct HardDisk *this);}; #endif SeagateHardDisk代码示例:
seagate_hard_disk.h:
#ifndef SEAGATE_HARD_DISK_H #define SEAGATE_HARD_DISK_H #include "hard_disk.h" struct SeagateHardDisk { struct HardDisk hardDisk; }; // 构造函数 void SeagateHardDisk(struct SeagateHardDisk *this); // 析构函数 void _SeagateHardDisk(struct SeagateHardDisk *this); #endif seagate_hard_disk.c:
#include "seagate_hard_disk.h" #include "stdio.h" void SeagateOperation(struct SeagateHardDisk *this) { printf("这是 Seagate 硬盘\n");} void SeagateHardDisk(struct SeagateHardDisk *this) { this->hardDisk.Operation = (void(*)(struct HardDisk *))SeagateOperation;} void _SeagateHardDisk(struct SeagateHardDisk *this){ this->hardDisk.Operation = NULL;} ToshibaHardDisk代码示例:
toshiba_hard_disk.h:
#ifndef TOSHIBA_HARD_DISK_H #define TOSHIBA_HARD_DISK_H #include "hard_disk.h" struct ToshibaHardDisk { struct HardDisk hardDisk; }; // 构造函数 void ToshibaHardDisk(struct ToshibaHardDisk *this); // 析构函数 void _ToshibaHardDisk(struct ToshibaHardDisk *this); #endif toshiba_hard_disk.c:
#include "toshiba_hard_disk.h" #include "stdio.h" void ToshibaOperation(struct ToshibaHardDisk *this) { printf("这是 Toshiba 硬盘\n");} void ToshibaHardDisk(struct ToshibaHardDisk *this) { this->hardDisk.Operation = (void(*)(struct HardDisk *))ToshibaOperation;} void _ToshibaHardDisk(struct ToshibaHardDisk *this){ this->hardDisk.Operation = NULL;} HardDiskFactory代码示例:
hard_disk_factory.h:
#ifndef HARD_DISK_FACTORY_H #define HARD_DISK_FACTORY_H #include "hard_disk.h" enum HARD_DISK_SUPPLIER_E { HARD_DISK_SUPPLIER_SEAGATE, HARD_DISK_SUPPLIER_TOSHIBA}; struct HardDiskFactory { struct HardDisk* (*Create)(struct HardDiskFactory *this, enum HARD_DISK_SUPPLIER_E supplier); void (*Destroy)(struct HardDiskFactory *this, struct HardDisk* hardDisk);}; // 构造函数 void HardDiskFactory(struct HardDiskFactory *this); // 析构函数 void _HardDiskFactory(struct HardDiskFactory *this); #endif hard_disk_factory.c:
#include "hard_disk_factory.h" #include "seagate_hard_disk.h" #include "toshiba_hard_disk.h" #include "stdio.h" #include "stdlib.h" struct HardDisk *Create(struct HardDiskFactory *this, enum HARD_DISK_SUPPLIER_E supplier) { switch (supplier) { case HARD_DISK_SUPPLIER_SEAGATE: { struct SeagateHardDisk *seagateHardDisk = NULL; if ((seagateHardDisk = malloc(sizeof(struct SeagateHardDisk))) == NULL) { printf("fail in malloc\n"); return NULL; } SeagateHardDisk(seagateHardDisk); return (struct HardDisk *)seagateHardDisk; } case HARD_DISK_SUPPLIER_TOSHIBA: { struct ToshibaHardDisk *toshibaHardDisk = NULL; if ((toshibaHardDisk = malloc(sizeof(struct ToshibaHardDisk))) == NULL) { printf("fail in malloc\n"); return NULL; } ToshibaHardDisk(toshibaHardDisk); return (struct HardDisk *)toshibaHardDisk; } default: printf("未知的供应商\n"); return NULL; }} void Destroy(struct HardDiskFactory *this, struct HardDisk* hardDisk) { if (hardDisk != NULL) { free(hardDisk); }} // 构造函数 void HardDiskFactory(struct HardDiskFactory *this) { this->Create = Create; this->Destroy = Destroy;} // 析构函数 void _HardDiskFactory(struct HardDiskFactory *this){ this->Create = NULL; this->Destroy = NULL;} 客户端代码示例:
#include "hard_disk.h" #include "hard_disk_factory.h" #include "stddef.h" void main() { struct HardDisk *hardDisk = NULL; struct HardDiskFactory hardDiskFactory; HardDiskFactory(&hardDiskFactory); // 创建 seagate 硬盘对象 hardDisk = hardDiskFactory.Create(&hardDiskFactory, HARD_DISK_SUPPLIER_SEAGATE); // 使用 seagate 硬盘对象 hardDisk->Operation(hardDisk); // 销毁 seagate 硬盘对象 hardDiskFactory.Destroy(&hardDiskFactory, hardDisk); // 创建 toshiba 硬盘对象 hardDisk = hardDiskFactory.Create(&hardDiskFactory, HARD_DISK_SUPPLIER_TOSHIBA); // 使用 seagate 硬盘对象 hardDisk->Operation(hardDisk); // 销毁 toshiba 硬盘对象 hardDiskFactory.Destroy(&hardDiskFactory, hardDisk); _HardDiskFactory(&hardDiskFactory);} 客户端显示示例:
./hard_disk这是 Seagate 硬盘这是 Toshiba 硬盘 版权声明:本文来源网络,免费传达知识,版权归原作者所有。如涉及作品版权问题,请联系我进行删除。
本文由编辑推荐,原出处:https://www.eet-china.com/mp/a131324.html



 /5
/5 


