总结了Java异常十个关键知识点,面试或者工作中都有用哦,加油。
一. 异常是什么
异常是指阻止当前方法或作用域继续执行的问题。比如你读取的文件不存在,数组越界,进行除法时,除数为0等都会导致异常。
一个文件找不到的异常:
- publicclassTestException{
- publicstaticvoid main(String[] args) throwsIOException{
- InputStreamis= newFileInputStream("jaywei.txt");
- int b;
- while((b = is.read) != -1) {
- }
- }
- }
- Exceptionin thread "main" java.io.FileNotFoundException: jaywei.txt (系统找不到指定的文件。)
- at java.io.FileInputStream.open0(NativeMethod)
- at java.io.FileInputStream.open(FileInputStream.java:195)
- at java.io.FileInputStream.<init>(FileInputStream.java:138)
- at java.io.FileInputStream.<init>(FileInputStream.java:93)
- at exception.TestException.main(TestException.java:10)
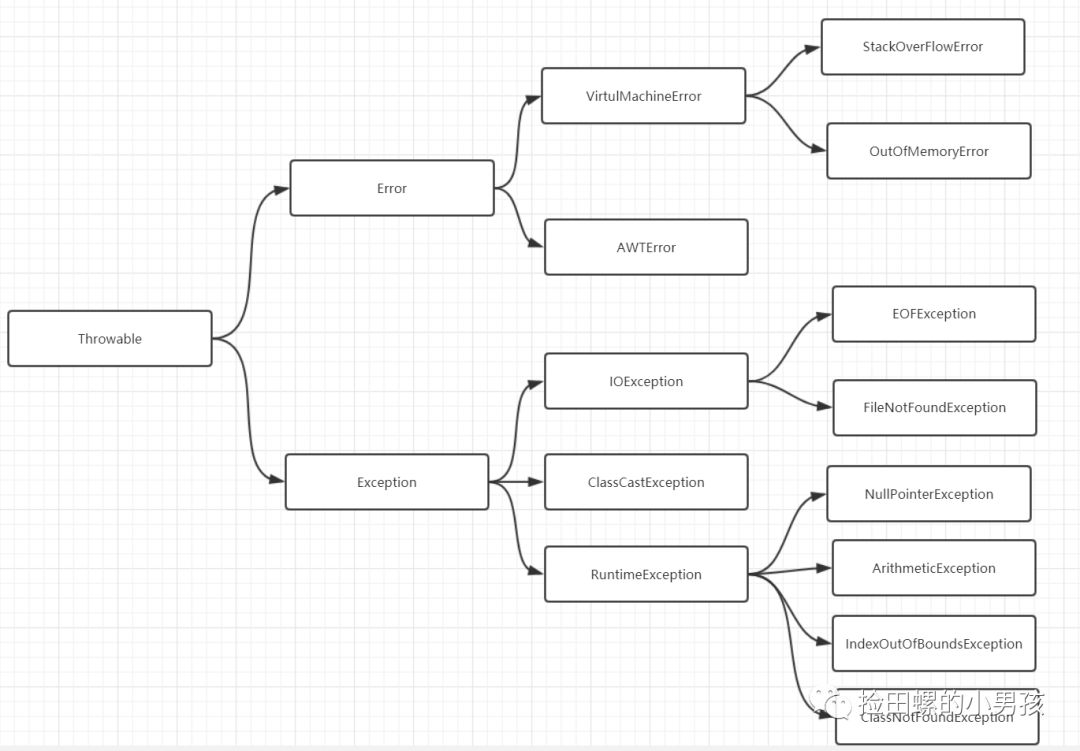
从前从前,有位老人,他的名字叫Throwable,他生了两个儿子,大儿子叫Error,二儿子叫Exception。
Error
表示编译时或者系统错误,如虚拟机相关的错误,OutOfMemoryError等,error是无法处理的。
Exception
代码异常,Java程序员关心的基类型通常是Exception。它能被程序本身可以处理,这也是它跟Error的区别。
它可以分为RuntimeException(运行时异常)和CheckedException(可检查的异常)。
常见的RuntimeException异常:
- - NullPointerException空指针异常
- - ArithmeticException出现异常的运算条件时,抛出此异常
- - IndexOutOfBoundsException数组索引越界异常
- - ClassNotFoundException找不到类异常
- - IllegalArgumentException(非法参数异常)
- - IOException(操作输入流和输出流时可能出现的异常)
- - ClassCastException(类型转换异常类)
- Checked Exception就是编译器要求你必须处置的异常。
- 与之相反的是,Unchecked Exceptions,它指编译器不要求强制处置的异常,它包括Error和RuntimeException 以及他们的子类。
异常处理主要有抛出异常、捕获异常、声明异常。如图:
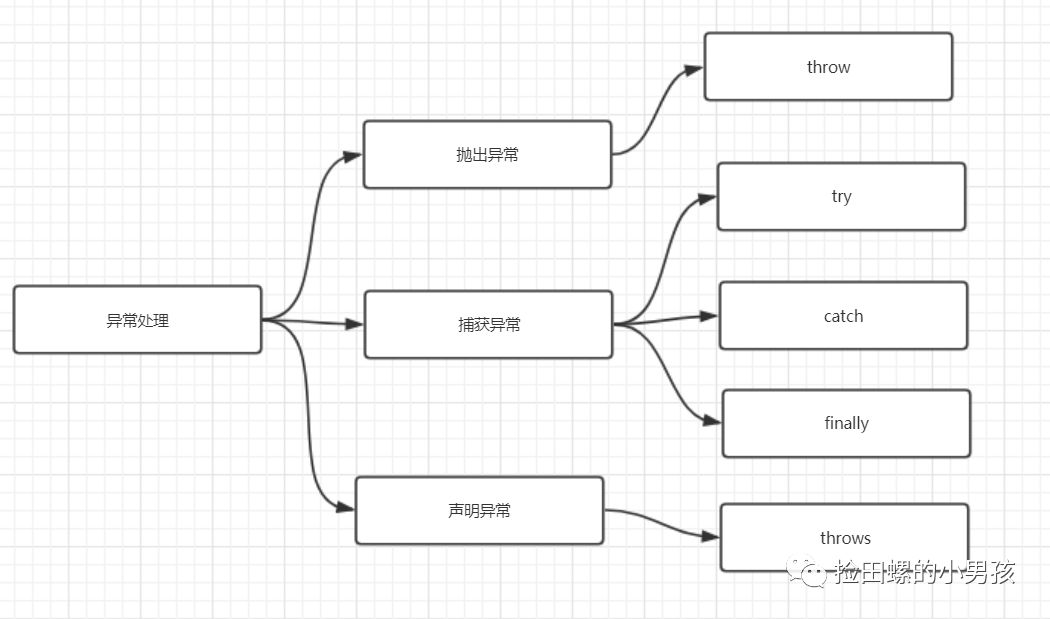
捕获异常
- try{
- // 程序代码
- }catch(Exception e){
- //Catch 块
- }finaly{
- //无论如何,都会执行的代码块
- }
声明抛出异常
除了 try...catch...捕获异常,我们还可以通过throws声明抛出异常。
当你定义了一个方法时,可以用 throws关键字声明。使用了 throws关键字表明,该方法不处理异常,而是把异常留给它的调用者处理。是不是觉得TA不负责任?
哈哈,看一下demo吧
- //该方法通过throws声明了IO异常。
- privatevoid readFile throwsIOException{
- InputStreamis= newFileInputStream("jaywei.txt");
- int b;
- while((b = is.read) != -1) {
- }
- }
抛出异常
throw关键字作用是抛出一个 Throwable类型的异常,它一般出现在函数体中。在异常处理中,try语句要捕获的是一个异常对象,其实此异常对象也可以自己抛出。
例如抛出一个 RuntimeException 类的异常对象:
- thrownewRuntimeException(e);
注意点
- 非检查异常(Error、RuntimeException 或它们的子类)不可使用 throws 关键字来声明要抛出的异常。
- 一个方法出现编译时异常,就需要 try-catch/ throws 处理,否则会导致编译错误。
- 如果不发生异常,不会执行catch部分。
- 不管有没有发生异常,finally都会执行到。
- 即使try和catch中有return时,finally仍然会执行
- finally是在return后面的表达式运算完后再执行的。(此时并没有返回运算后的值,而是先把要返回的值保存起来,若finally中无return,则不管finally中的代码怎么样,返回的值都不会改变,仍然是之前保存的值),该情况下函数返回值是在finally执行前确定的)
- finally部分就不要return了,要不然,就回不去try或者catch的return了。
- publicstaticvoid main(String[] args) throwsIOException{
- System.out.println("result:"+ test);
- }
- privatestaticint test {
- int temp = 1;
- try{
- System.out.println("start execute try,temp is:"+temp);
- return++temp;
- } catch(Exception e) {
- System.out.println("start execute catch temp is: "+temp);
- return++temp;
- } finally{
- System.out.println("start execute finally,temp is:"+ temp);
- ++temp;
- }
- }
- start execute try,temp is:1
- start execute finally,temp is:2
- result:2
- 先执行try部分,输出日志,执行 ++temp表达式,temp变为2,这个值被保存起来。
- 因为没有发生异常,所以catch代码块跳过。
- 执行finally代码块,输出日志,执行 ++temp表达式.
- 返回try部分保存的值2.
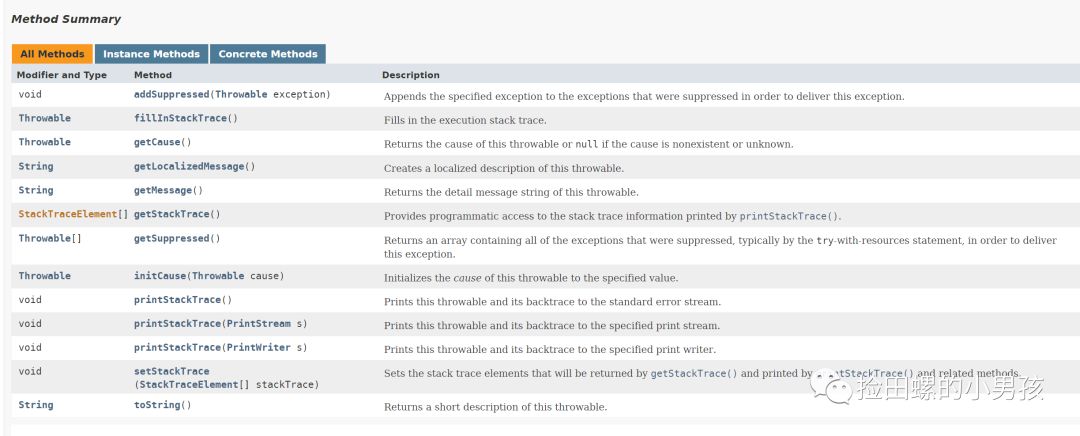
getMessage
- Returns the detail message string of this throwable.
举个例子, FileNotFoundException异常发生时,这个 detailMessage就包含这个找不到文件的名字。
getLocalizedMessage
- Creates a localized deion of this throwable.Subclasses may overridethis
- method in order to produce alocale-specific message. For subclasses that donot
- override thismethod, the default implementation returns the same result
- as getMessage
getCause
- Returns the cause of this throwable ornullif thecause is nonexistent or unknown.
printStackTrace
- Printsthis throwable and its backtrace to thestandard error stream.
- The first line of output contains the result of the toString method for
- thisobject.Remaining lines represent data previously recorded by the
- method fillInStackTrace.
输出的第一行,包含此对象toString方法的结果。剩余的行表示,先前被方法fillInStackTrace记录的数据。如下例子:
- java.lang.NullPointerException
- at MyClass.mash(MyClass.java:9)
- at MyClass.crunch(MyClass.java:6)
- at MyClass.main(MyClass.java:3)
那么,为什么需要自定义异常?
- Java提供的异常体系不可能预见所有的错误。
- 业务开发中,使用自定义异常,可以让项目代码更加规范,也便于管理。
- publicclassBizExceptionextendsException{
- //错误信息
- privateString message;
- //错误码
- privateString errorCode;
- publicBizException {
- }
- publicBizException(String message, String errorCode) {
- this.message = message;
- this.errorCode = errorCode;
- }
- @Override
- publicString getMessage {
- return message;
- }
- publicvoid setMessage(String message) {
- this.message = message;
- }
- publicString getErrorCode {
- return errorCode;
- }
- publicvoid setErrorCode(String errorCode) {
- this.errorCode = errorCode;
- }
- }
- publicclassTestBizException{
- publicstaticvoid testBizException throwsBizException{
- System.out.println("throwing BizException from testBizException");
- thrownewBizException("100","哥,我错了");
- }
- publicstaticvoid main(String[] args) {
- try{
- testBizException;
- } catch(BizException e) {
- System.out.println("自己定义的异常");
- e.printStackTrace;
- }
- }
- }
- exception.BizException: 100
- throwing BizExceptionfrom testBizException
- 自己定义的异常
- at exception.TestBizException.testBizException(TestBizException.java:7)
- at exception.TestBizException.main(TestBizException.java:12)
- 资源是指在程序用完了之后必须要关闭的对象。
- try-with-resources保证了每个声明了的资源在语句结束的时候会被关闭
- 什么样的对象才能当做资源使用呢?只要实现了java.lang.AutoCloseable接口或者java.io.Closeable接口的对象,都OK。
- try{
- //open resources like File, Database connection, Sockets etc
- } catch(FileNotFoundException e) {
- // Exception handling like FileNotFoundException, IOException etc
- }finally{
- // close resources
- }
- try(// open resources here){
- // use resources
- } catch(FileNotFoundException e) {
- // exception handling
- }
- // resources are closed as soon as try-catch block is executed.
- publicclassJava7TryResourceTest{
- publicstaticvoid main(String[] args) {
- try(BufferedReader br = newBufferedReader(newFileReader(
- "C:/jaywei.txt"))) {
- System.out.println(br.readLine);
- } catch(IOException e) {
- e.printStackTrace;
- }
- }
- }
- 代码更加优雅,行数更少。
- 资源自动管理,不用担心内存泄漏问题。
throw抛出的是一个新的异常信息,这样会导致原有的异常信息丢失。在JDk1.4以前,程序员必须自己编写代码来保存原始异常信息。现在所有 Throwable子类在构造器中都可以接受一个 cause(异常因由)对象作为参数。
这个 cause就用来表示原始异常,这样通过把原始异常传递给新的异常,使得即使当前位置创建并抛出了新的异常,也能通过这个异常链追踪到异常最初发生的位置。
使用方式如下:
- publicclassTestChainException{
- publicvoid readFile throwsMyException{
- try{
- InputStreamis= newFileInputStream("jay.txt");
- Scannerin= newScanner(is);
- while(in.hasNext) {
- System.out.println(in.next);
- }
- } catch(FileNotFoundException e) {
- //e 保存异常信息
- thrownewMyException("文件在哪里呢", e);
- }
- }
- publicvoid invokeReadFile throwsMyException{
- try{
- readFile;
- } catch(MyException e) {
- //e 保存异常信息
- thrownewMyException("文件找不到", e);
- }
- }
- publicstaticvoid main(String[] args) {
- TestChainException t = newTestChainException;
- try{
- t.invokeReadFile;
- } catch(MyException e) {
- e.printStackTrace;
- }
- }
- }
- //MyException 构造器
- publicMyException(String message, Throwable cause) {
- super(message, cause);
- }
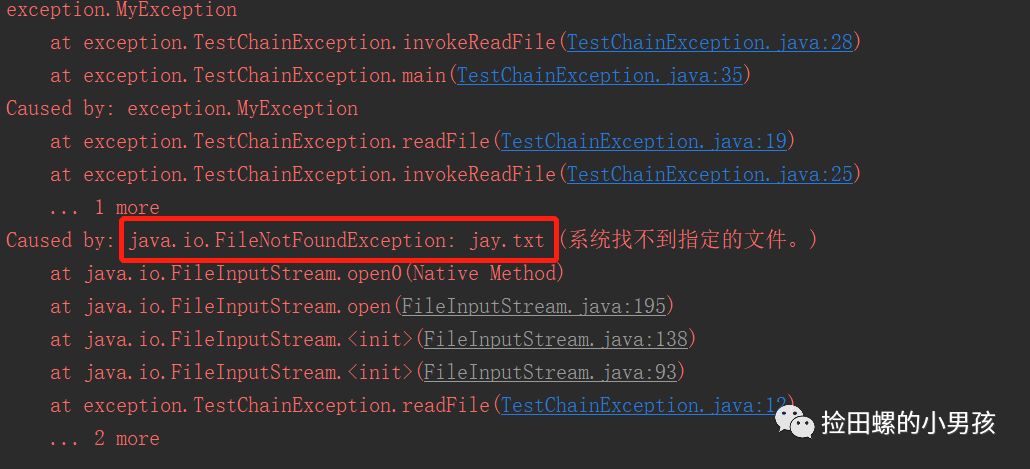
我们可以看到异常信息有保存下来的,如果把cause(也就是FileNotFoundException 的e)去掉呢,看一下运行结果:

可以发现,少了 Throwablecause,原始异常信息不翼而飞了。
九、异常匹配
抛出异常的时候,异常处理系统会按照代码的书写顺序找出"最近"的处理程序。找到匹配的处理程序之后,它就认为异常将得到处理,然后就不再继续查找。
查找的时候并不要求抛出的异常同处理程序的异常完全匹配。派生类的对象也可以配备其基类的处理程序
看demo
- package exceptions;
- //: exceptions/Human.java
- // Catching exception hierarchies.
- classAnnoyanceextendsException{}
- classSneezeextendsAnnoyance{}
- publicclassHuman{
- publicstaticvoid main(String[] args) {
- // Catch the exact type:
- try{
- thrownewSneeze;
- } catch(Sneeze s) {
- System.out.println("Caught Sneeze");
- } catch(Annoyance a) {
- System.out.println("Caught Annoyance");
- }
- // Catch the base type:
- try{
- thrownewSneeze;
- } catch(Annoyance a) {
- System.out.println("Caught Annoyance");
- }
- }
- }
catch(Annoyance a)会捕获Annoyance以及所有从它派生的异常。捕获基类的异常,就可以匹配所有派生类的异常
- try{
- thrownewSneeze;
- } catch(Annoyance a) {
- } catch(Sneeze s) { //这句编译器会报错,因为异常已由前面catch子句处理
- }
ArithmeticException
算术异常类,程序中出现了除数为0这样的运算,就会出现这样的异常。
ClassCastException
类型强制转换异常,它是JVM在检测到两个类型间转换不兼容时引发的运行时异常。
ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException
数组下标越界异常,跟数组打交道时,需要注意一下这个异常。
FileNotFoundException
文件未找到异常,一般是要读或者写的文件,找不到,导致该异常。
SQLException
操作数据库异常,它是Checked Exception(检查异常);
IOException
IO异常,一般跟读写文件息息相关,它也是Checked Exception(检查异常)。平时读写文件,记得IO流关闭!
NoSuchMethodException
方法未找到异常
NumberFormatException
字符串转换为数字异常







 /2
/2 

