摘要
YOLOV5严格意义上说并不是YOLO的第五个版本,因为它并没有得到YOLO之父Joe Redmon的认可,但是给出的测试数据总体表现还是不错。详细数据如下
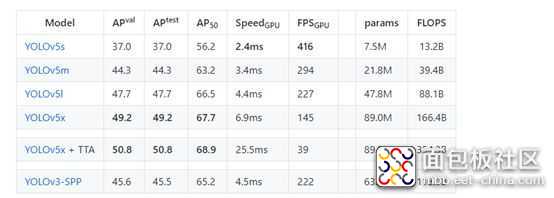
YOLOv5并不是一个单独的模型,而是一个模型家族,包括了YOLOv5s、YOLOv5m、YOLOv5l、YOLOv5x、YOLOv5x+TTA,这点有点儿像EfficientDet。由于没有找到V5的论文,我们也只能从代码去学习它。总体上和YOLOV4差不多,可以认为是YOLOV5的加强版。
训练 1、下载代码
项目地址:https://github.com/ultralytics/YOLOv5,最近作者又更新了一些代码。
2、配置环境
matplotlib>=3.2.2numpy>=1.18.5 opencv-python>=4.1.2 pillow PyYAML>=5.3 scipy>=1.4.1 tensorboard>=2.2 torch>=1.6.0 torchvision>=0.7.0 tqdm>=4.41.0
复制代码数据集采用Labelme标注的数据格式,数据集从RSOD数据集中获取了飞机和油桶两类数据集,并将其转为Labelme标注的数据集。
数据集的地址: https://pan.baidu.com/s/1iTUpvA9_cwx1qiH8zbRmDg
提取码:gr6g
或者:LabelmeData.zip_yolov5实战-深度学习文档类资源-CSDN下载
将下载的数据集解压后放到工程的根目录。为下一步生成测试用的数据集做准备。如下图:
4、生成数据集
YoloV5的数据集和以前版本的数据集并不相同,我们先看一下转换后的数据集。
数据结构如下图:
images文件夹存放train和val的图片
labels里面存放train和val的物体数据,里面的每个txt文件和images里面的图片是一一对应的。
txt文件的内容如下:
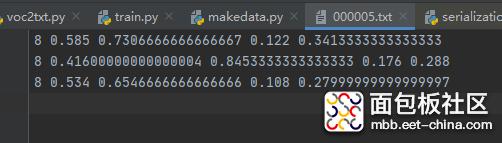
格式:物体类别 x y w h
坐标是不是真实的坐标,是将坐标除以宽高后的计算出来的,是相对于宽和高的比例。
下面我们编写生成数据集的代码,新建LabelmeToYoloV5.py,然后写入下面的代码。
import osimport numpy as np import json from glob import glob import cv2 from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split from os import getcwd classes = ["aircraft", "oiltank"] # 1.标签路径 labelme_path = "LabelmeData/" isUseTest = True # 是否创建test集 # 3.获取待处理文件 files = glob(labelme_path + "*.json") files = [i.replace("\", "/").split("/")[-1].split(".json")[0] for i in files] print(files) if isUseTest: trainval_files, test_files = train_test_split(files, test_size=0.1, random_state=55) else: trainval_files = files # split train_files, val_files = train_test_split(trainval_files, test_size=0.1, random_state=55) def convert(size, box): dw = 1. / (size[0]) dh = 1. / (size[1]) x = (box[0] + box[1]) / 2.0 - 1 y = (box[2] + box[3]) / 2.0 - 1 w = box[1] - box[0] h = box[3] - box[2] x = x * dw w = w * dw y = y * dh h = h * dh return (x, y, w, h) wd = getcwd() print(wd) def ChangeToYolo5(files, txt_Name): if not os.path.exists('tmp/'): os.makedirs('tmp/') list_file = open('tmp/%s.txt' % (txt_Name), 'w') for json_file_ in files: json_filename = labelme_path + json_file_ + ".json" imagePath = labelme_path + json_file_ + ".jpg" list_file.write('%s/%s\n' % (wd, imagePath)) out_file = open('%s/%s.txt' % (labelme_path, json_file_), 'w') json_file = json.load(open(json_filename, "r", encoding="utf-8")) height, width, channels = cv2.imread(labelme_path + json_file_ + ".jpg").shape for multi in json_file["shapes"]: points = np.array(multi["points"]) xmin = min(points[:, 0]) if min(points[:, 0]) > 0 else 0 xmax = max(points[:, 0]) if max(points[:, 0]) > 0 else 0 ymin = min(points[:, 1]) if min(points[:, 1]) > 0 else 0 ymax = max(points[:, 1]) if max(points[:, 1]) > 0 else 0 label = multi["label"] if xmax <= xmin: pass elif ymax <= ymin: pass else: cls_id = classes.index(label) b = (float(xmin), float(xmax), float(ymin), float(ymax)) bb = convert((width, height), b) out_file.write(str(cls_id) + " " + " ".join([str(a) for a in bb]) + '\n') print(json_filename, xmin, ymin, xmax, ymax, cls_id) ChangeToYolo5(train_files, "train") ChangeToYolo5(val_files, "val") ChangeToYolo5(test_files, "test")
复制代码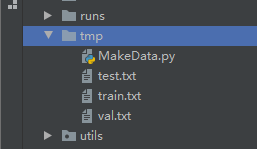
打开MakeData.py,写入下面的代码。
import shutilimport os file_List = ["train", "val", "test"] for file in file_List: if not os.path.exists('../VOC/images/%s' % file): os.makedirs('../VOC/images/%s' % file) if not os.path.exists('../VOC/labels/%s' % file): os.makedirs('../VOC/labels/%s' % file) print(os.path.exists('../tmp/%s.txt' % file)) f = open('../tmp/%s.txt' % file, 'r') lines = f.readlines() for line in lines: print(line) line = "/".join(line.split('/')[-5:]).strip() shutil.copy(line, "../VOC/images/%s" % file) line = line.replace('JPEGImages', 'labels') line = line.replace('jpg', 'txt') shutil.copy(line, "../VOC/labels/%s/" % file)
复制代码
5、修改配置参数
打开voc.yaml文件,修改里面的配置参数train: VOC/images/train/ # 训练集图片的路径 val: VOC/images/val/ # 验证集图片的路径 # number of classes nc: 2 #检测的类别,本次数据集有两个类别所以写2 # class names names: ["aircraft", "oiltank"]#类别的名称,和转换数据集时的list对应
复制代码6、修改train.py的参数
cfg参数是YoloV5 模型的配置文件,模型的文件存放在models文件夹下面,按照需求填写不同的文件。weights参数是YoloV5的预训练模型,和cfg对应,例:cfg配置的是yolov5s.yaml,weights就要配置yolov5s.pt data是配置数据集的配置文件,我们选用的是voc.yaml,所以配置data/voc.yaml 修改上面三个参数就可以开始训练了,其他的参数根据自己的需求修改。修改后的参数配置如下: parser.add_argument('--weights', type=str, default='yolov5s.pt', help='initial weights path') parser.add_argument('--cfg', type=str, default='yolov5s.yaml', help='model.yaml path') parser.add_argument('--data', type=str, default='data/voc.yaml', help='data.yaml path')
复制代码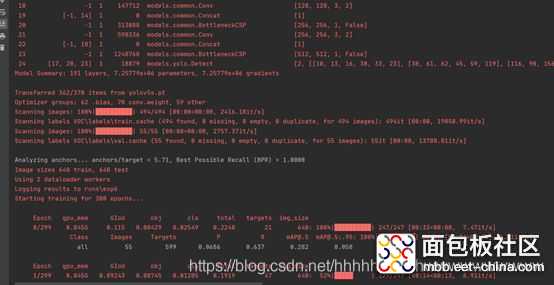
7、查看训练结果
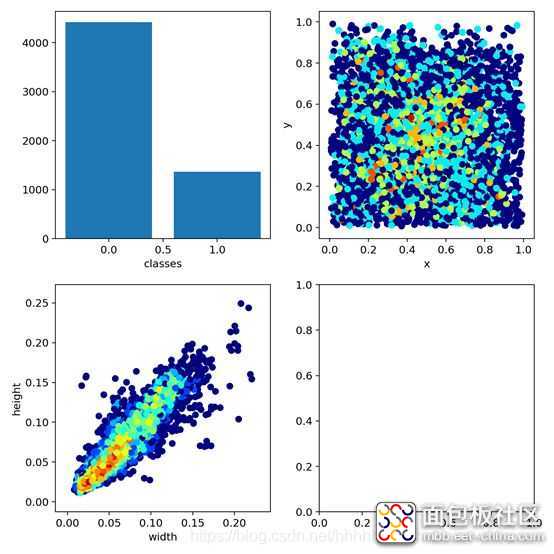
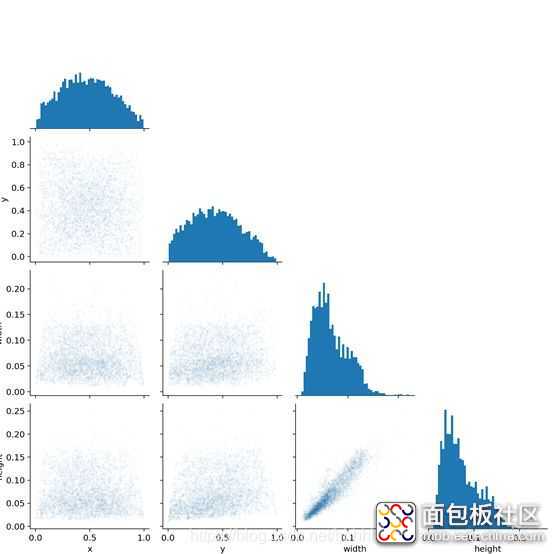
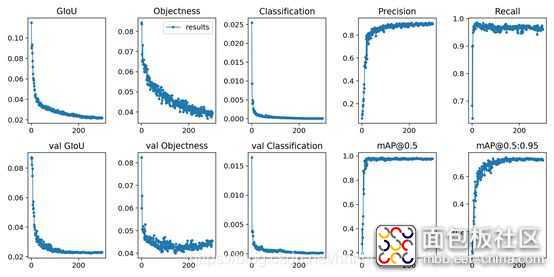
在经历了300epoch训练之后,我们会在runs文件夹下面找到训练好的权重文件和训练过程的一些文件。如图:

测试
首先需要在voc.yaml中增加测试集的路径,打开voc.yaml,在val字段后面增加test: tmp/test.txt这行代码,如图:
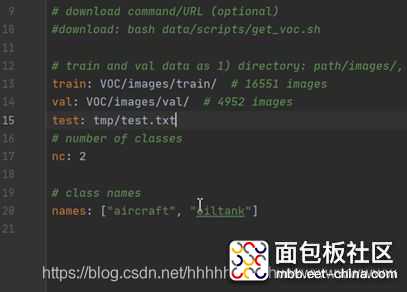
修改test.py中的参数,下面的这几个参数要修改。
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(prog='test.py')parser.add_argument('--weights', nargs='+', type=str, default='runs/exp7/weights/best.pt', help='model.pt path(s)') parser.add_argument('--data', type=str, default='data/voc.yaml', help='*.data path') parser.add_argument('--batch-size', type=int, default=2, help='size of each image batch') parser.add_argument('--save-txt', default='True', action='store_true', help='save results to *.txt')
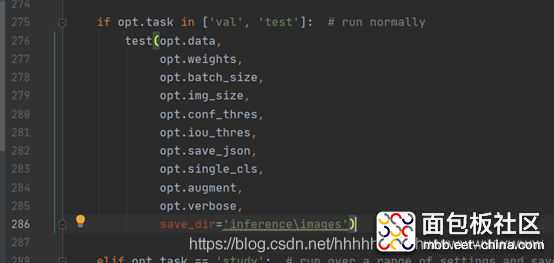
复制代码在275行 修改test的方法,增加保存测试结果的路径。这样测试完成后就可以在inference\images查看到测试的图片,在inference\output中查看到保存的测试结果。
如图:
下面是运行的结果:
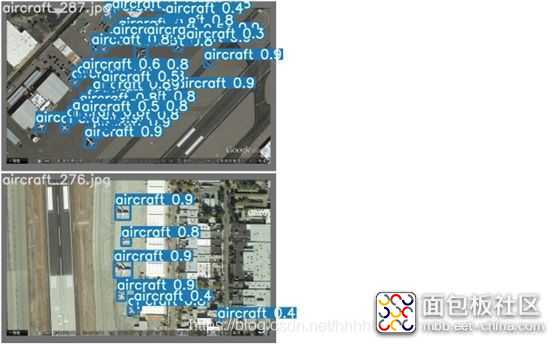






 /5
/5 


