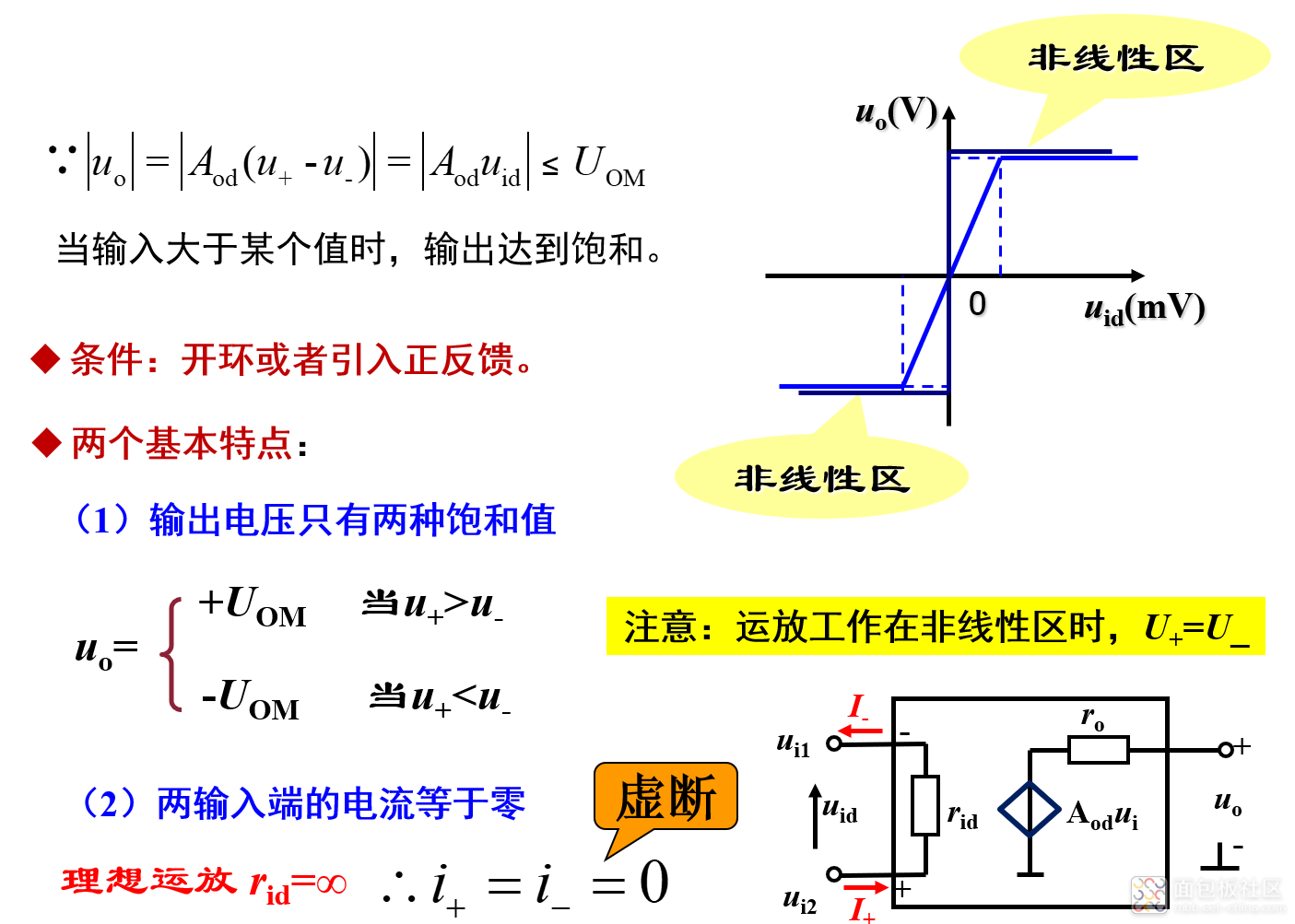
1 概述
(1)集成运放的等效电路模型
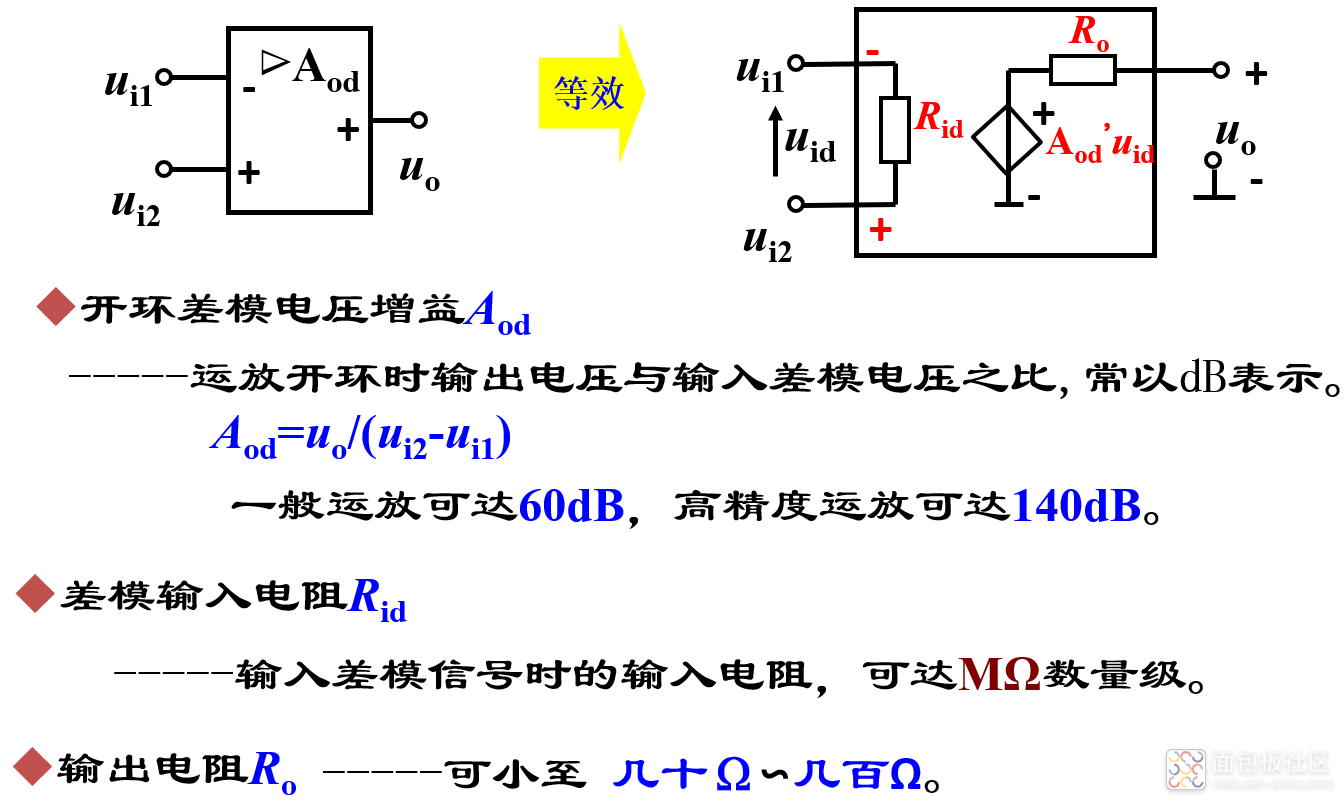
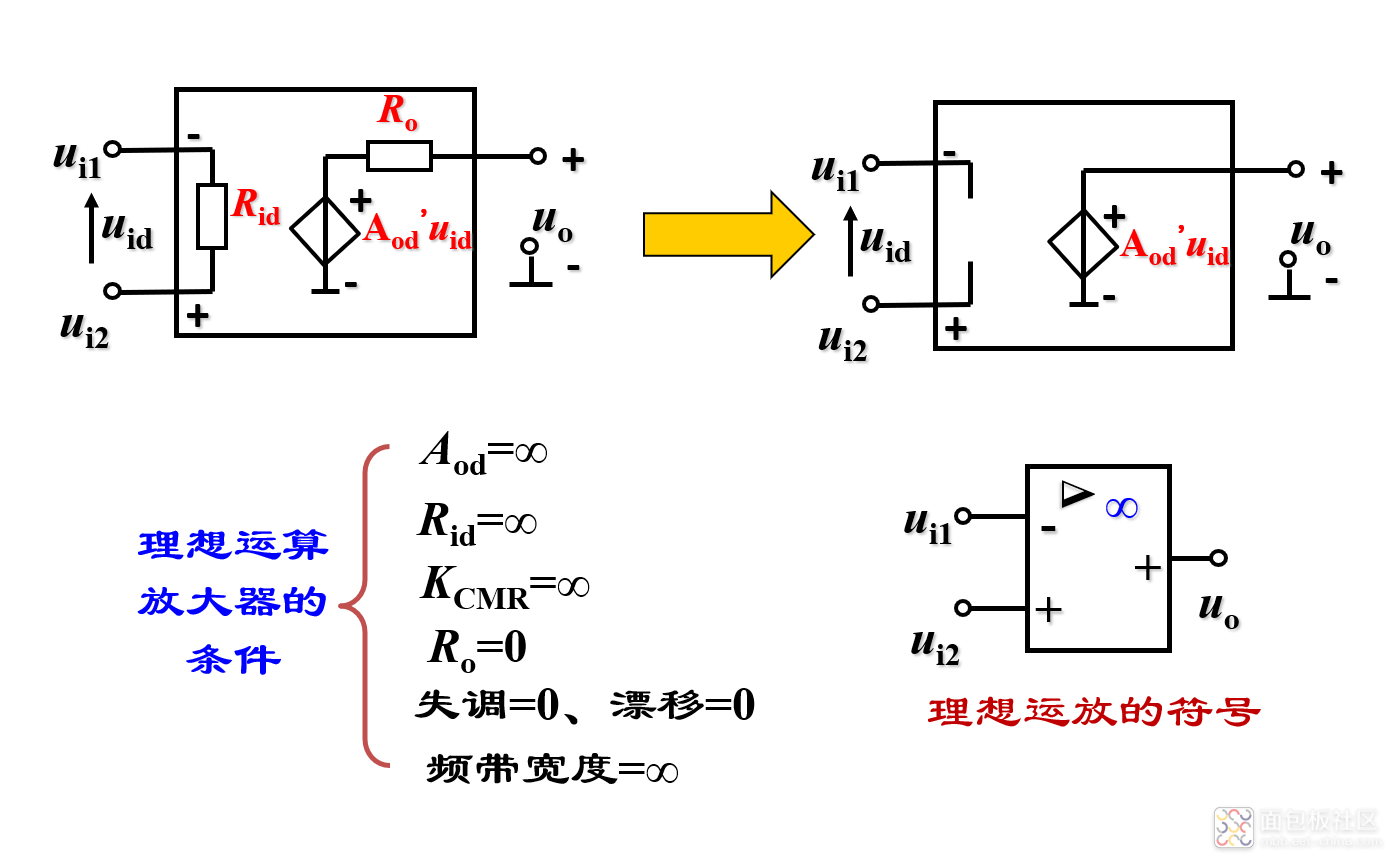
(2)理想运放的两个工作区域
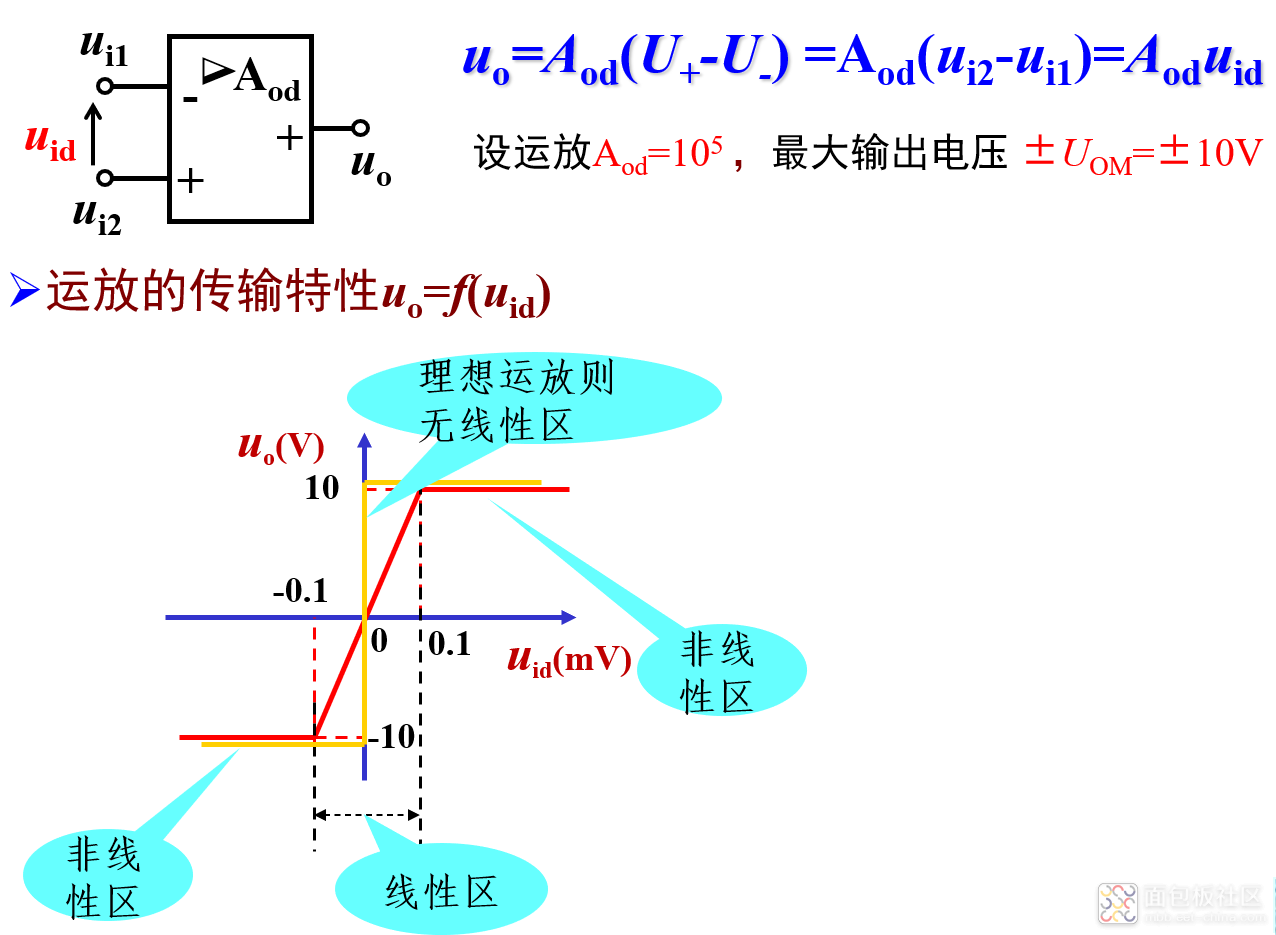
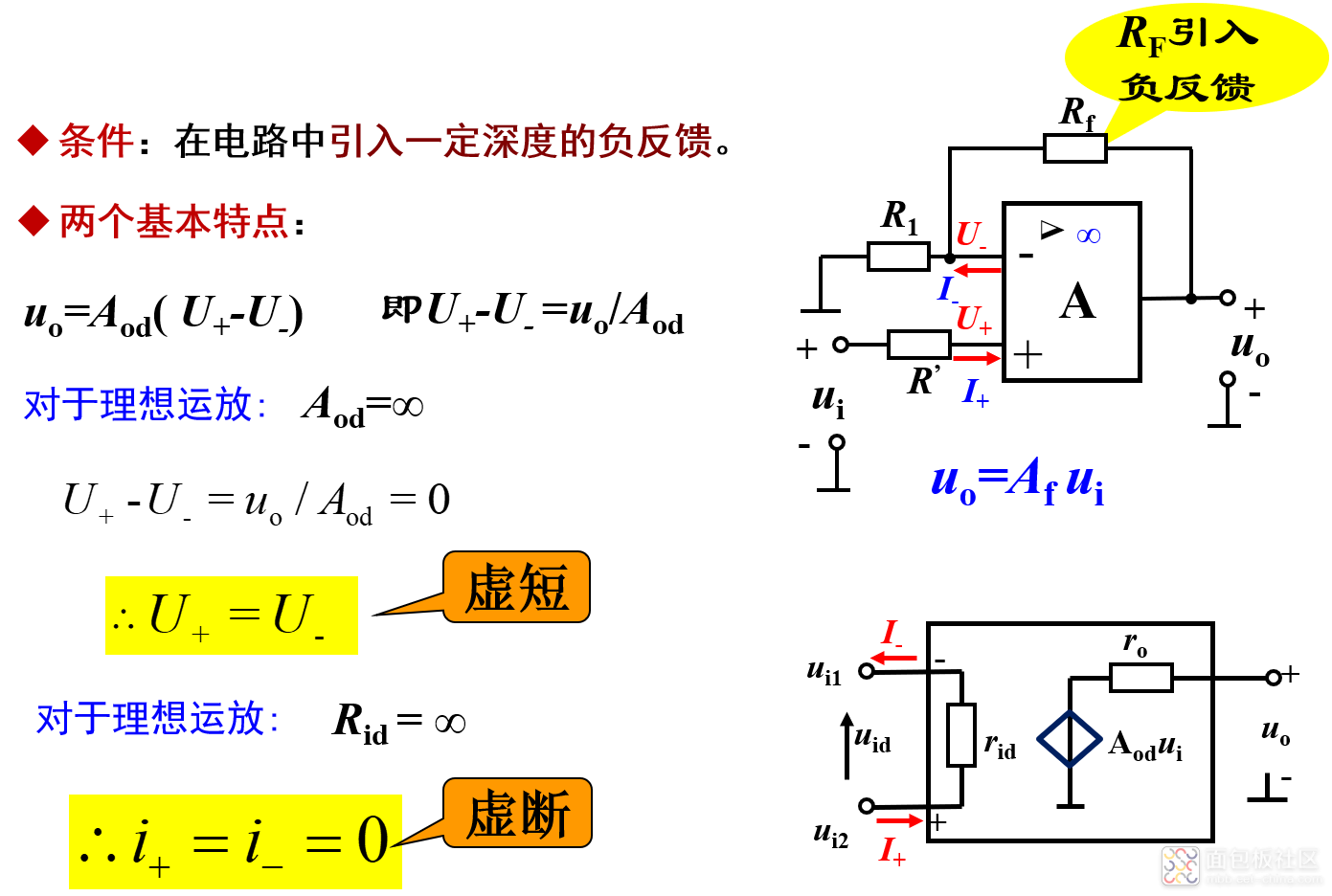
注意:运放在开环状态下线性区很窄,即开环运放只能工作在非线性区;运放工作在线性区的条件是在电路中引入一定深度的负反馈,以减小净输入电压uid。
具体如下:
1)线性区
2)非线性区
2 基本运算电路
(1)比例运算电路
实现将输入信号按比例放大的电路,称为比例运算电路,分为反相比例运算和同相比例运算。
1)反相比例运算电路
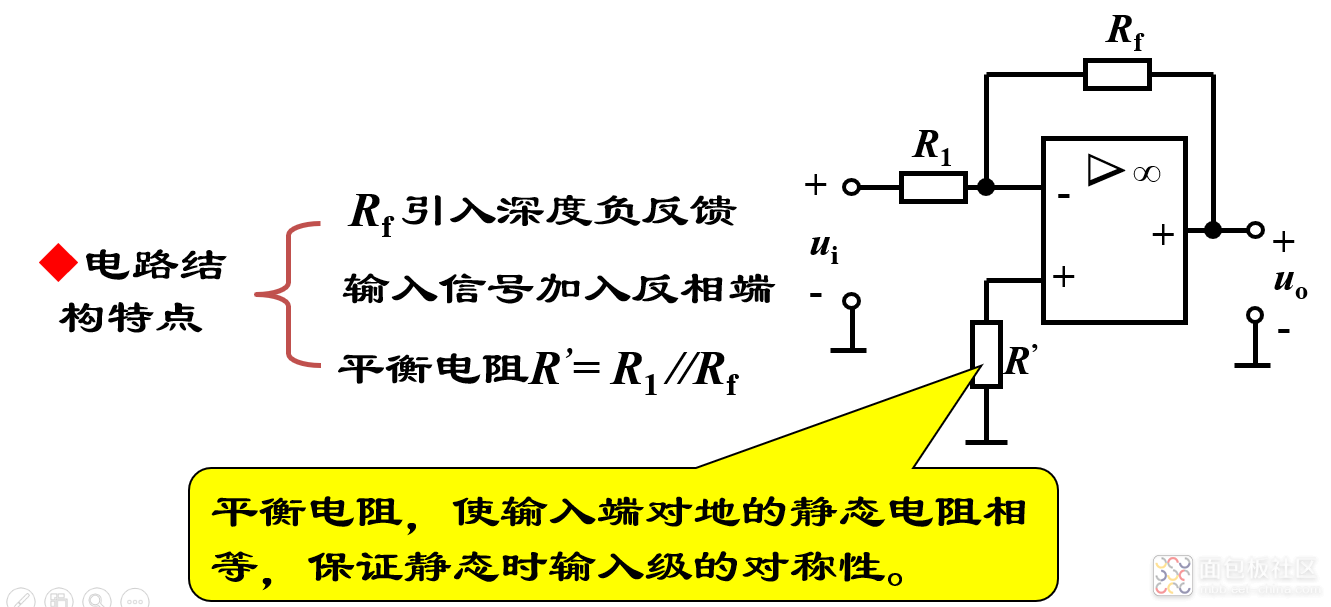
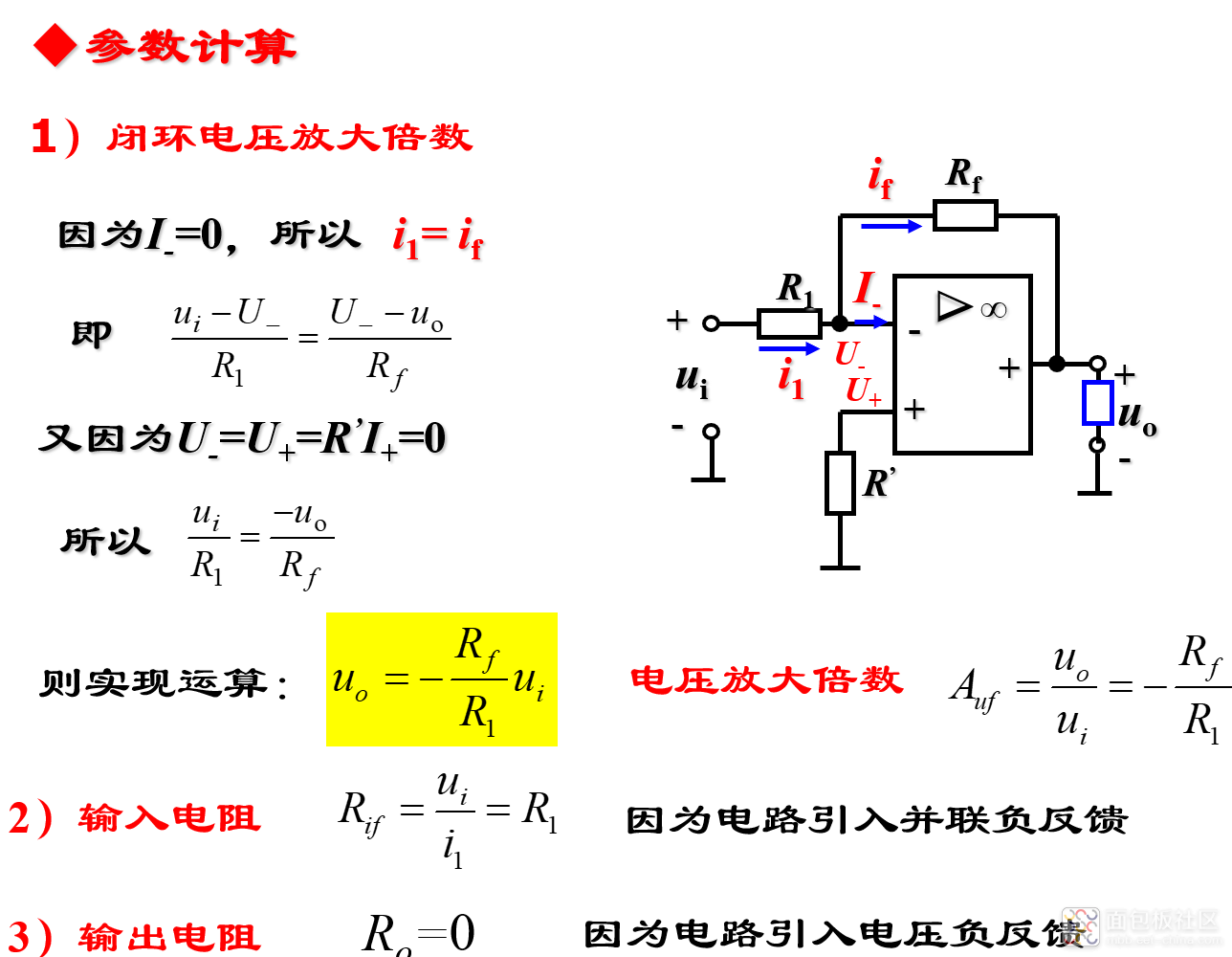
反相比例电路的特点:
优点:共模输入电压为0,因此对运放的共模抑制比要求低;由于电压负反馈的作用,输出电阻小,可认为是0,因此带负载能力强。
缺点:由于并联负反馈的作用,输入电阻小,因此对输入电流有一定的要求。
一句话:输入电阻小、共模电压为 0 以及“虚地” 。
例:要求设计一反相比例运算电路,输入电阻为100kΩ,比例系数为-100。
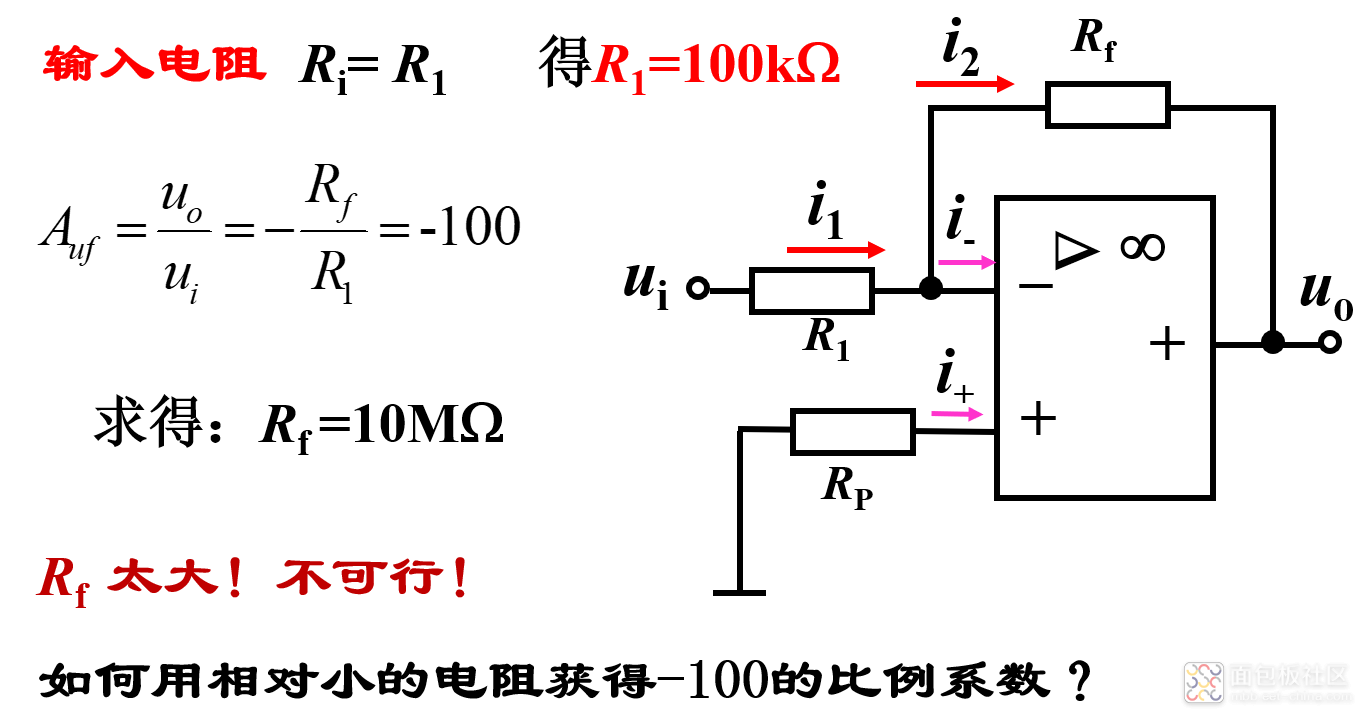
解决此问题的方法是:引入T型反馈网络反相比例运算电路 :
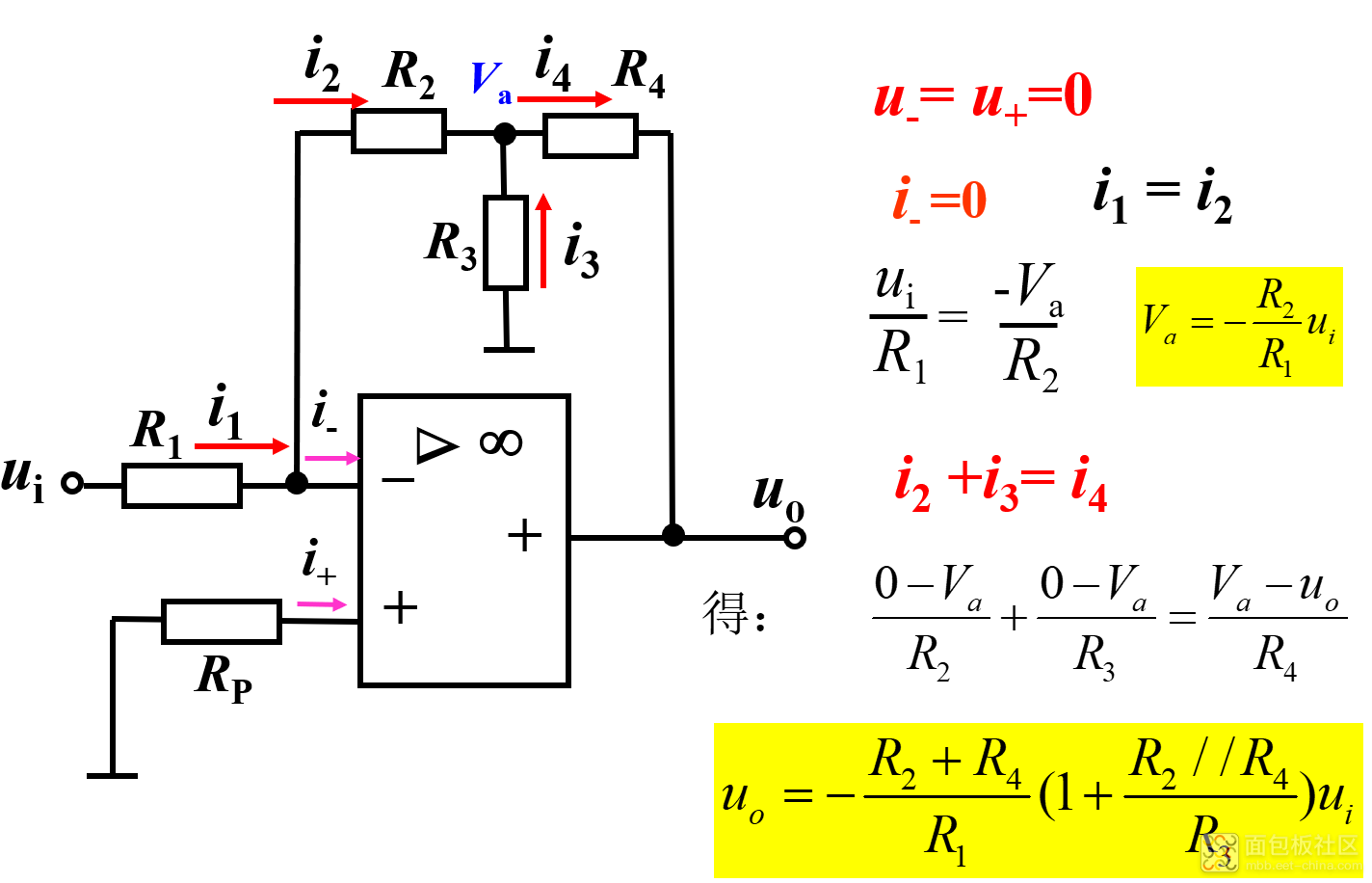
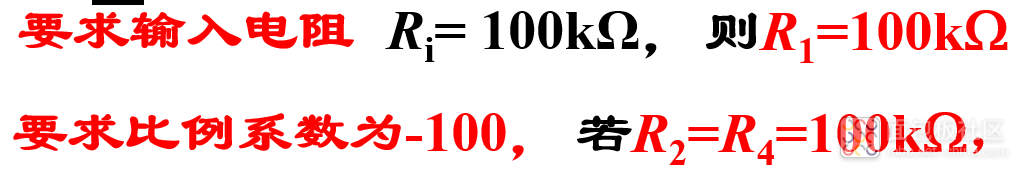
2)同相比例运算电路
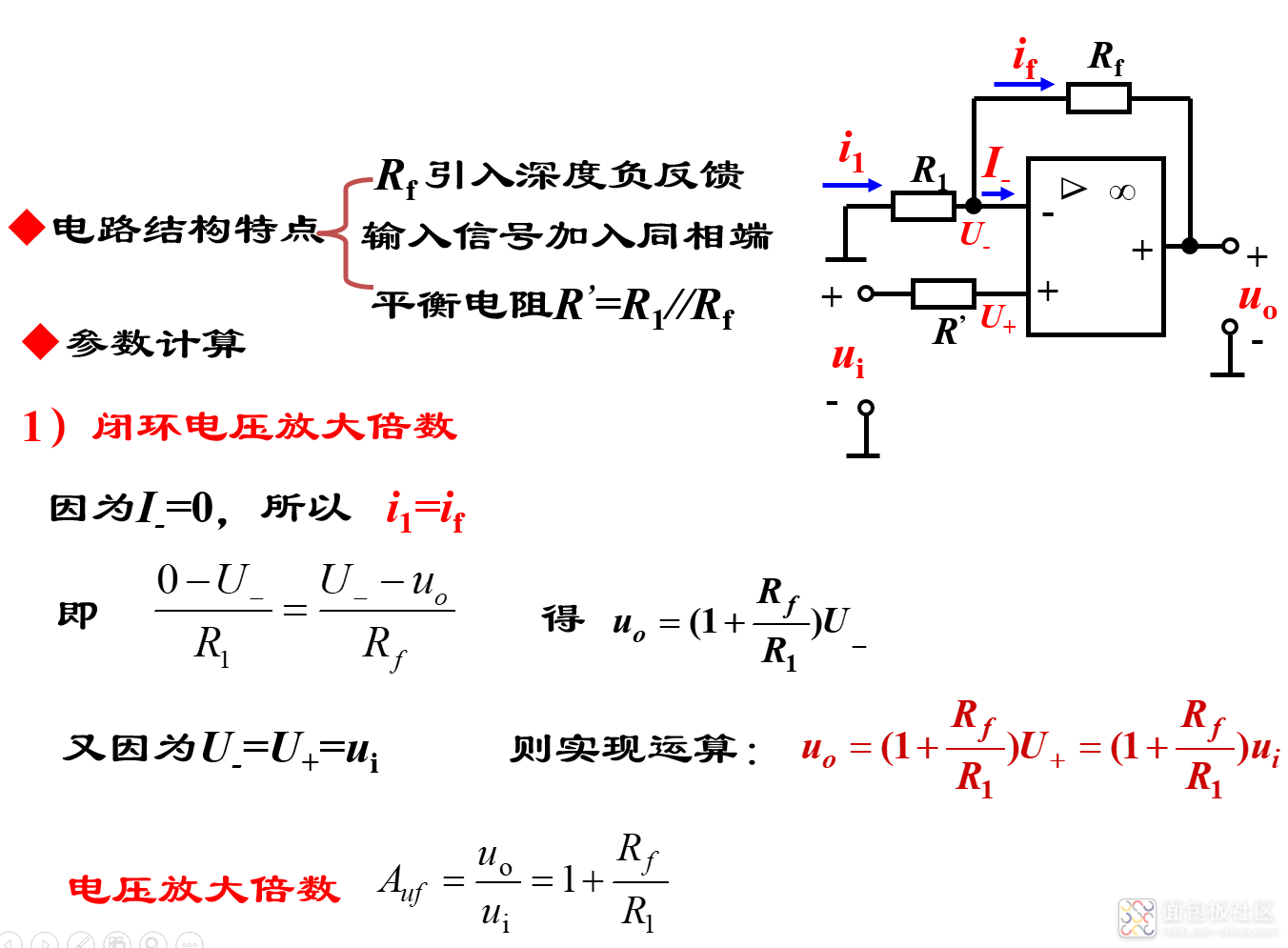
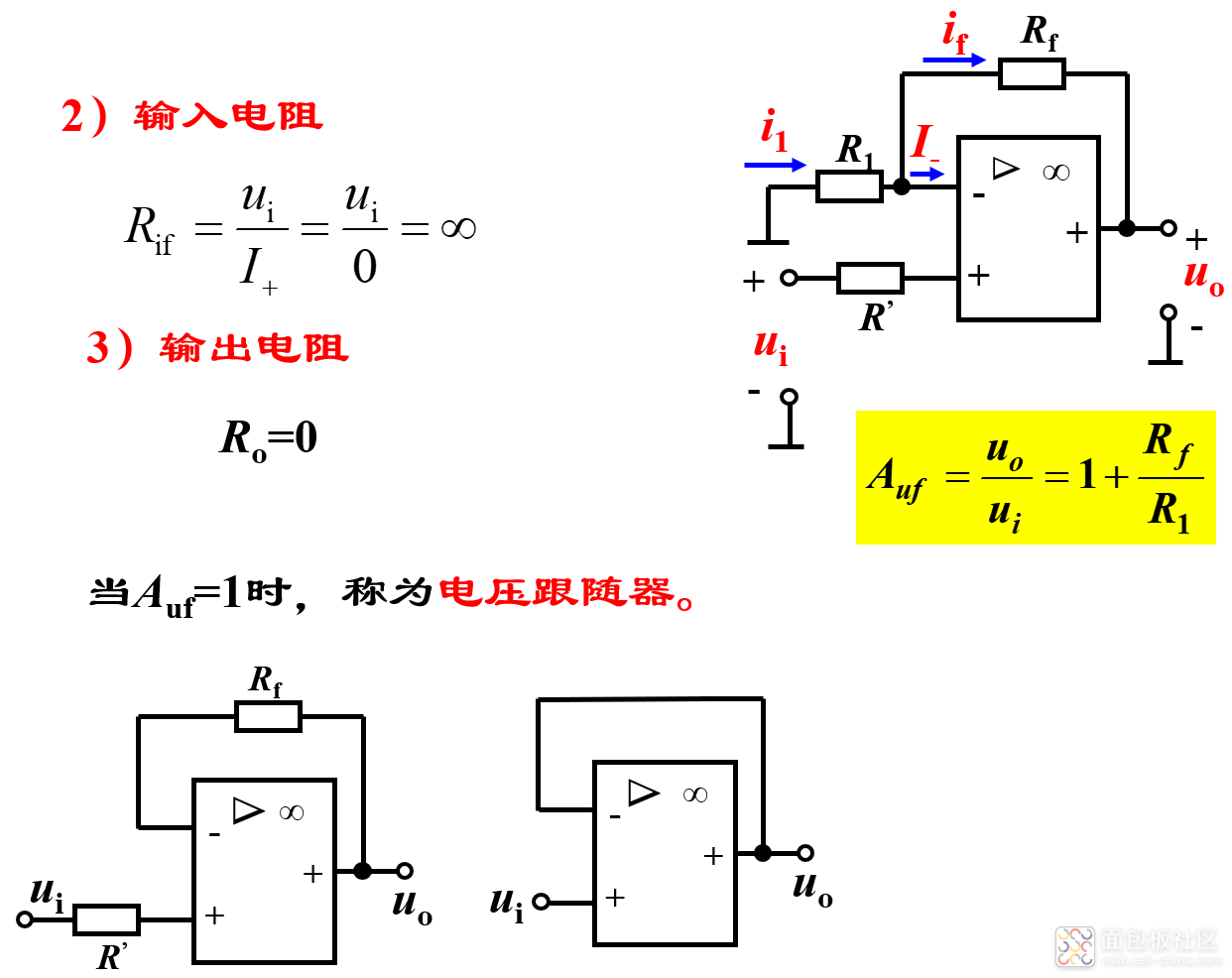
电路引入电压串联负反馈,输入电阻大,输出电阻小,在电路中作用与射极输出器相同,但是电压跟随性能好。
同相比例电路的特点:
优点:由于电压负反馈的作用,输出电阻小,可认为是0,因此带负载能力强;由于串联负反馈的作用,输入电阻大。
缺点:共模输入电压为ui,因此对运放的共模抑制比要求高。
(2)加减运算电路
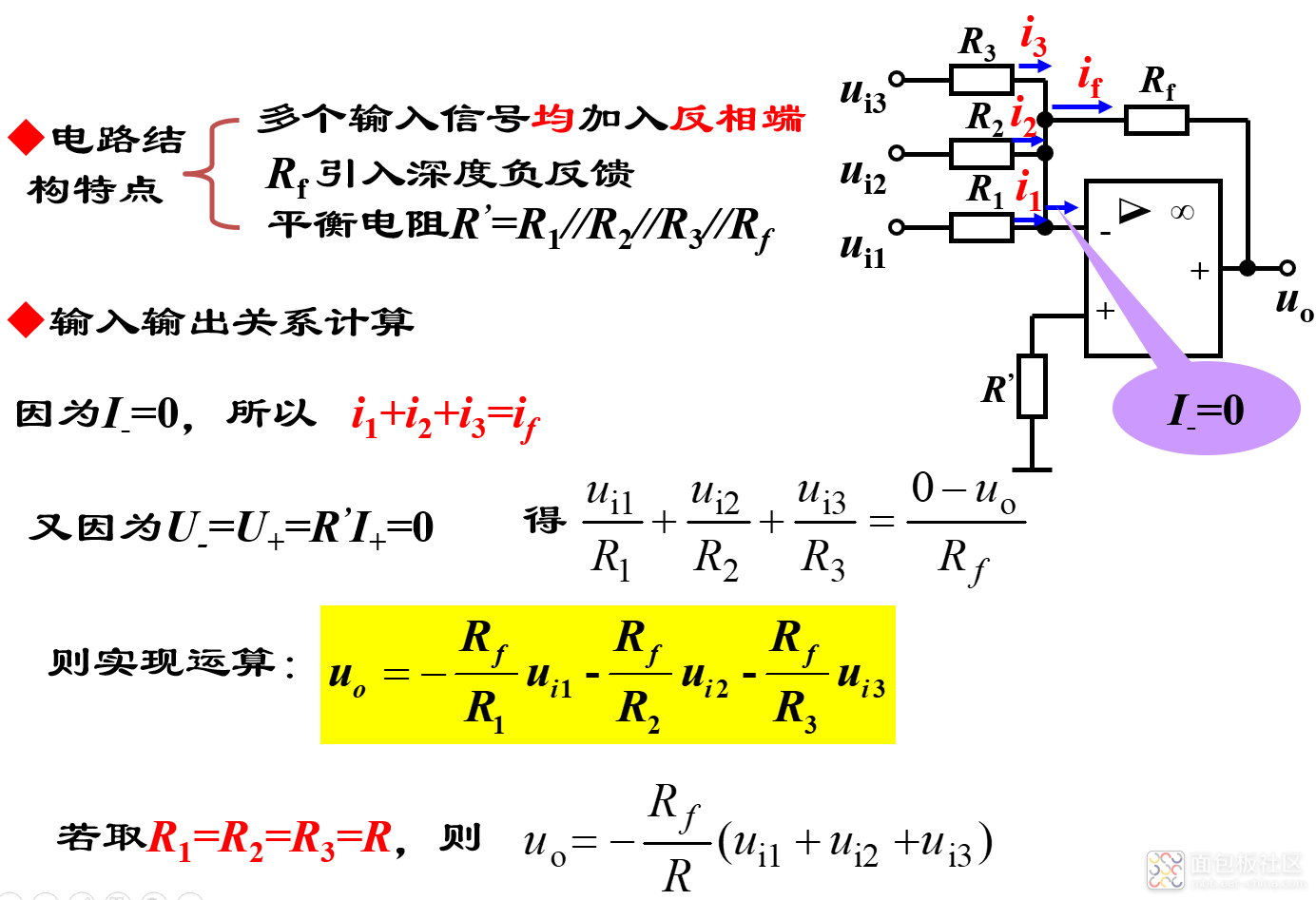
1)反相加法器
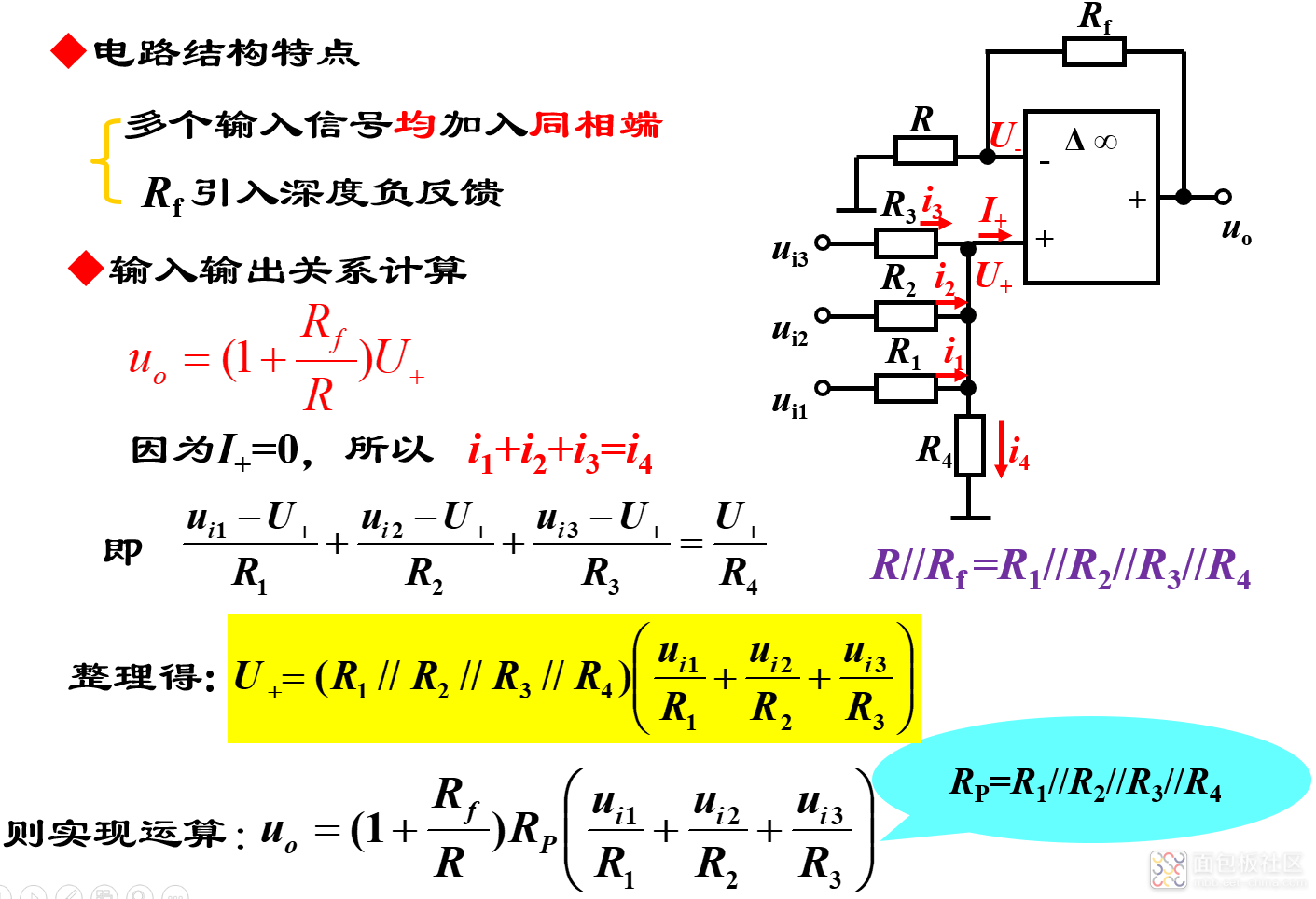
2)同相加法器
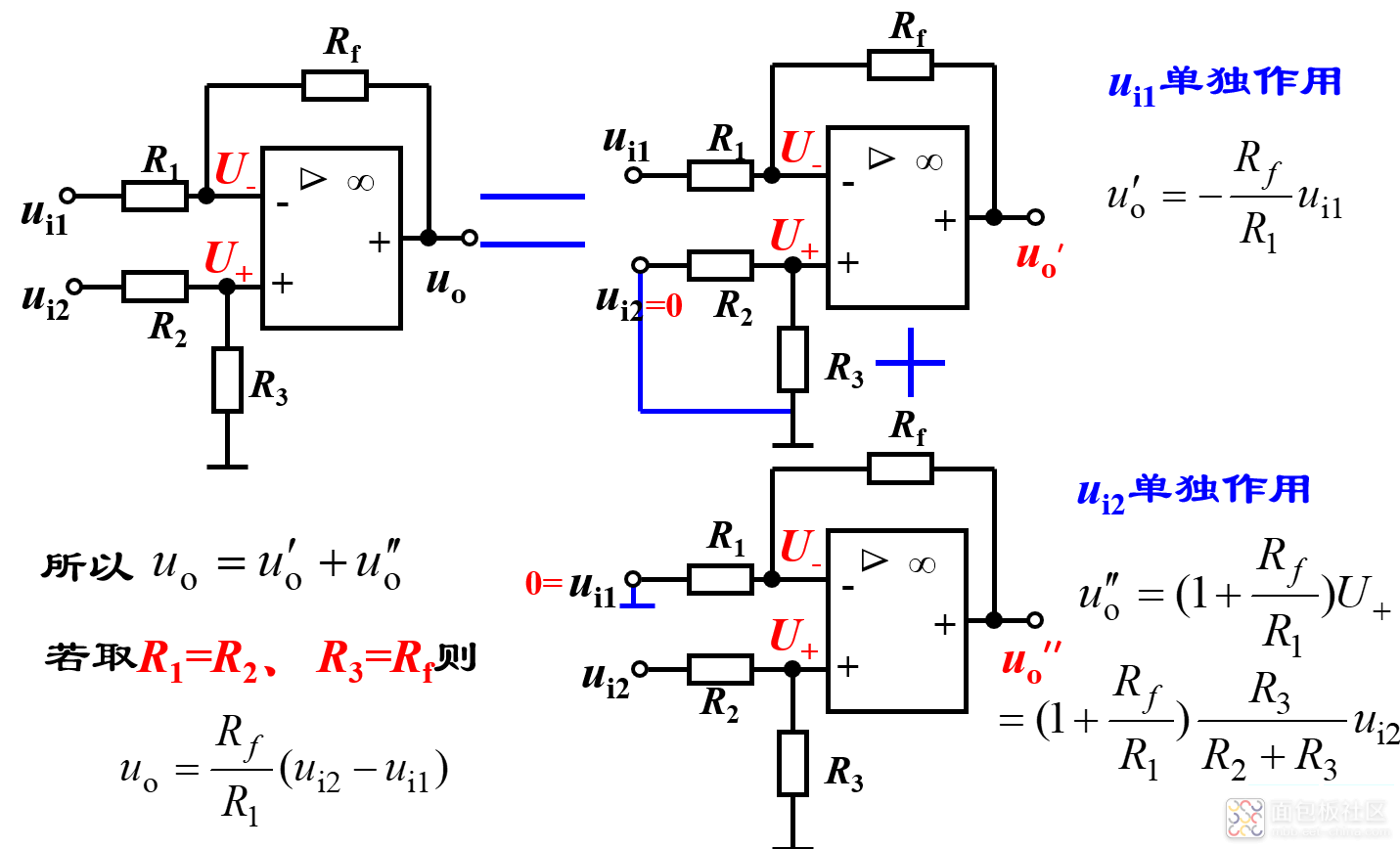
3)减法器
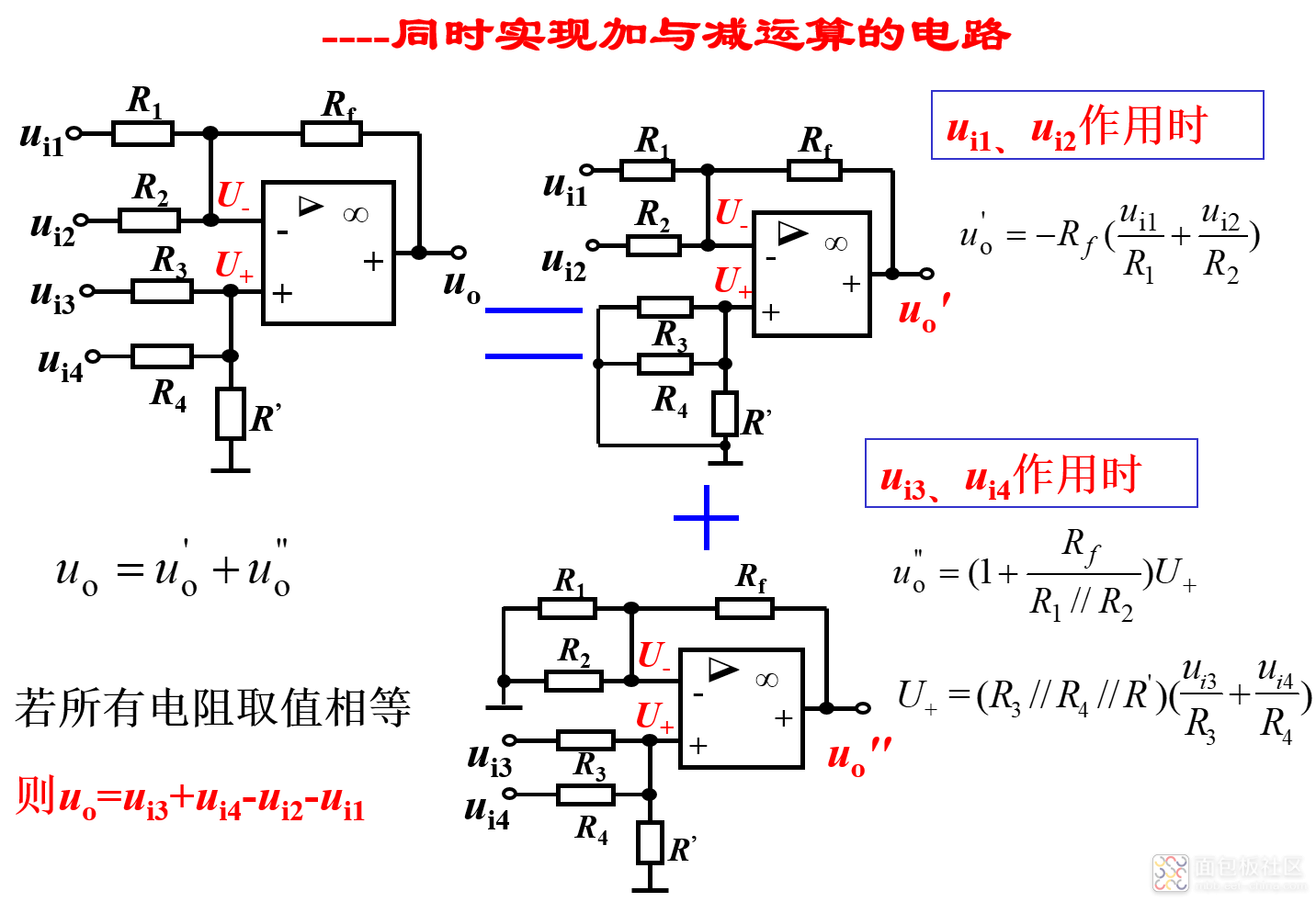
4)加减器
比例运算电路与加减运算电路小结:
1)它们都引入电压负反馈,因此输出电阻都比较小 。
2)反相输入的输入电阻小,同相输入的输入电阻高。
3)同相输入的共模电压高,反相输入的共模电压小。
4 积分运算电路与微分运算电路
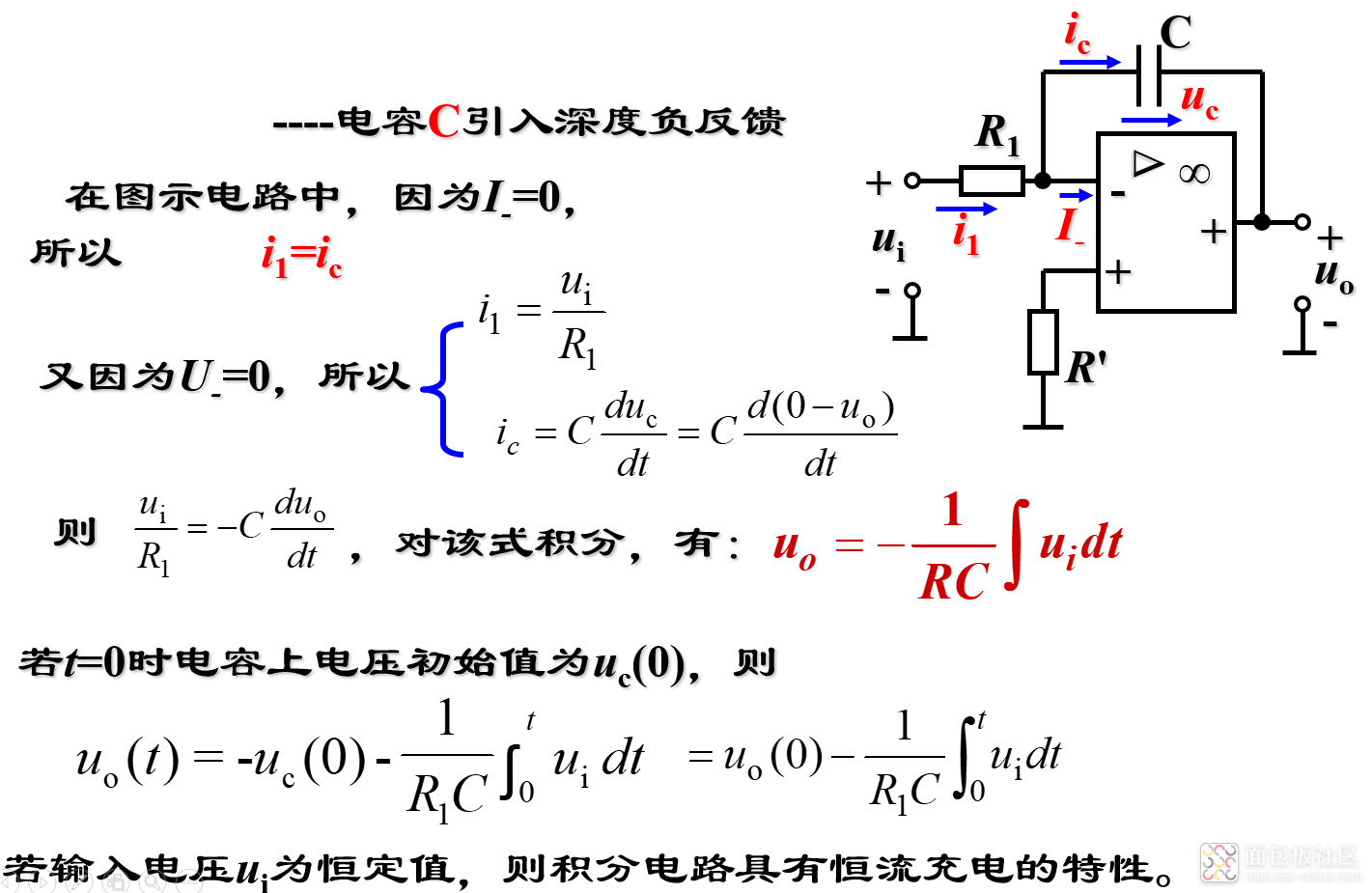
(1)积分运算电路
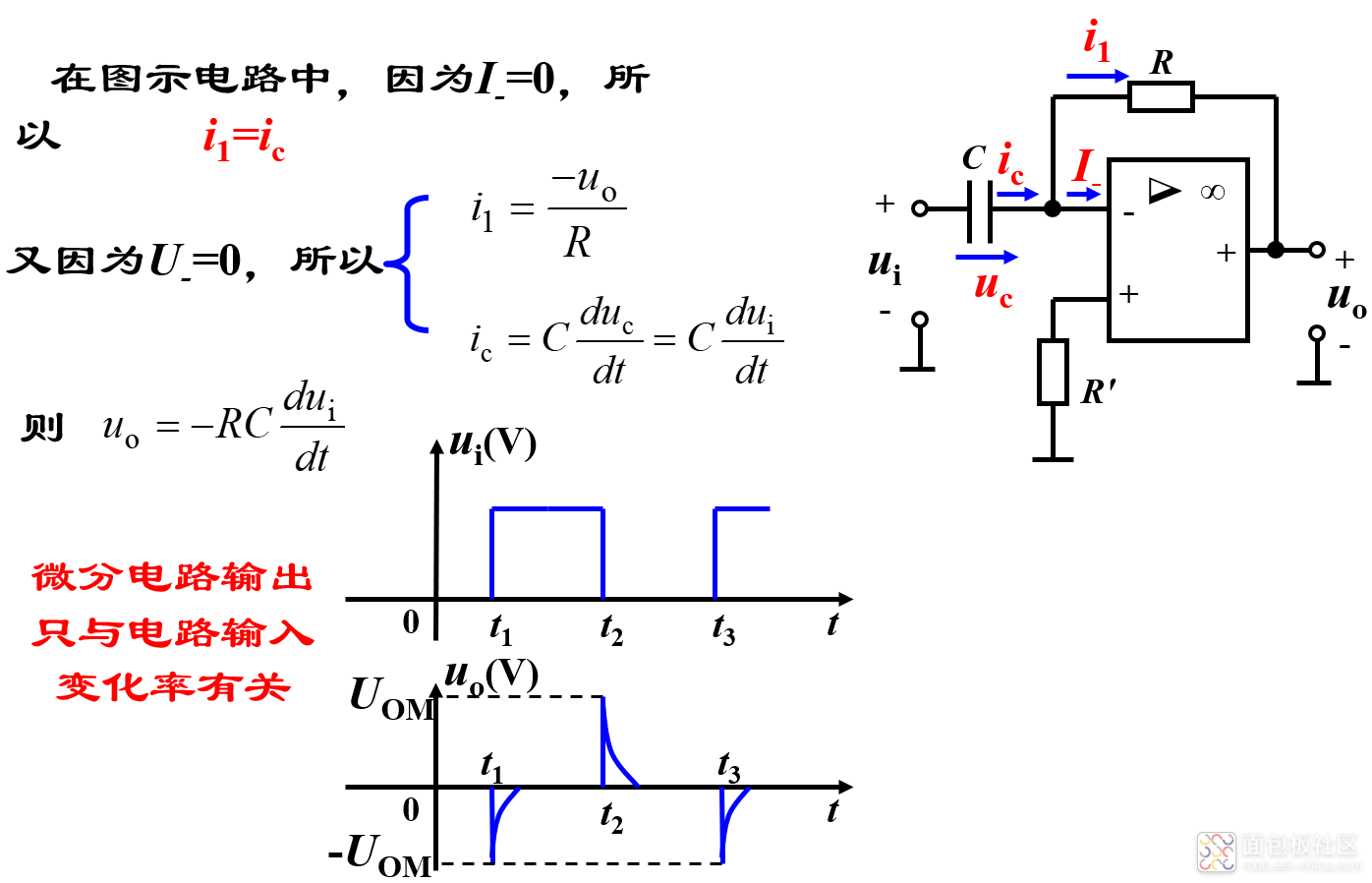
(2)微分运算电路
5 对数运算电路与指数运算电路
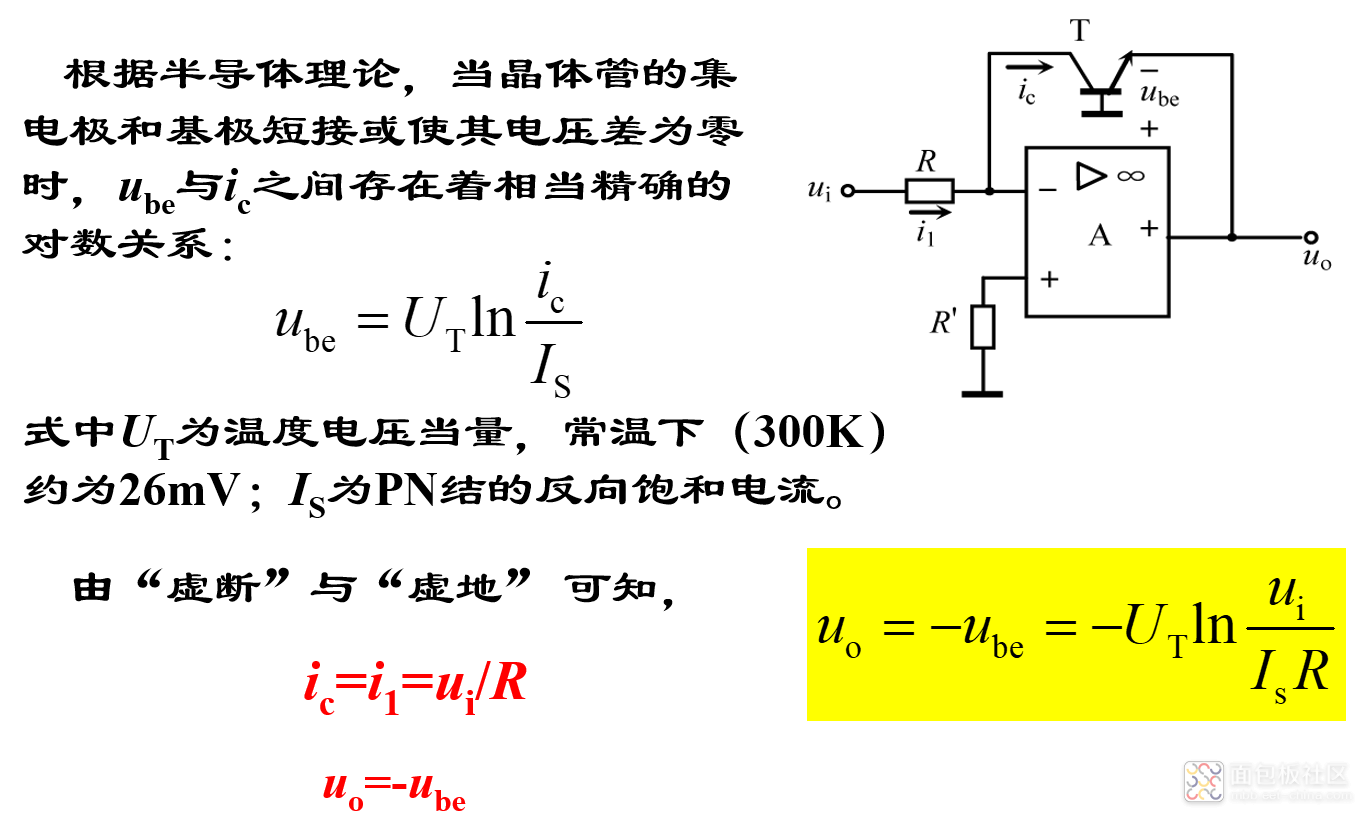
(1)对数运算电路
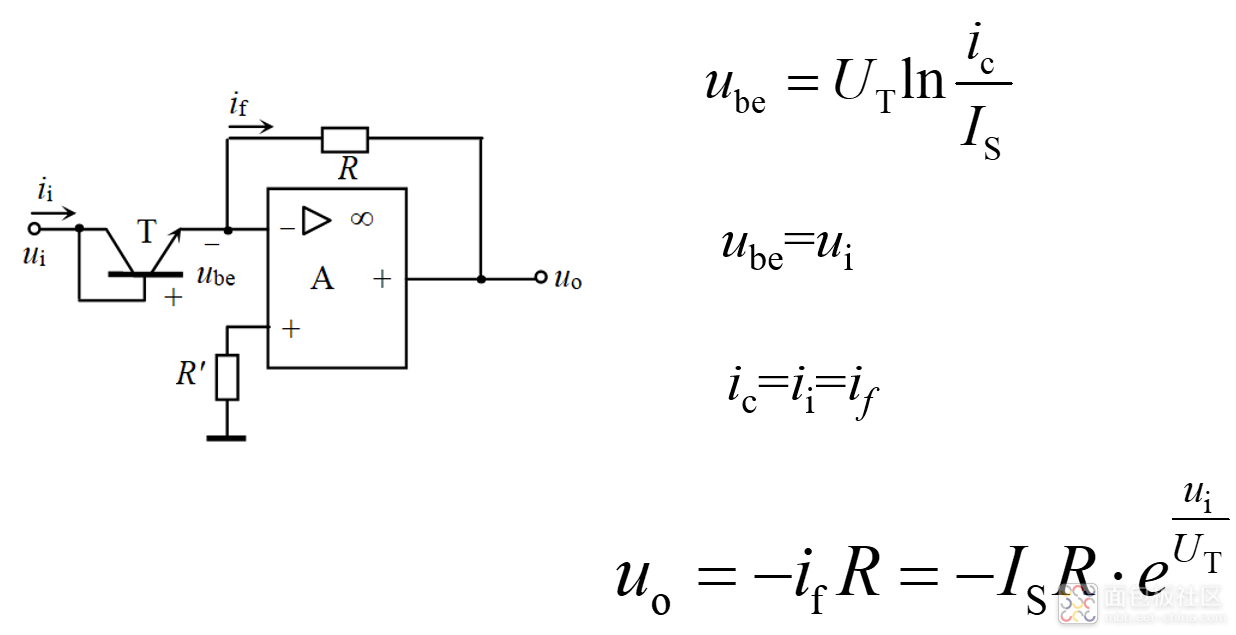
(2)指数运算电路
6 运算电路应用实例
(1)电压/电流变换
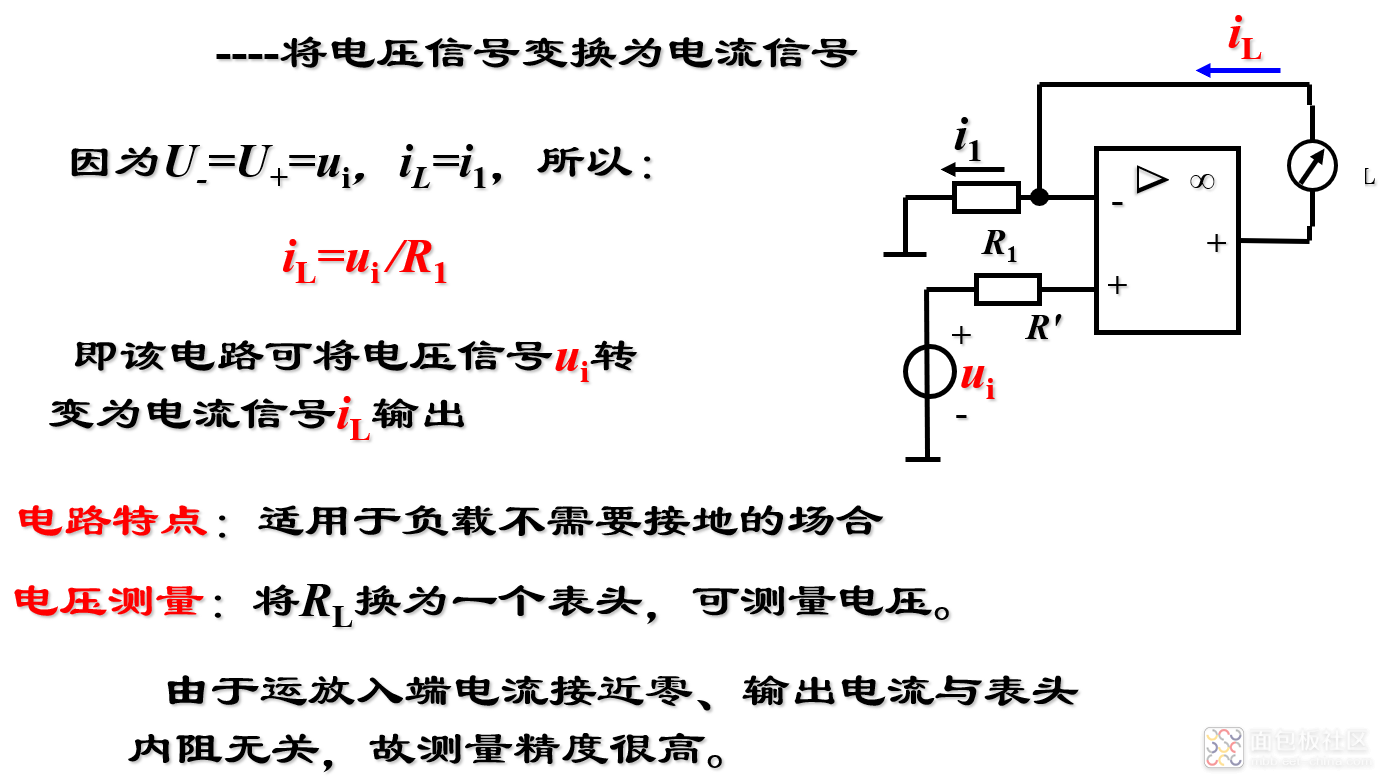
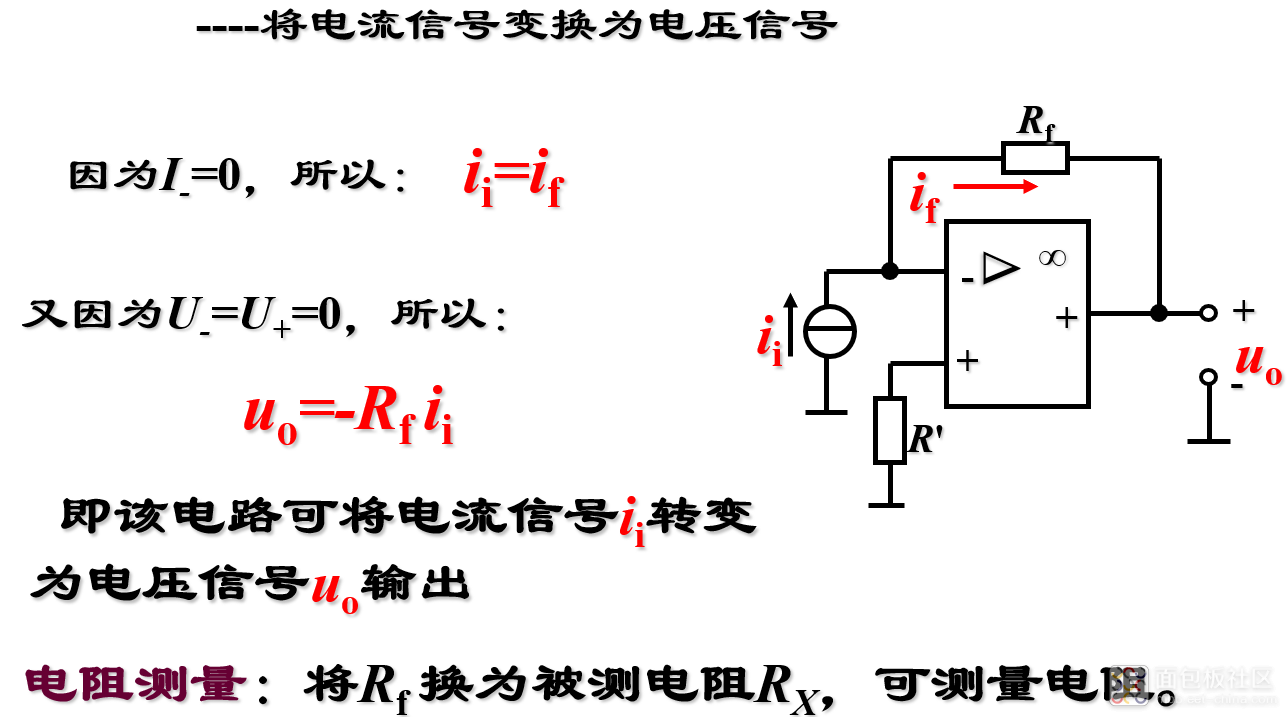
(2)电流/电压变换
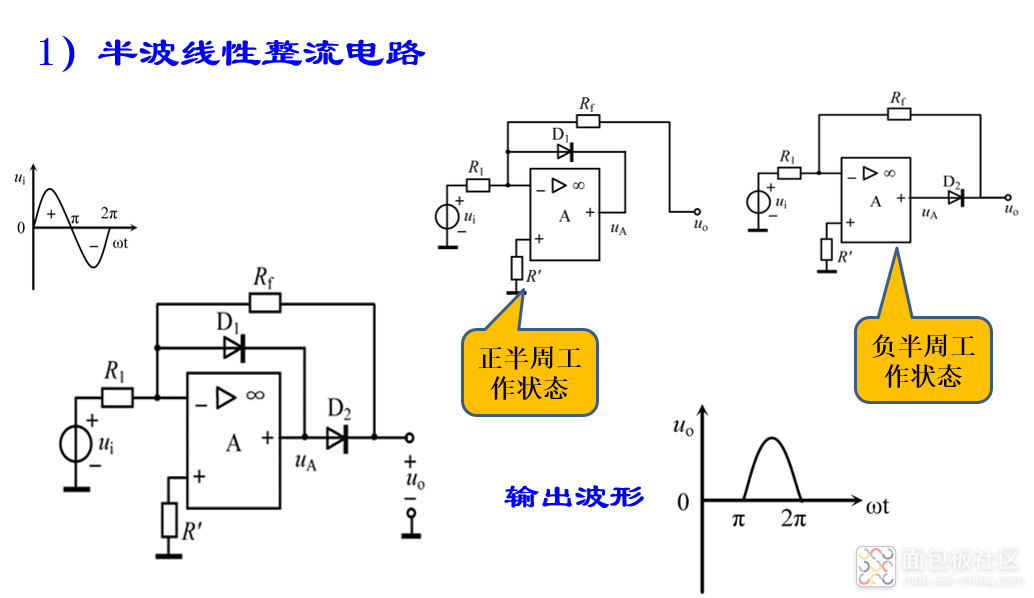
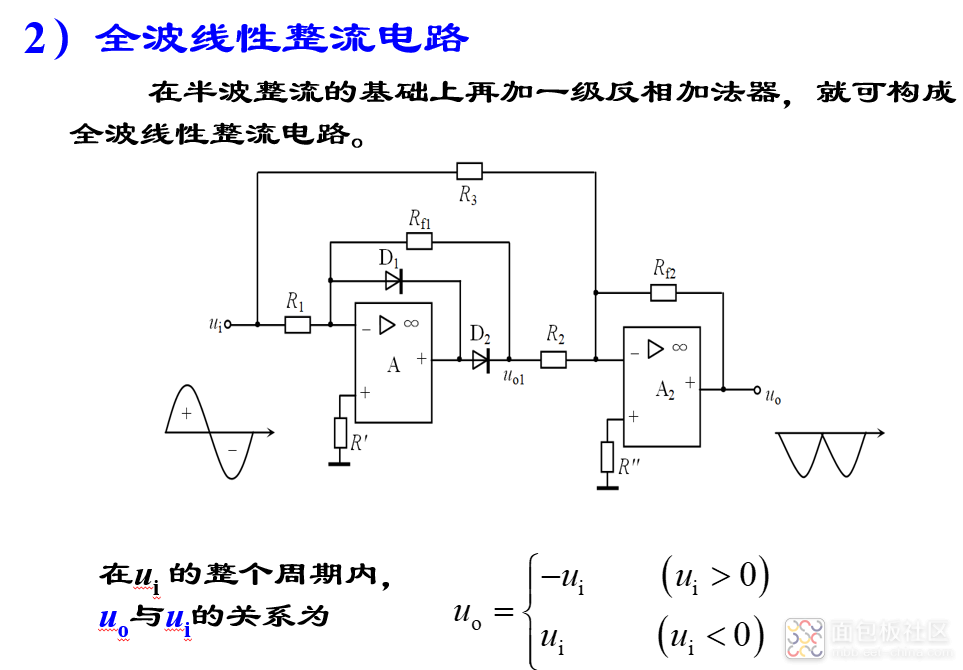
(3)线性整流电路
单纯由二极管构成的整流电路误差较大、精度较低。为克服这一缺点,可将二极管与集成运放结合起来,就能得到近乎理想的整流特性。
(4)限幅电路(又称钳位电路)
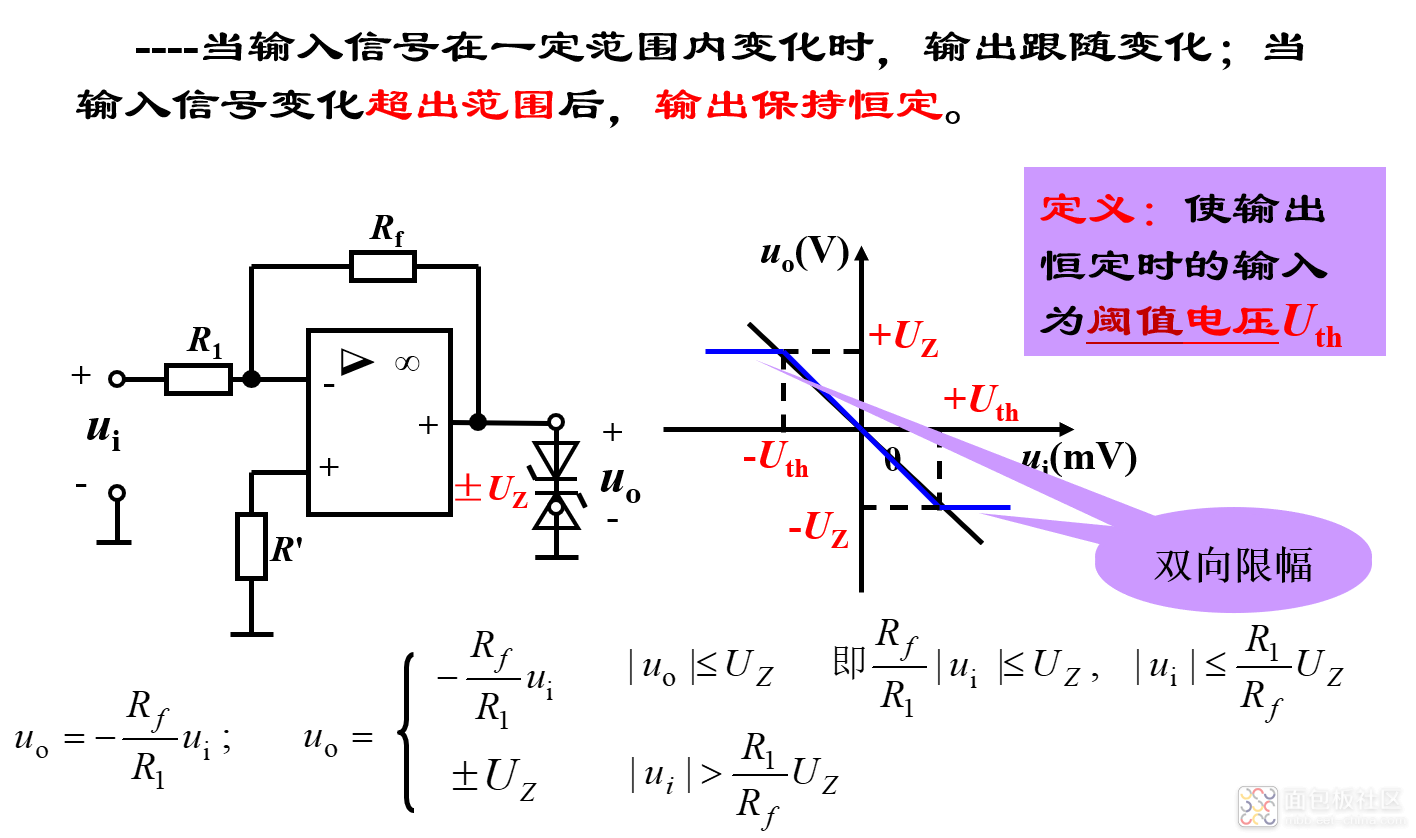






 /1
/1 

