1.概述
FatFs是一个应用在小型嵌入式系统中的通用文件系统(FAT / exFAT)模块。FatFs模块是遵循ANSI C(C89)编写的,与磁盘I/O层是完全分离的。因此,它是独立于平台的。它可以被整合到资源有限的小型微控制器中,如8051、PIC、AVR、ARM、Z80、RX等等;
本文中使用的是FatFs_R0.14版本,结合GD32 RISV-V开发平台板载的SPI FLASH来实现文件系统的功能。FatFs官网及下载地址:
http://elm-chan.org/fsw/ff/00index_e.html,当然也可以到面包板下载中心下载:https://mbb.eet-china.com/download/36035.html
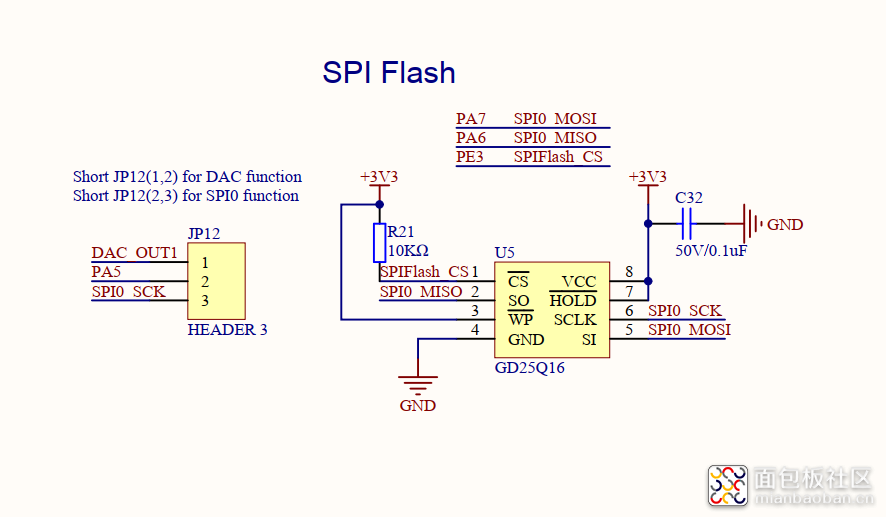
2.硬件原理图
从原理图上我们可以看到,SPI Flash使用的GD25Q16这颗芯片,其存储容量为2M字节;与MCU连接的接口使用的是硬件SPI0,另外CS操作引脚使用的是PE3。需要注意的是有一个JP12的跳线设置,需要将PA5与SPI0_SCK进行短接。
3.移植前准备
实现FatFs的移植是基于《【兆易创新RISC-V开发板评测】03.实现uGUI移植到GD32 RISC-V开发平台》的工程上实现的。通过NucleiStudio IDE打开工程,在gd32vf103_eval.c文件中对硬件SPI接口进行配置初始化:
\param[in] none
\param[out] none
\retval none
*/
void gd_eval_spi_init(void)
{
spi_parameter_struct spi_init_struct;
spi_struct_para_init(&spi_init_struct);
/* peripheral clock enable */
rcu_periph_clock_enable(RCU_GPIOA);
rcu_periph_clock_enable(RCU_GPIOE);
rcu_periph_clock_enable(RCU_AF);
rcu_periph_clock_enable(RCU_SPI0);
/* SPI0 GPIO config : SCK/PA5, MISO/PA6, MOSI/PA7 */
gpio_init(GPIOA, GPIO_MODE_AF_PP, GPIO_OSPEED_50MHZ, GPIO_PIN_5 | GPIO_PIN_7);
gpio_init(GPIOA, GPIO_MODE_IN_FLOATING, GPIO_OSPEED_50MHZ, GPIO_PIN_6);
/* SPI flash CS pin config : SPIFlashCS/PE3 */
gpio_init(GPIOE, GPIO_MODE_OUT_PP, GPIO_OSPEED_50MHZ, GPIO_PIN_3);
/* deinitilize SPI and the parameters */
spi_i2s_deinit(SPI0);
/* SPI0 parameter config */
spi_init_struct.trans_mode = SPI_TRANSMODE_FULLDUPLEX;
spi_init_struct.device_mode = SPI_MASTER;
spi_init_struct.frame_size = SPI_FRAMESIZE_8BIT;
spi_init_struct.clock_polarity_phase = SPI_CK_PL_HIGH_PH_2EDGE;
spi_init_struct.nss = SPI_NSS_SOFT;
spi_init_struct.prescale = SPI_PSC_8;
spi_init_struct.endian = SPI_ENDIAN_MSB;
spi_init(SPI0, &spi_init_struct);
/* SPI enable */
spi_enable(SPI0);
}
/*!
\brief read and write spi flash by spi0
\param[in] data : write to spi flash
\param[out] data : read from spi flash
\retval none
*/
uint16_t gd_eval_spi_rw(uint16_t data)
{
while(RESET == spi_i2s_flag_get(SPI0, SPI_FLAG_TBE));
spi_i2s_data_transmit(SPI0, data);
while(RESET == spi_i2s_flag_get(SPI0, SPI_FLAG_RBNE));
return spi_i2s_data_receive(SPI0);
}
新建gd32vf103v_spi_flash_eval.c和gd32vf103v_spi_flash_eval.h两个文件,在这个文件中实现对SPI Flash的操作函数:
#include <stdarg.h>
#include <string.h>
unsigned long xUserPow(int x, int y)
{
unsigned long sum = 1;
while(y--)
{
sum *= x;
}
return sum;
}
void xUserPutChar(const char ch)
{
usart_data_transmit(USART0, (uint8_t)ch);
while (usart_flag_get(USART0, USART_FLAG_TBE)== RESET){
}
}
void xUserPutString(const char *str)
{
while(*str)
{
xUserPutChar(*str++);
}
}
void xUserPrintNum(const int value, const int pow)
{
int temp, count = 0, data;
temp = value;
if(temp == 0)
{
xUserPutChar('0');
}
else
{
while(temp)
{
count++; temp /= pow;
}
temp = value;
while(count)
{
data = temp / xUserPow(pow, count - 1);
temp = temp % xUserPow(pow, count - 1);
if(data <= 9) xUserPutChar(data + '0');
else xUserPutChar(data + 'a' - 10);
count--;
}
}
}
void xUserPrintf(const char *str, ...)
{
va_list ap;
int val, r_val;
char count, ch;
va_start(ap, str);
while(*str)
{
switch(*str)
{
case '%':
str++;
switch(*str)
{
case 'd':
xUserPrintNum(va_arg(ap, int), 10);
break;
case 'x':
xUserPrintNum(va_arg(ap, int), 16);
break;
case 's':
xUserPutString(va_arg(ap, char *));
break;
case 'c':
xUserPutChar((char)va_arg(ap, int));
break;
default: break;
}
break;
case '\n': xUserPutChar('\n'); break;
case '\r': xUserPutChar('\r'); break;
default : xUserPutChar(*str); break;
}
str++;
}
va_end(ap);
}
void spi_flash_write_enable(void)
{
SPIFlashCS_L();
gd_eval_spi_rw(SPI_FLASH_CMD_WREN);
SPIFlashCS_H();
}
void spi_flash_write_disable(void)
{
SPIFlashCS_L();
gd_eval_spi_rw(SPI_FLASH_CMD_WRDI);
SPIFlashCS_H();
}
void spi_flash_wait_for_write_end(void)
{
uint8_t flag = 0;
SPIFlashCS_L();
gd_eval_spi_rw(SPI_FLASH_CMD_RDSR);
do
{
flag = gd_eval_spi_rw(SPI_FLASH_DUMMY);
} while(flag & 0x01);
SPIFlashCS_H();
}
void spi_flash_erase_sector(uint32_t address)
{
spi_flash_write_enable();
spi_flash_wait_for_write_end();
SPIFlashCS_L();
gd_eval_spi_rw(SPI_FLASH_CMD_SE);
gd_eval_spi_rw((address & 0x00FF0000) >> 0x10);
gd_eval_spi_rw((address & 0x0000FF00) >> 0x08);
gd_eval_spi_rw((address & 0x000000FF) >> 0x00);
SPIFlashCS_H();
spi_flash_wait_for_write_end();
}
void spi_flash_erase_block32(uint32_t address)
{
spi_flash_write_enable();
spi_flash_wait_for_write_end();
SPIFlashCS_L();
gd_eval_spi_rw(SPI_FLASH_CMD_BE32);
gd_eval_spi_rw((address & 0x00FF0000) >> 0x10);
gd_eval_spi_rw((address & 0x0000FF00) >> 0x08);
gd_eval_spi_rw((address & 0x000000FF) >> 0x00);
SPIFlashCS_H();
spi_flash_wait_for_write_end();
}
void spi_flash_fast_read(uint32_t address, uint8_t *buffer, uint16_t length)
{
SPIFlashCS_L();
gd_eval_spi_rw(SPI_FLASH_CMD_FastRead);
gd_eval_spi_rw((address & 0x00FF0000) >> 0x10);
gd_eval_spi_rw((address & 0x0000FF00) >> 0x08);
gd_eval_spi_rw((address & 0x000000FF) >> 0x00);
gd_eval_spi_rw(SPI_FLASH_DUMMY);
for(uint16_t i = 0; i < length; i++)
{
buffer
= gd_eval_spi_rw(SPI_FLASH_DUMMY);
}
SPIFlashCS_H();
}
void spi_flash_page_program(uint32_t address, uint8_t *buffer, uint16_t length)
{
spi_flash_write_enable();
SPIFlashCS_L();
gd_eval_spi_rw(SPI_FLASH_CMD_PP);
gd_eval_spi_rw((address & 0x00FF0000) >> 0x10);
gd_eval_spi_rw((address & 0x0000FF00) >> 0x08);
gd_eval_spi_rw((address & 0x000000FF) >> 0x00);
for(uint16_t i = 0; i < length; i++)
{
gd_eval_spi_rw(buffer
);
}
SPIFlashCS_H();
spi_flash_wait_for_write_end();
}
void spi_flash_init(void)
{
gd_eval_spi_init();
SPIFlashCS_H();
xUserPrintf("\r\nSPI Flash Init OK!\r\n");
}
void spi_flash_read(uint32_t address, uint8_t *buffer, uint16_t length)
{
spi_flash_fast_read(address, buffer, length);
}
void spi_flash_write(uint32_t address, uint8_t *buffer, uint16_t length)
{
uint16_t offset = 0;
uint16_t num_head = 0, num_tail = 0, num_page = 0;
num_head = PAGE_SIZE - (address % PAGE_SIZE);
// xUserPrintf("\r\nnum_head = %d, length = %d\r\n", num_head, length);
if(num_head >= length)
{
// xUserPrintf("\r\nLength PP\r\n");
spi_flash_page_program(address, &buffer[offset], length);
}
else
{
// xUserPrintf("\r\nHead PP\r\n");
spi_flash_page_program(address, &buffer[offset], num_head);
offset += num_head;
length -= num_head;
address += num_head;
num_page = length / PAGE_SIZE;
num_tail = length % PAGE_SIZE;
// xUserPrintf("\r\nnum_page = %d\r\n", num_page);
// xUserPrintf("\r\nnum_tail = %d\r\n", num_tail);
for(uint16_t i = 0; i < num_page; i++)
{
// xUserPrintf("\r\nPage PP\r\n");
spi_flash_page_program(address, &buffer[offset], PAGE_SIZE);
offset += PAGE_SIZE;
address += PAGE_SIZE;
}
if(num_tail)
{
// xUserPrintf("\r\nTail PP\r\n");
spi_flash_page_program(address, &buffer[offset], num_tail);
}
}
}
void spi_flash_shell_rdid(void)
{
uint32_t id = 0;
SPIFlashCS_L();
gd_eval_spi_rw(SPI_FLASH_CMD_RDID);
id = gd_eval_spi_rw(SPI_FLASH_DUMMY);
id <<= 8;
id |= gd_eval_spi_rw(SPI_FLASH_DUMMY);
id <<= 8;
id |= gd_eval_spi_rw(SPI_FLASH_DUMMY);
xUserPrintf("\r\nSPI Flash RDID : 0x%x\r\n", id);
SPIFlashCS_H();
}
void spi_flash_shell_erase(uint32_t address)
{
spi_flash_erase_sector(address);
xUserPrintf("\r\nSPI Flash Sector Erase : 0x%x\r\n", address);
}
void spi_flash_shell_erase_all(void)
{
for(uint16_t i = 0; i < SECTOR_COUNT; i++)
{
spi_flash_shell_erase(i * SECTOR_SIZE);
}
}
void spi_flash_shell_read(uint32_t address, uint16_t length)
{
uint8_t buffer[500];
memset(buffer, 0, sizeof(buffer));
spi_flash_read(address, buffer, length);
xUserPrintf("\r\nSPI Flash Read : \r\n");
for(uint16_t i = 0; i < length; i++)
{
xUserPrintf("0x%x ", buffer
);
}
xUserPrintf("\r\n");
}
void spi_flash_shell_write(uint32_t address, uint16_t length)
{
uint8_t buffer[500];
for(uint16_t i = 0; i < sizeof(buffer); i++)
{
buffer
= i % 256;
}
spi_flash_write(address, buffer, length);
}
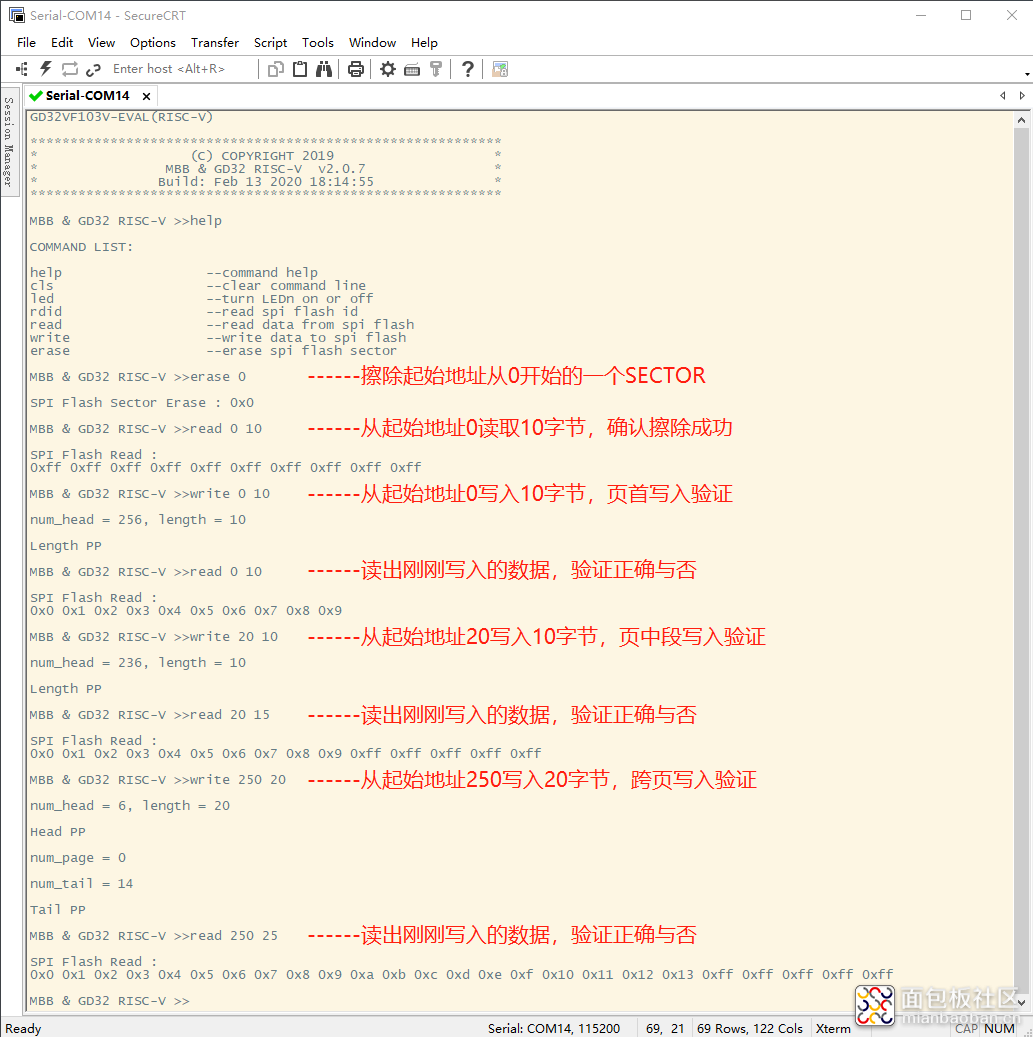
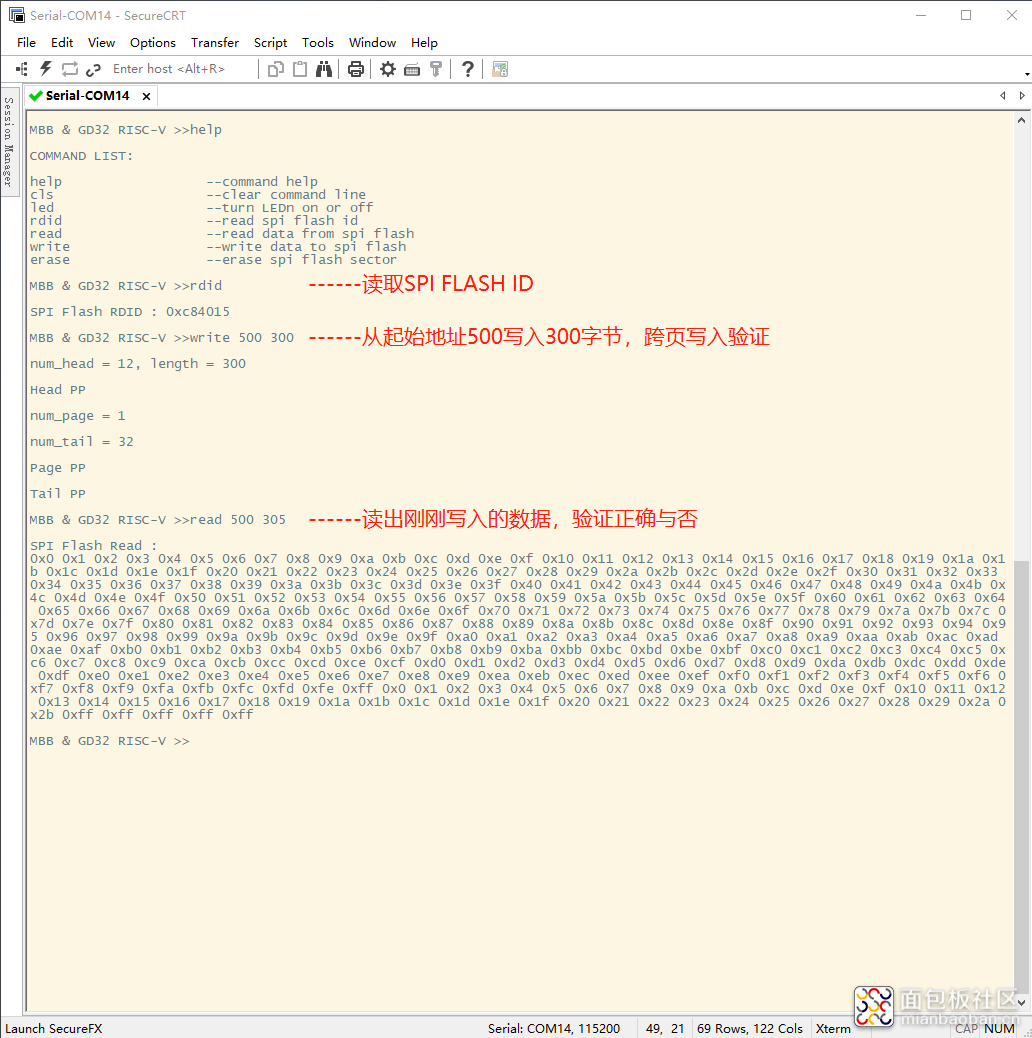
为了调试测试方便,将对SPI Flash的read、write、erase等操作添加到shell命令当中了,在完成了SPI Flash底层驱动后,做了如下的测试:
4.移植FatFs
将FatFs源文件ff14文件夹复制到工程的Utilities文件夹下,并刷新工程,即可显示出目录结构及对应的源文件了。在SPI Flash上实现FatFs文件系统主要是对 diskio.c接口文件和ffconf.h配置文件的修改。
diskio.c接口文件源码如下所示:
/*-----------------------------------------------------------------------*/
/* If a working storage control module is available, it should be */
/* attached to the FatFs via a glue function rather than modifying it. */
/* This is an example of glue functions to attach various exsisting */
/* storage control modules to the FatFs module with a defined API. */
/*-----------------------------------------------------------------------*/
#include "ff.h" /* Obtains integer types */
#include "diskio.h" /* Declarations of disk functions */
#include "gd32vf103v_spi_flash_eval.h"
/* Definitions of physical drive number for each drive */
#define DEV_SPI_FLASH 0
/*-----------------------------------------------------------------------*/
/* Get Drive Status */
/*-----------------------------------------------------------------------*/
DSTATUS disk_status (
BYTE pdrv /* Physical drive nmuber to identify the drive */
)
{
DSTATUS stat;
int result;
switch (pdrv)
{
case DEV_SPI_FLASH : return RES_OK;
}
return STA_NOINIT;
}
/*-----------------------------------------------------------------------*/
/* Inidialize a Drive */
/*-----------------------------------------------------------------------*/
DSTATUS disk_initialize (
BYTE pdrv /* Physical drive nmuber to identify the drive */
)
{
DSTATUS stat;
int result;
switch (pdrv)
{
case DEV_SPI_FLASH : return RES_OK;
}
return STA_NOINIT;
}
/*-----------------------------------------------------------------------*/
/* Read Sector(s) */
/*-----------------------------------------------------------------------*/
DRESULT disk_read (
BYTE pdrv, /* Physical drive nmuber to identify the drive */
BYTE *buff, /* Data buffer to store read data */
LBA_t sector, /* Start sector in LBA */
UINT count /* Number of sectors to read */
)
{
DRESULT res;
int result;
// xUserPrintf("\r\ndr pdrv = %d, sector = %d, count = %d\r\n", pdrv, sector, count);
switch (pdrv)
{
case DEV_SPI_FLASH :
for(; count > 0; count--)
{
spi_flash_read(sector * SECTOR_SIZE, buff, SECTOR_SIZE);
sector += 1;
buff += SECTOR_SIZE;
}
return RES_OK;
}
return RES_PARERR;
}
/*-----------------------------------------------------------------------*/
/* Write Sector(s) */
/*-----------------------------------------------------------------------*/
#if FF_FS_READONLY == 0
DRESULT disk_write (
BYTE pdrv, /* Physical drive nmuber to identify the drive */
const BYTE *buff, /* Data to be written */
LBA_t sector, /* Start sector in LBA */
UINT count /* Number of sectors to write */
)
{
DRESULT res;
int result;
// xUserPrintf("\r\ndw pdrv = %d, sector = %d, count = %d\r\n", pdrv, sector, count);
switch (pdrv)
{
case DEV_SPI_FLASH :
for(; count > 0; count--)
{
spi_flash_erase_sector(sector * SECTOR_SIZE);
spi_flash_write(sector * SECTOR_SIZE, (uint8_t *)buff, SECTOR_SIZE);
sector += 1;
buff += SECTOR_SIZE;
}
return RES_OK;
}
return RES_PARERR;
}
#endif
/*-----------------------------------------------------------------------*/
/* Miscellaneous Functions */
/*-----------------------------------------------------------------------*/
DRESULT disk_ioctl (
BYTE pdrv, /* Physical drive nmuber (0..) */
BYTE cmd, /* Control code */
void *buff /* Buffer to send/receive control data */
)
{
DRESULT res;
int result;
switch (pdrv)
{
case DEV_SPI_FLASH :
switch(cmd)
{
case CTRL_SYNC :
res = RES_OK;
break;
case GET_SECTOR_SIZE :
*(WORD *)buff = SECTOR_SIZE;
res = RES_OK;
break;
case GET_BLOCK_SIZE :
*(DWORD *)buff = 1;
res = RES_OK;
break;
case GET_SECTOR_COUNT :
*(DWORD *)buff = SECTOR_COUNT;
res = RES_OK;
break;
default :
res = RES_PARERR;
break;
}
break;
default : res = RES_PARERR; break;
}
return res;
}
DWORD get_fattime (void)
{
return 0;
}
ffconf.h配置文件源码如下所示:
/---------------------------------------------------------------------------*/
#define FFCONF_DEF 86606 /* Revision ID */
/*---------------------------------------------------------------------------/
/ Function Configurations
/---------------------------------------------------------------------------*/
#define FF_FS_READONLY 0
/* This option switches read-only configuration. (0:Read/Write or 1:Read-only)
/ Read-only configuration removes writing API functions, f_write(), f_sync(),
/ f_unlink(), f_mkdir(), f_chmod(), f_rename(), f_truncate(), f_getfree()
/ and optional writing functions as well. */
#define FF_FS_MINIMIZE 0
/* This option defines minimization level to remove some basic API functions.
/
/ 0: Basic functions are fully enabled.
/ 1: f_stat(), f_getfree(), f_unlink(), f_mkdir(), f_truncate() and f_rename()
/ are removed.
/ 2: f_opendir(), f_readdir() and f_closedir() are removed in addition to 1.
/ 3: f_lseek() function is removed in addition to 2. */
#define FF_USE_STRFUNC 0
/* This option switches string functions, f_gets(), f_putc(), f_puts() and f_printf().
/
/ 0: Disable string functions.
/ 1: Enable without LF-CRLF conversion.
/ 2: Enable with LF-CRLF conversion. */
#define FF_USE_FIND 0
/* This option switches filtered directory read functions, f_findfirst() and
/ f_findnext(). (0:Disable, 1:Enable 2:Enable with matching altname[] too) */
#define FF_USE_MKFS 1
/* This option switches f_mkfs() function. (0:Disable or 1:Enable) */
#define FF_USE_FASTSEEK 0
/* This option switches fast seek function. (0:Disable or 1:Enable) */
#define FF_USE_EXPAND 0
/* This option switches f_expand function. (0:Disable or 1:Enable) */
#define FF_USE_CHMOD 0
/* This option switches attribute manipulation functions, f_chmod() and f_utime().
/ (0:Disable or 1:Enable) Also FF_FS_READONLY needs to be 0 to enable this option. */
#define FF_USE_LABEL 0
/* This option switches volume label functions, f_getlabel() and f_setlabel().
/ (0:Disable or 1:Enable) */
#define FF_USE_FORWARD 0
/* This option switches f_forward() function. (0:Disable or 1:Enable) */
/*---------------------------------------------------------------------------/
/ Locale and Namespace Configurations
/---------------------------------------------------------------------------*/
#define FF_CODE_PAGE 936
/* This option specifies the OEM code page to be used on the target system.
/ Incorrect code page setting can cause a file open failure.
/
/ 437 - U.S.
/ 720 - Arabic
/ 737 - Greek
/ 771 - KBL
/ 775 - Baltic
/ 850 - Latin 1
/ 852 - Latin 2
/ 855 - Cyrillic
/ 857 - Turkish
/ 860 - Portuguese
/ 861 - Icelandic
/ 862 - Hebrew
/ 863 - Canadian French
/ 864 - Arabic
/ 865 - Nordic
/ 866 - Russian
/ 869 - Greek 2
/ 932 - Japanese (DBCS)
/ 936 - Simplified Chinese (DBCS)
/ 949 - Korean (DBCS)
/ 950 - Traditional Chinese (DBCS)
/ 0 - Include all code pages above and configured by f_setcp()
*/
#define FF_USE_LFN 0
#define FF_MAX_LFN 255
/* The FF_USE_LFN switches the support for LFN (long file name).
/
/ 0: Disable LFN. FF_MAX_LFN has no effect.
/ 1: Enable LFN with static working buffer on the BSS. Always NOT thread-safe.
/ 2: Enable LFN with dynamic working buffer on the STACK.
/ 3: Enable LFN with dynamic working buffer on the HEAP.
/
/ To enable the LFN, ffunicode.c needs to be added to the project. The LFN function
/ requiers certain internal working buffer occupies (FF_MAX_LFN + 1) * 2 bytes and
/ additional (FF_MAX_LFN + 44) / 15 * 32 bytes when exFAT is enabled.
/ The FF_MAX_LFN defines size of the working buffer in UTF-16 code unit and it can
/ be in range of 12 to 255. It is recommended to be set it 255 to fully support LFN
/ specification.
/ When use stack for the working buffer, take care on stack overflow. When use heap
/ memory for the working buffer, memory management functions, ff_memalloc() and
/ ff_memfree() exemplified in ffsystem.c, need to be added to the project. */
#define FF_LFN_UNICODE 0
/* This option switches the character encoding on the API when LFN is enabled.
/
/ 0: ANSI/OEM in current CP (TCHAR = char)
/ 1: Unicode in UTF-16 (TCHAR = WCHAR)
/ 2: Unicode in UTF-8 (TCHAR = char)
/ 3: Unicode in UTF-32 (TCHAR = DWORD)
/
/ Also behavior of string I/O functions will be affected by this option.
/ When LFN is not enabled, this option has no effect. */
#define FF_LFN_BUF 255
#define FF_SFN_BUF 12
/* This set of options defines size of file name members in the FILINFO structure
/ which is used to read out directory items. These values should be suffcient for
/ the file names to read. The maximum possible length of the read file name depends
/ on character encoding. When LFN is not enabled, these options have no effect. */
#define FF_STRF_ENCODE 3
/* When FF_LFN_UNICODE >= 1 with LFN enabled, string I/O functions, f_gets(),
/ f_putc(), f_puts and f_printf() convert the character encoding in it.
/ This option selects assumption of character encoding ON THE FILE to be
/ read/written via those functions.
/
/ 0: ANSI/OEM in current CP
/ 1: Unicode in UTF-16LE
/ 2: Unicode in UTF-16BE
/ 3: Unicode in UTF-8
*/
#define FF_FS_RPATH 0
/* This option configures support for relative path.
/
/ 0: Disable relative path and remove related functions.
/ 1: Enable relative path. f_chdir() and f_chdrive() are available.
/ 2: f_getcwd() function is available in addition to 1.
*/
/*---------------------------------------------------------------------------/
/ Drive/Volume Configurations
/---------------------------------------------------------------------------*/
#define FF_VOLUMES 1
/* Number of volumes (logical drives) to be used. (1-10) */
#define FF_STR_VOLUME_ID 0
#define FF_VOLUME_STRS "RAM","NAND","CF","SD","SD2","USB","USB2","USB3"
/* FF_STR_VOLUME_ID switches support for volume ID in arbitrary strings.
/ When FF_STR_VOLUME_ID is set to 1 or 2, arbitrary strings can be used as drive
/ number in the path name. FF_VOLUME_STRS defines the volume ID strings for each
/ logical drives. Number of items must not be less than FF_VOLUMES. Valid
/ characters for the volume ID strings are A-Z, a-z and 0-9, however, they are
/ compared in case-insensitive. If FF_STR_VOLUME_ID >= 1 and FF_VOLUME_STRS is
/ not defined, a user defined volume string table needs to be defined as:
/
/ const char* VolumeStr[FF_VOLUMES] = {"ram","flash","sd","usb",...
*/
#define FF_MULTI_PARTITION 0
/* This option switches support for multiple volumes on the physical drive.
/ By default (0), each logical drive number is bound to the same physical drive
/ number and only an FAT volume found on the physical drive will be mounted.
/ When this function is enabled (1), each logical drive number can be bound to
/ arbitrary physical drive and partition listed in the VolToPart[]. Also f_fdisk()
/ funciton will be available. */
#define FF_MIN_SS 512
#define FF_MAX_SS 4096
/* This set of options configures the range of sector size to be supported. (512,
/ 1024, 2048 or 4096) Always set both 512 for most systems, generic memory card and
/ harddisk. But a larger value may be required for on-board flash memory and some
/ type of optical media. When FF_MAX_SS is larger than FF_MIN_SS, FatFs is configured
/ for variable sector size mode and disk_ioctl() function needs to implement
/ GET_SECTOR_SIZE command. */
#define FF_LBA64 0
/* This option switches support for 64-bit LBA. (0:Disable or 1:Enable)
/ To enable the 64-bit LBA, also exFAT needs to be enabled. (FF_FS_EXFAT == 1) */
#define FF_MIN_GPT 0x100000000
/* Minimum number of sectors to switch GPT format to create partition in f_mkfs and
/ f_fdisk function. 0x100000000 max. This option has no effect when FF_LBA64 == 0. */
#define FF_USE_TRIM 0
/* This option switches support for ATA-TRIM. (0:Disable or 1:Enable)
/ To enable Trim function, also CTRL_TRIM command should be implemented to the
/ disk_ioctl() function. */
/*---------------------------------------------------------------------------/
/ System Configurations
/---------------------------------------------------------------------------*/
#define FF_FS_TINY 0
/* This option switches tiny buffer configuration. (0:Normal or 1:Tiny)
/ At the tiny configuration, size of file object (FIL) is shrinked FF_MAX_SS bytes.
/ Instead of private sector buffer eliminated from the file object, common sector
/ buffer in the filesystem object (FATFS) is used for the file data transfer. */
#define FF_FS_EXFAT 0
/* This option switches support for exFAT filesystem. (0:Disable or 1:Enable)
/ To enable exFAT, also LFN needs to be enabled. (FF_USE_LFN >= 1)
/ Note that enabling exFAT discards ANSI C (C89) compatibility. */
#define FF_FS_NORTC 0
#define FF_NORTC_MON 1
#define FF_NORTC_MDAY 1
#define FF_NORTC_YEAR 2019
/* The option FF_FS_NORTC switches timestamp functiton. If the system does not have
/ any RTC function or valid timestamp is not needed, set FF_FS_NORTC = 1 to disable
/ the timestamp function. Every object modified by FatFs will have a fixed timestamp
/ defined by FF_NORTC_MON, FF_NORTC_MDAY and FF_NORTC_YEAR in local time.
/ To enable timestamp function (FF_FS_NORTC = 0), get_fattime() function need to be
/ added to the project to read current time form real-time clock. FF_NORTC_MON,
/ FF_NORTC_MDAY and FF_NORTC_YEAR have no effect.
/ These options have no effect in read-only configuration (FF_FS_READONLY = 1). */
#define FF_FS_NOFSINFO 0
/* If you need to know correct free space on the FAT32 volume, set bit 0 of this
/ option, and f_getfree() function at first time after volume mount will force
/ a full FAT scan. Bit 1 controls the use of last allocated cluster number.
/
/ bit0=0: Use free cluster count in the FSINFO if available.
/ bit0=1: Do not trust free cluster count in the FSINFO.
/ bit1=0: Use last allocated cluster number in the FSINFO if available.
/ bit1=1: Do not trust last allocated cluster number in the FSINFO.
*/
#define FF_FS_LOCK 0
/* The option FF_FS_LOCK switches file lock function to control duplicated file open
/ and illegal operation to open objects. This option must be 0 when FF_FS_READONLY
/ is 1.
/
/ 0: Disable file lock function. To avoid volume corruption, application program
/ should avoid illegal open, remove and rename to the open objects.
/ >0: Enable file lock function. The value defines how many files/sub-directories
/ can be opened simultaneously under file lock control. Note that the file
/ lock control is independent of re-entrancy. */
/* #include <somertos.h> // O/S definitions */
#define FF_FS_REENTRANT 0
#define FF_FS_TIMEOUT 1000
#define FF_SYNC_t HANDLE
/* The option FF_FS_REENTRANT switches the re-entrancy (thread safe) of the FatFs
/ module itself. Note that regardless of this option, file access to different
/ volume is always re-entrant and volume control functions, f_mount(), f_mkfs()
/ and f_fdisk() function, are always not re-entrant. Only file/directory access
/ to the same volume is under control of this function.
/
/ 0: Disable re-entrancy. FF_FS_TIMEOUT and FF_SYNC_t have no effect.
/ 1: Enable re-entrancy. Also user provided synchronization handlers,
/ ff_req_grant(), ff_rel_grant(), ff_del_syncobj() and ff_cre_syncobj()
/ function, must be added to the project. Samples are available in
/ option/syscall.c.
/
/ The FF_FS_TIMEOUT defines timeout period in unit of time tick.
/ The FF_SYNC_t defines O/S dependent sync object type. e.g. HANDLE, ID, OS_EVENT*,
/ SemaphoreHandle_t and etc. A header file for O/S definitions needs to be
/ included somewhere in the scope of ff.h. */
/*--- End of configuration options ---*/
5.FatFs演示示例
在FatFs接口文件和配置文件移植完成后,我们在main.c中对文件系统进行初始化,主要是对磁盘的初始化和挂载操作,便于后面的文件操作:
uint8_t fsFlag = 0;
uint8_t fsTest = 0;
void xInitFileSystem(void)
{
FRESULT res;
res = f_mount(&fs, "0:", 1);
if(res == FR_NO_FILESYSTEM)
{
res = f_mkfs("0:", 0, work, sizeof(work));
if(res == FR_OK)
{
xUserPrintf("\r\nCreate an FAT/exFAT volume on the logical drive\r\n");
res = f_mount(&fs, "0:", 1);
if(res == FR_OK) fsFlag = 1;
}
}
else
{
fsFlag = 1;
}
if(fsFlag)
{
xUserPrintf("\r\nRegister the work area of the volume success\r\n");
}
}
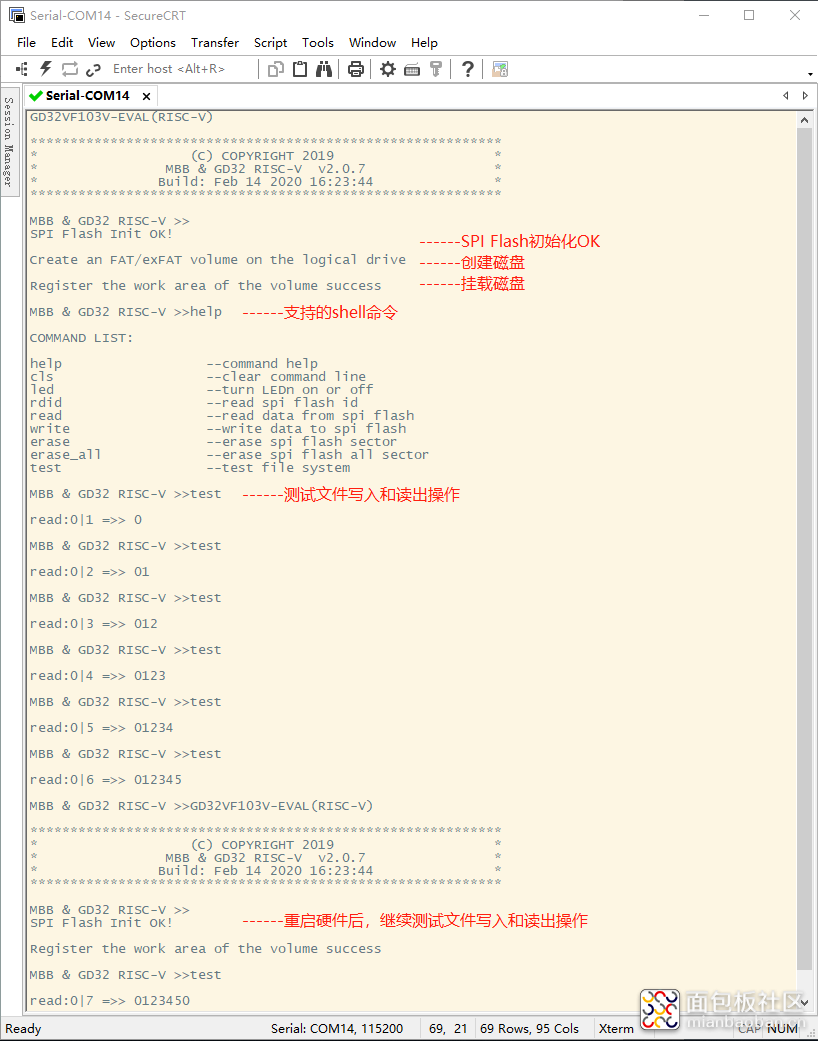
然后我们添加一个简单的测试DEMO程序,主要功能是在hello.txt文件的尾部不断的插入新数据,然后再把hello.txt的内容读取出来并打印出来;为了方便测试,将这个函数添加到shell命令中了:
FIL fil;
UINT bw;
FRESULT res;
if(fsFlag)
{
char buffer[200];
res = f_open(&fil, "0:hello.txt", FA_OPEN_APPEND | FA_WRITE);
if(res == FR_OK)
{
memset(buffer, 0, sizeof(buffer));
sprintf(buffer, "%d", fsTest++%100);
res = f_write(&fil, buffer, 1, &bw);
f_close(&fil);
}
res = f_open(&fil, "0:hello.txt", FA_OPEN_EXISTING | FA_READ);
if(res == FR_OK)
{
memset(buffer, 0, sizeof(buffer));
res = f_read(&fil, buffer, 200, &bw);
xUserPrintf("\r\nread:%d|%d =>> %s\r\n", res, bw, buffer);
f_close(&fil);
}
}
else
{
xUserPrintf("\r\nFile System Init Failed!\r\n");
}
}
如下图所示是测试过程和结果:
6.工程 & 资料
 GD25Q16CSIG.PDF
(1.27 MB, 下载次数: 8)
GD25Q16CSIG.PDF
(1.27 MB, 下载次数: 8)
 /5
/5 
-
 返回顶部
返回顶部
-









