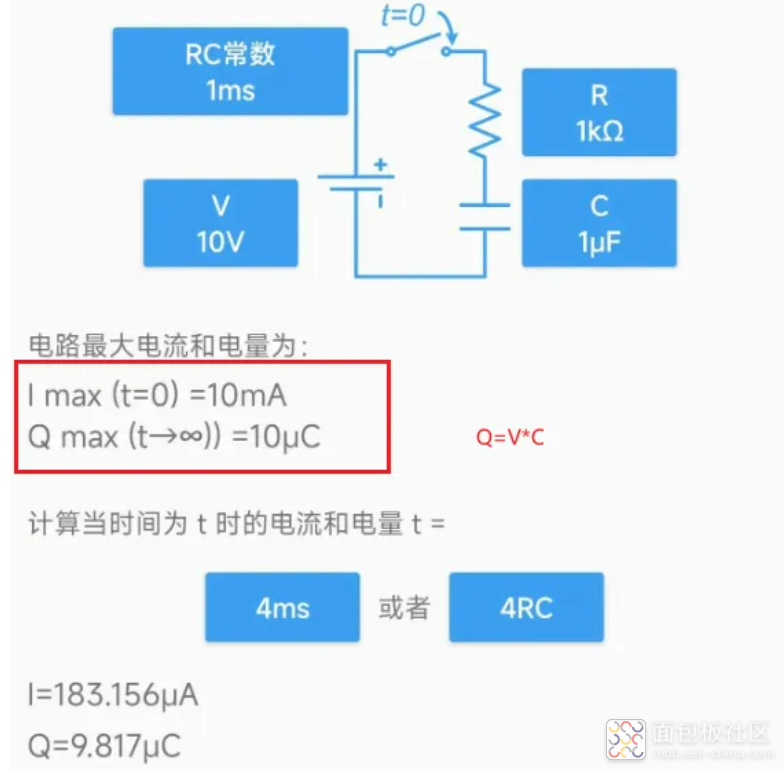
例如下图仿真,R=1KΩ,C=1uF,那么τ=R*C=1ms。
1个时间常数1ms的时间,电容电压充到63%,前半段电容的充电电流还是很大的,此时反推回去1τ下的充电电流为0.37*V1/R1。绿色的为电容的充电电流曲线,红色的为电容的充电电压曲线。
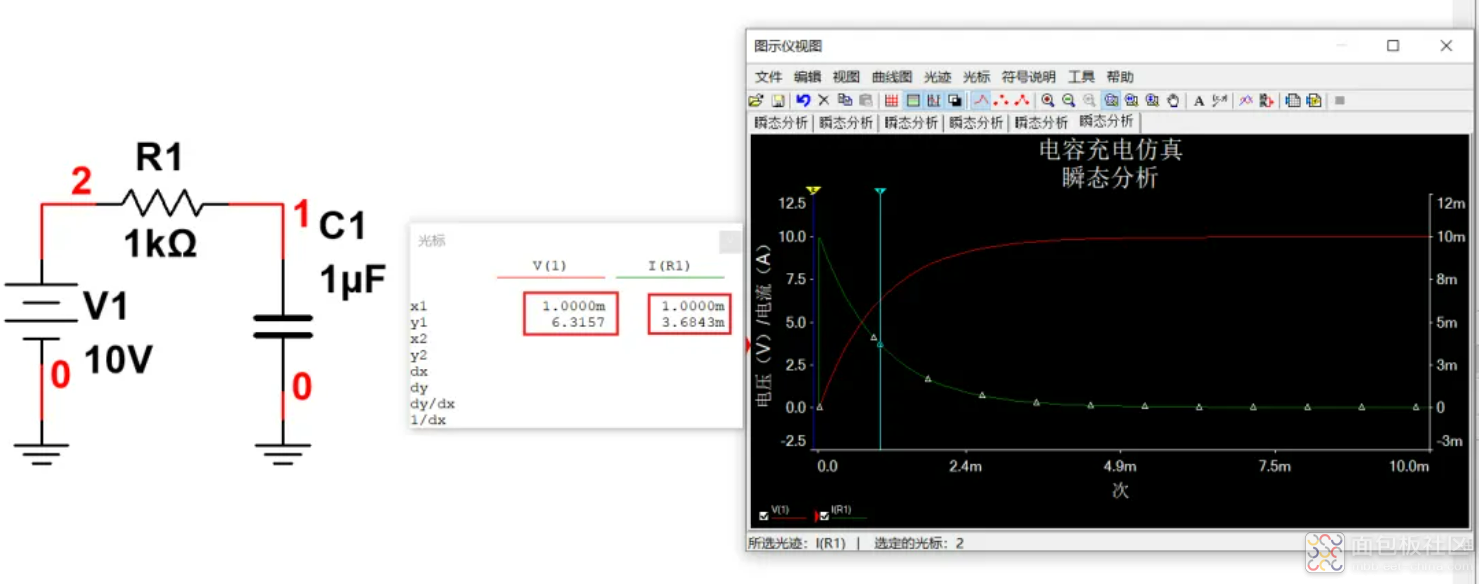
2个时间常数2ms的时间,电容电压充到86%
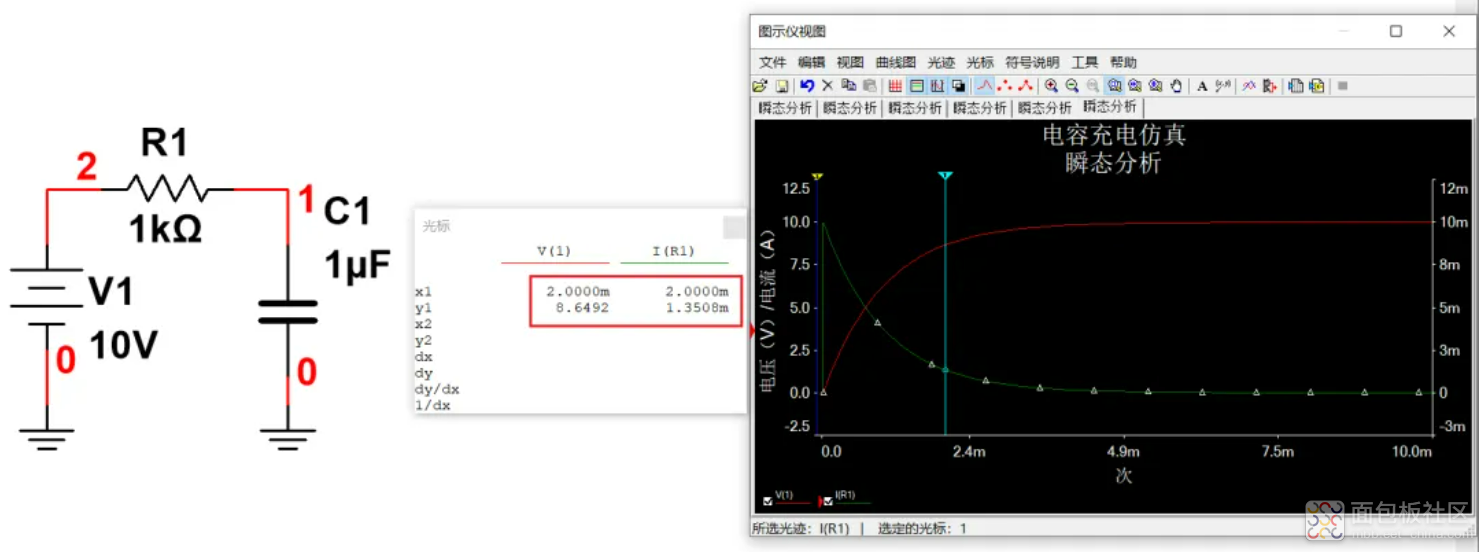
3个时间常数3ms的时间,电容电压充到95%
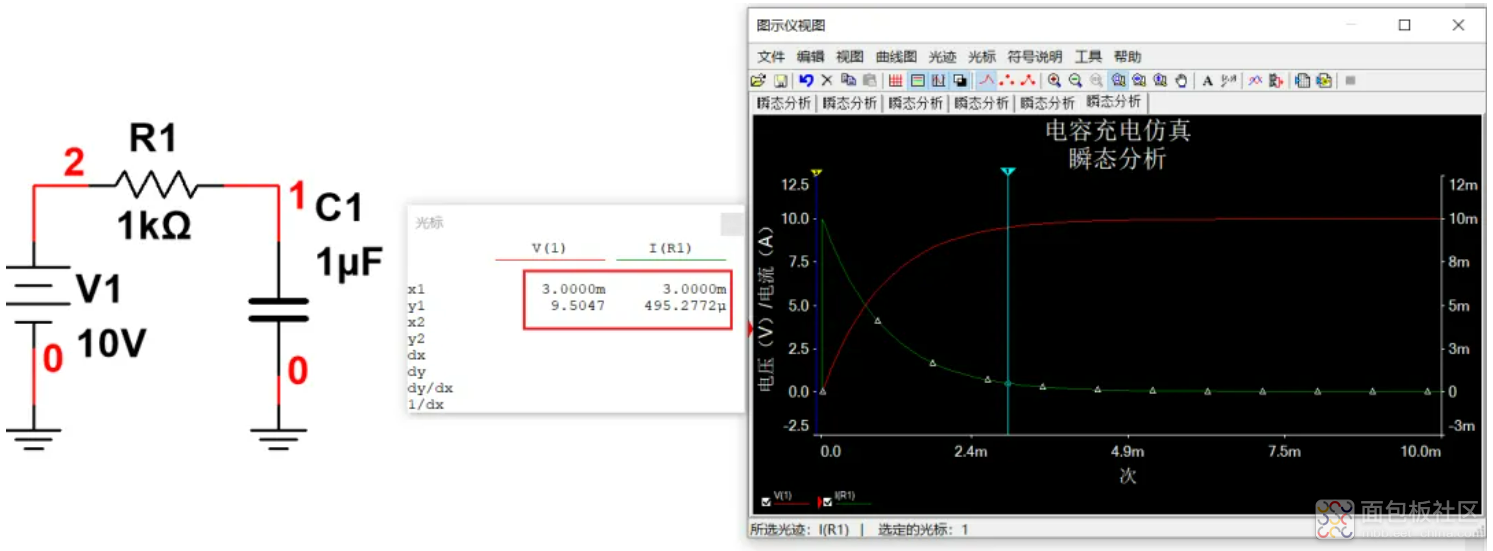
4个时间常数4ms的时间,电容电压充到98%
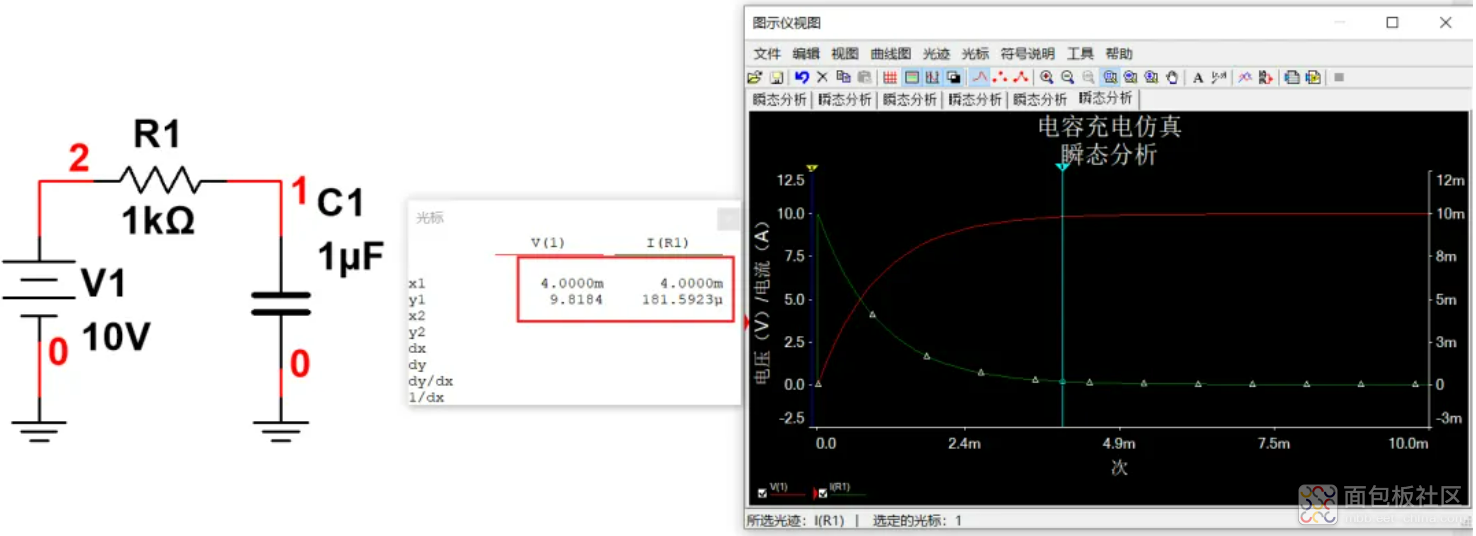
所以可以认为3个时间常数电容就基本充满了(95%),而且在上电瞬间,电容等效为短路,此时电流最大,等效为V1/R1。随着时间的增加,电容上的电压越来越高,充电电流越来越小,t趋向于无穷的时候,电流趋向于0。下图工具里的计算器也可以计算。





 /1
/1 

