随着物联网的兴起,越来越多的传统工业设备需要和外界通信,但很多情况下,类似PLC的微控制器经常会由于自身硬件因素而无法与外界直接互联互通。PC作为一个中介桥梁,为PLC与外界的沟通打开了一扇门。
而Python作为当前最火的语言,不仅在AI、云计算等诸多方面都能看到它的身影,在工业控制中也不能少了它。本文就来分享下如何使用Python构建PC与PLC的通信,也算展示一把Python在工控领域的风采。
Snap7简介
当前市场上主流的PLC通信方式为网络通信和串行通信。网络通信这块主要协议有profinet,modbus-tcp等,串行通信主要是基于RS232/485的modbus。
本次接触到的是西门子S7系列的PLC,通信方式都为网络型的,而Snap7(http://snap7.sourceforge.net/)正是一个开源的、32/64位的、多平台的以太网通讯库:
支持多硬件体系结构(i386/x86_64、ARM/ARM64、Sun Sparc、Mips);
支持多系统(Windows、Linux、BSD、Solaris);
支持多语言(C/C++、Phyton、Node.js、Pascal、C#、VB)。
Python对其进行了封装,具体可以参见:https://github.com/gijzelaerr/python-snap7。
开发环境搭建
这里主要从Windows和Linux(Ubuntu)两个平台,说说如何搭建Python环境下的Snap7开发环境。Python的安装这里就不再赘述,环境搭建主要就是Snap7和python-snap7两个库的安装。
1、安装Snap7
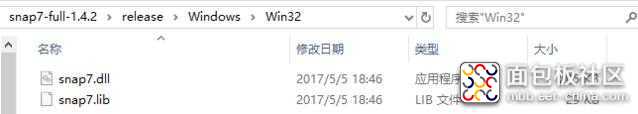
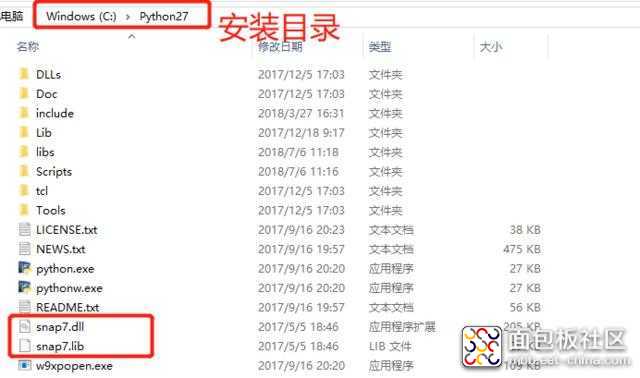
Windows下,需要根据Python的结构版本(32位/64位),将下载的Snap7的发布库copy到对应的Python安装根目录下即可。
如上图所示,我的Python是32bit,所以需要将Snap7中Win32目录下的文件Copy到Python的安装根目录下,如下图所示:
$ sudo -s$ add-apt-repository ppa:gijzelaar/snap7 $ apt-get update $ apt-get install libsnap71 libsnap7-dev
复制代码2、安装python-snap7
Snap7的Python库安装就简单很多了,不管是Windows还是Linux,直接pip安装即可。
$ pip install python-snap7
复制代码import snap7client = snap7.client.Client() client.connect('192.168.0.1', 0, 1) client.disconnect()
复制代码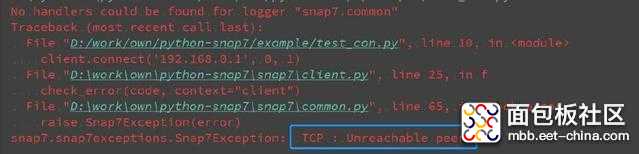
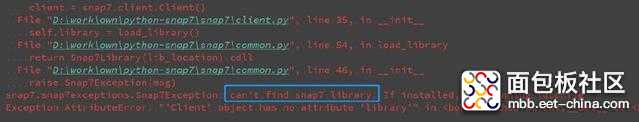
读写PLC
环境搭建正常后,在正式建立通信前PLC还需做些配置工作,主要是开发自身的读写权限。具体参照下图配置:
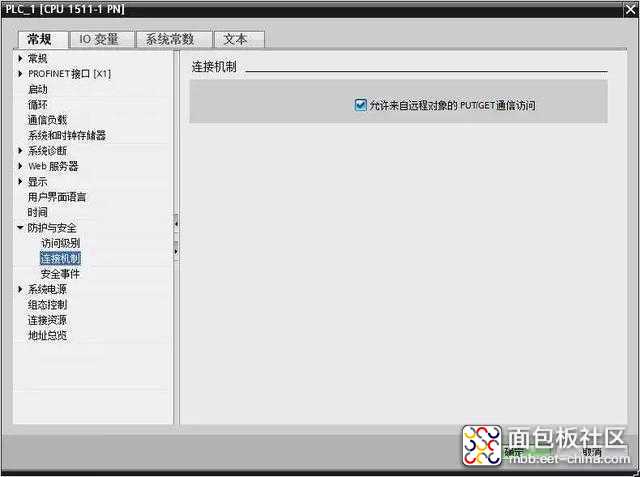
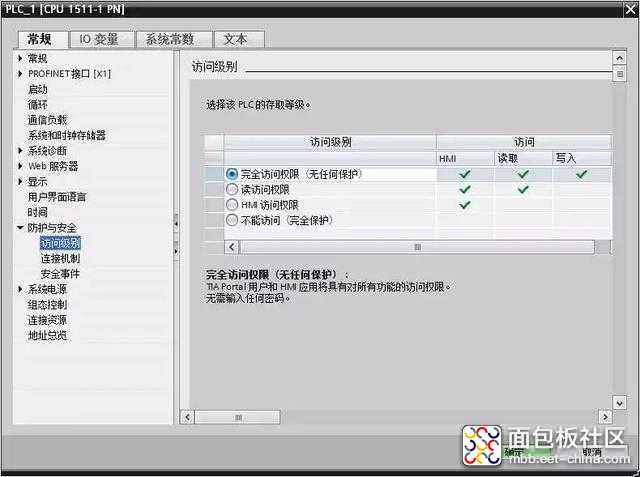
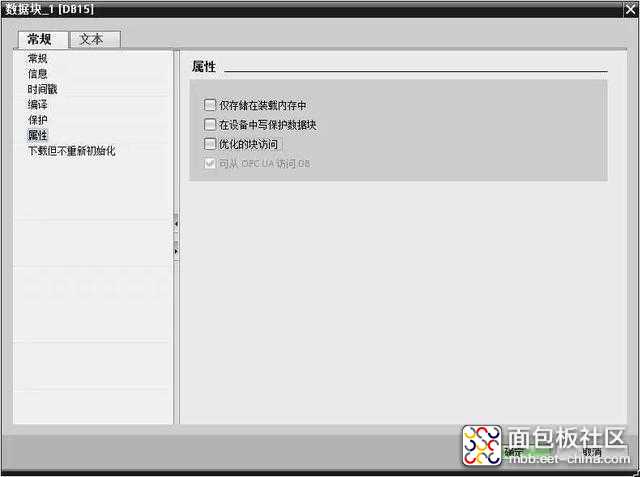
1、python-snap7读写分析
结合python-snap7的文档API和源码分析,python-sna7重要的两个方法是read_area和write_area,通过这两个方法就能读和写PLC的对应存储地址。
def read_area(self, area, dbnumber, start, size): """This is the main function to read data from a PLC. With it you can read DB, Inputs, Outputs, Merkers, Timers and Counters. :param dbnumber: The DB number, only used when area= S7AreaDB :param start: offset to start writing :param size: number of units to read """ assert area in snap7.snap7types.areas.values() wordlen = snap7.snap7types.S7WLByte type_ = snap7.snap7types.wordlen_to_ctypes[wordlen] logger.debug("reading area: %s dbnumber: %s start: %s: amount %s: " "wordlen: %s" % (area, dbnumber, start, size, wordlen)) data = (type_ * size)() result = self.library.Cli_ReadArea(self.pointer, area, dbnumber, start, size, wordlen, byref(data)) check_error(result, context="client") return bytearray(data) @error_wrap def write_area(self, area, dbnumber, start, data): """This is the main function to write data into a PLC. It's the complementary function of Cli_ReadArea(), the parameters and their meanings are the same. The only difference is that the data is transferred from the buffer pointed by pUsrData into PLC. :param dbnumber: The DB number, only used when area= S7AreaDB :param start: offset to start writing :param data: a bytearray containing the payload """ wordlen = snap7.snap7types.S7WLByte type_ = snap7.snap7types.wordlen_to_ctypes[wordlen] size = len(data) logger.debug("writing area: %s dbnumber: %s start: %s: size %s: " "type: %s" % (area, dbnumber, start, size, type_)) cdata = (type_ * len(data)).from_buffer_copy(data) return self.library.Cli_WriteArea(self.pointer, area, dbnumber, start, size, wordlen, byref(cdata))
复制代码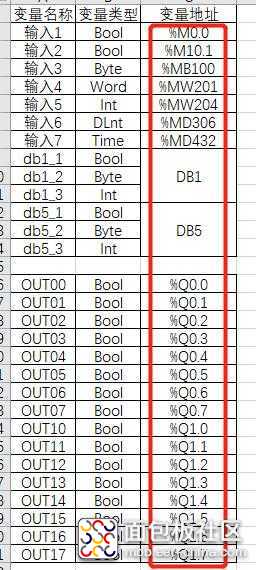
2、PLC数据存储和地址
通过阅读PLC的手册获取到如下信息:

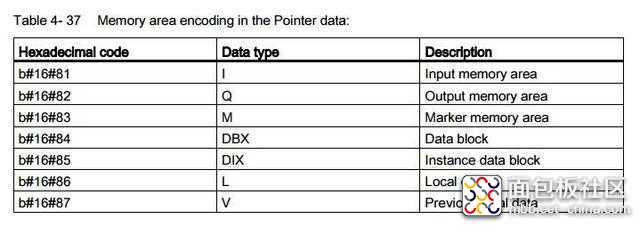
areas = ADict({ 'PE': 0x81, #input 'PA': 0x82, #output 'MK': 0x83, #bit memory 'DB': 0x84, #DB 'CT': 0x1C, #counters 'TM': 0x1D, #Timers })
复制代码
实战
经过上面的精心准备,下面就来一波实战。通过读写PLC的M10.1、MW201来具体看看如何读写PLC。
import structimport time import snap7 def plc_connect(ip, rack=0, slot=1): """ 连接初始化 :param ip: :param rack: 通常为0 :param slot: 根据plc安装,一般为0或1 :return: """ client = snap7.client.Client() client.connect(ip, rack, slot) return client def plc_con_close(client): """ 连接关闭 :param client: :return: """ client.disconnect() def test_mk10_1(client): """ 测试M10.1 :return: """ area = snap7.snap7types.areas.MK dbnumber = 0 amount = 1 start = 10 print(u'初始值') mk_data = client.read_area(area, dbnumber, start, amount) print(struct.unpack('!c', mk_data)) print(u'置1') client.write_area(area, dbnumber, start, b'\x01') print(u'当前值') mk_cur = client.read_area(area, dbnumber, start, amount) print(struct.unpack('!c', mk_cur)) def test_mk_w201(client): """ 测试MW201,数据类型为word :param client: :return: """ area = snap7.snap7types.areas.MK dbnumber = 0 amount = 2 start = 201 print(u'初始值') mk_data = client.read_area(area, dbnumber, start, amount) print(struct.unpack('!h', mk_data)) print(u'置12') client.write_area(area, dbnumber, start, b'\x00\x0C') print(u'当前值') mk_cur = client.read_area(area, dbnumber, start, amount) print(struct.unpack('!h', mk_cur)) time.sleep(3) print(u'置3') client.write_area(area, dbnumber, start, b'\x00\x03') print(u'当前值') mk_cur = client.read_area(area, dbnumber, start, amount) print(struct.unpack('!h', mk_cur)) if __name__ == "__main__": client_fd = plc_connect('192.168.0.1') test_mk10_1(client_fd) test_mk10_1(client_fd) plc_con_close(client_fd)
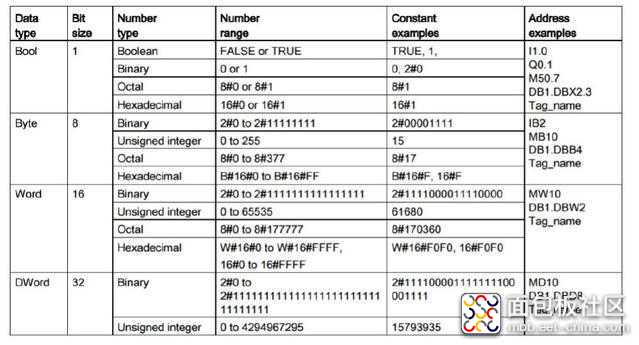
复制代码这里给出PLC变量类型和大小,这样对应确定读写的amount。
本文分享自微信公众号 - chafezhou(gh_5b8f0c59b682)
原文出处及转载信息见文内详细说明,如有侵权,请联系删除。
https://cloud.tencent.com/developer/article/1163231






 /3
/3 
